fabric8 Camel Maven Plugin
Video recording demonstrating the new fabric8 camel-maven-plugin that is able to validate your Camel endpoints from the source code, so you can catch those typo errors before running the application.

Video recording demonstrating the new fabric8 camel-maven-plugin that is able to validate your Camel endpoints from the source code, so you can catch those typo errors before running the application.

JBoss A-MQ 6.1 Getting Started Part 3: This introduction has been setup to get you started as quickly as possible with JBoss A-MQ. We have put together a three part video tour of the product, an example quick setup of the product and the installation of an existing project that is then deployed to JBoss A-MQ. The product is installed and configured right before your very eyes in no time at all with a fully automated project setup script. The server setup is shown using the latest JBoss Developer Studio and you are ready to get going.

Getting Started With A-MQ 6.1: This introduction has been setup to get you started as quickly as possible with JBoss A-MQ. We have put together a three part video tour of the product, an example quick setup of the product and the installation of an existing project that is then deployed to JBoss A-MQ. The product is installed and configured right before your very eyes in no time at all with a fully automated project setup script. The server setup is shown using the latest JBoss Developer Studio and you are ready to get going.

This introduction has been setup to get you started as quickly as possible with JBoss A-MQ. We have put together a three part video tour of the product, an example quick setup of the product and the installation of an existing project that is then deployed to JBoss A-MQ. The product is installed and configured right before your very eyes in no time at all with a fully automated project setup script. The server setup is shown using the latest JBoss Developer Studio and you are ready to get going. (Part 2)

In this session, Mark Wagner reviews enhancements in Red Hat Enterprise Linux 6 and show attendees how to take advantage of them in their environments. Mark uses test results from Red Hat's performance lab to highlight the various differences, advantages, and tradeoffs for many technologies, including Kernel-based Virtual Machine (KVM) virtualization technology, 10Gbit Ethernet, Infiniband, FCoE, Packet Flow Control, and RDMA. Mark also presents guidelines and tools for planning and tuning network configurations for low latency and high throughput. He covers the differences between tuning for baremetal, a KVM guest, a Red Hat Storage file system, and NFS. He also touches upon some tricks developers can use when writing network-based applications.
Using Raspberry Pis to track moving iBeacons, Apache ActiveMQ, Apache Spark

Using Apache ActiveMQ, JBoss Fuse A-MQ and its MQTT capabilities to read temperature from TI SensorTag, analyze the temp via Apache Camel, and if it is "HOT" send out a message to another Intel Edison tied to a Lightblue Bean animating a servo.

JBoss A-MQ - Dave Ingham

Messaging has become a critical infrastructure component for both developers and systems administrators. Scaling infrastructure in an efficient and manageable way is critical in modern physical, virtual and cloud infrastructures. To provide value to the business, developers and systems administrators must understand technical and business advantages of current and future architectures. Join Scott McCarty and Scott Cranton as they bring years of experience in building scalable, fault tolerant, distributed systems to the architectural challenges of building durable messaging platforms. Attendees will receive guidance on emerging technologies as well as an understanding of the strengths of current solutions like Red Hat JBoss A-MQ. This discussion will include enterprise requirements such as fault tolerance, high performance, durability, fault detection, return to service, auto-scaling, cloud readiness, and governance. You'll also will explore several open source, high availability architectures spanning multiple Red Hat technologies, including Red Hat Enterprise Linux, the High Availability and Resilient Storage Add-Ons, and OpenShift by Red Hat.

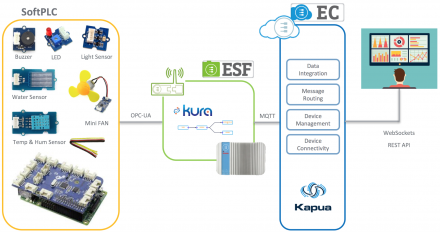
This session will be a deep dive into the world of open source software, open hardware, and the open standards that are fueling the IoT’s momentum. We will explore how to design hardware & software for connecting the physical world (the world of things) into your traditional enterprise IT infrastructure by walking through a real production IoT system. We will demonstrate connectivity technologies like Bluetooth Low Energy and MQTT as well as developer prototyping platforms like Raspberry Pi, Arduino, Intel Edison, Spark.io microcontrollers, and more.

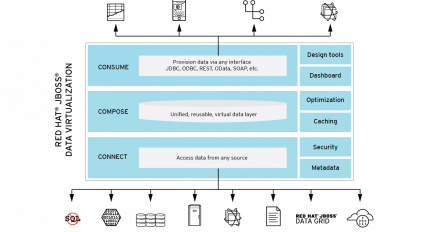
How do we get our software out on the Internet of Things (IoT)? Many current deployment practices won’t work. Devices can be occasionally connected, through low-bandwidth networks, but are generally outside of direct control. Manually shuffling around binaries is not an option. Apache ACE is an open source Java provisioning tool that tackles such challenges. This software distribution framework allows you to centrally manage and distribute software components, configuration data, and other artifacts to target systems. In this session, learn how Apache ACE enables you to push out incremental updates and manage numerous devices. We’ll show how to update and extend a fictional car entertainment system using Apache ACE.

The Internet of Things (IoT) is made up of many interconnected devices that need to be able to talk to each other. Because these devices are developed by different organizations and have different requirements, they speak many different languages and protocols. There are standard protocols used by these devices, as well as industry-specific protocols. Join us as we discuss the benefits, drawbacks, and applicable use cases for certain protocols, including MQTT, AMQP, STOMP, and others. We will look at how Red Hat JBoss A-MQ and Red Hat JBoss Fuse can assist with implementing and managing these protocols. In addition, we’ll discuss how the transformation and routing capabilities of JBoss A-MQ and JBoss Fuse can be applied to IoT use cases and can be used to create and implement new protocols.

As enterprises look at ways they can transform their business with the Internet of Things (IoT), IT and development teams are left to figure out how each of these devices work together to create an experience that both delights users and meets company goals. Learn how to shape an ideal user experience using the IoT. We’ll show you how to create and extend possibilities for users to holistically connect with your brand and offerings.

== Abstract == Scale changes everything. What once was quite adequate for enterprise messaging can't scale to support "Internet of Things". We need new protocols, patterns and architectures to support this new world. This session will start with basic introduction to the concept of Internet of Things. Next it will discuss general technical challenges involved with the concept and explain why it is becoming mainstream now. Now we're ready to start talking about solutions. We will introduce some messaging patterns (like telemetry and command/control) and protocols (such as MQTT and AMQP) used in these scenarios. Finally we will see how Apache ActiveMQ is gearing up for this race. We will show tips for horizontal and vertical scaling of the broker, related projects that can help with deployments and what the future development road map looks like. == Speaker == Martyn Taylor is a senior software engineer at Red Hat, with over 7 years' experience working on cloud, middleware and messaging software. Martyn currently works on the Apache ActiveMQ suite of projects.