Red Hat OpenShift 4.21, based on CRI-O 1.34 and Kubernetes 1.34, is now generally available. Red Hat OpenShift 4.21 introduces AI-driven insights, automated security signing, and local development tools to help you build and deploy faster.
Red Hat Developer Hub
Red Hat Developer Hub 1.8 is a supported, enterprise-grade internal developer portal (IDP) built on the open source Backstage framework. The latest update introduces the Model Context Protocol (MCP) server and an OpenShift AI connector. This allows platform engineers to integrate software catalogs and AI assets directly into their IDP.
Red Hat Developer Lightspeed, a set of intelligent assistants for Red Hat developer tools, is now based on the Llama Stack framework for greater flexibility. The MCP server allows AI agents to access your Developer Hub software catalog and technical documentation to provide context-aware answers.
The OpenShift AI connector automatically syncs AI models and assets with the Developer Hub catalog.
For platform engineers, Red Hat OpenShift 4.21 introduces the Scorecard plug-in (Developer Preview). This plug-in provides visibility into project health and compliance metrics directly within the portal. The Dynamic Plug-in Factory allows you to simplify custom plug-in development.
To help developers scale adoption, Red Hat Developer Hub 1.8 includes localization support (starting with French language translations) and persona-based homepages that let you tailor the view for different users.
The onboarding experience is also streamlined with a new quickstart option for developers and expanded bulk import capabilities to support GitLab, with the capability to use an existing scaffolder template for importing with custom steps.
Red Hat OpenShift Dev Spaces
Red Hat OpenShift Dev Spaces versions 3.24 and 3.25 are now available. Red Hat OpenShift Dev Spaces is a cloud development environment (CDE) platform that allows developers to remotely code and run applications using Red Hat OpenShift.
Versions 3.24 and 3.25 now support running nested containers in OpenShift Dev Spaces. This allows for podman run capabilities and removes the need for workarounds like Kubedock.
VS Code local to remote with OpenShift Dev Spaces is now available as tech preview, which allows extensions from the Microsoft Extension Store. This feature will run code, compute, IDE server, and extensions on OpenShift, while the local VS Code acts as a thin UI shell.
You can now connect to multiple OpenShift Dev Spaces workspaces simultaneously by using the JetBrains Gateway plug-in. Previously, the plugin restricted you to a single active connection.
A new auto pruner, when configured, reduces the etcd usage of OpenShift Dev Spaces and helps it run at scale for expanded adoption across the enterprise.
Red Hat Trusted Artifact Signer 1.3
Red Hat Trusted Artifact Signer gives you enterprise protection across your entire software supply chain, including AI deployments.
Red Hat Trusted Artifact Signer is a production-ready deployment of the Sigstore project. It allows cryptographic signing, attestations, and verification for enterprise software artifacts. This means every component in your pipeline can be verified for integrity and non-repudiation.
Red Hat Trusted Artifact Signer 1.3 introduces the Model Transparency Library, which brings the same cryptographic protection to AI deployments. When a machine learning (ML) model is ready for deployment, a cryptographic hash of the model and all its files and metadata are generated and written to a serialized manifest. The manifest is cryptographically signed and stored as a detached signature in a separate file.
The 1.3 release also introduces the Model Validation Operator, which helps verify models before they reach production—ensuring only trusted AI models are loaded into the Red Hat OpenShift namespace. This functionality is similar to the Kubernetes admission controller for container images.
For enterprise operations, Red Hat Trusted Artifact Signer 1.3 introduces fine-grained high availability controls to configure pod affinity, set up multiple replicas, and define resource limits to handle peak loads or infrastructure failures.
This version also enhances transparency and monitoring with continuous verification of Rekor transparency logs to ensure they remain tamper-resistent, as well as new integrations with S3 and Google Cloud Storage for flexible attestation storage.
Red Hat Advanced Developer Suite software supply chain
Software supply chain 1.8, part of Red Hat Advanced Developer Suite, makes it easier to set up a secure development environment. It comes with ready-to-use templates in Red Hat Developer Hub that help you build safer CI/CD pipelines, and uses OpenID Connect (OIDC) authentication instead of GitHub. With security checks preinstalled in your development process, it protects your software artifacts from tampering and helps you meet important security standards.
Platform services
Red Hat OpenShift 4.21 includes improvements to Red Hat OpenShift Service Mesh, Red Hat OpenShift GitOps, builds for Red Hat OpenShift, Red Hat OpenShift Pipelines, and Red Hat OpenShift Serverless.
Red Hat OpenShift Service Mesh
Red Hat OpenShift Service Mesh 3.3 follows the introduction of Istio's ambient mode in the previous release. This release updates Istio to 1.28 and Kiali 2.22.
Notably, this release introduces initial support for post-quantum cryptographic (PQC) algorithms with service mesh. This is enabled using the ML-KEM algorithm that is now included with OpenSSL—the encryption module behind OpenShift Service Mesh.
We are continuing to evolve ambient mode, including initial support on FIPS clusters with 140-2 support, and 140-3 to follow later. The multiprimary multicluster topology is now also available as technology preview with ambient mode.
Kiali's AI chatbot is offered in developer preview. It lets you query your service mesh and workloads using natural language prompts. Kiali's MCP integrations lets you use these features with Red Hat OpenShift Lightspeed or your AI agent of choice.
Zero trust workload identity manager will be available in a few weeks. It extends the service mesh's management of workload identities with deeper workload attestation features, and offers the ability to federate workload identities across meshes, clusters, and data centers.
OpenShift Service Mesh 3.3 introduces (as a developer preview feature) the ability to include external workloads, including virtual machines (VMs).
Red Hat OpenShift GitOps
Red Hat OpenShift GitOps 1.19 includes several key updates. The Argo CD Agent architecture is now generally available and production-ready. This pull-based deployment model offers better scalability and security for multicluster environments.
Red Hat OpenShift GitOps 1.19 introduces the Argo CD Image Updater in tech preview so you can automate container image updates for your applications.
Operations teams now have granular control over image pull policies across all components, and can manage their own notification configurations without needing control plane access. Users can also tune resource limits for plugin components independently.
Builds and pipelines
The release of Red Hat OpenShift Pipelines 1.21 includes the event-driven pruner and Tekton cache as generally available, providing more robust resource management and faster execution.
OpenShift Pipelines 1.21 also introduces functionality for debugging pipeline runs with OpenShift Lightspeed, to help developers resolve failed pipeline runs and get potential root case and recommendations to solve issues faster (included as developer preview). See Figure 1.
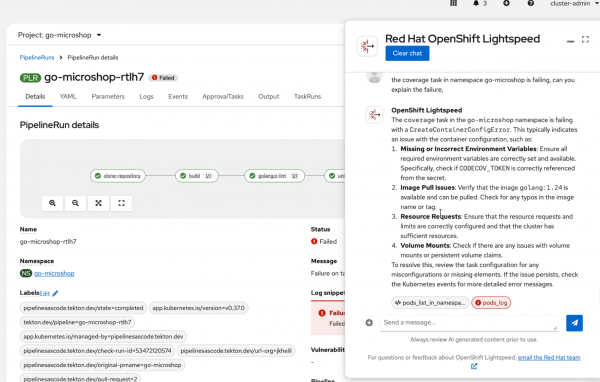
Following Kubernetes best practices, controllers and webhooks focus on security with the root file system set to read-only by default.
For greater flexibility, developers can now override individual TaskRun timeouts within a PipelineRun. This allows finer-grained control over task execution duration without affecting the overall PipelineRun timeout.
Enhanced resolver caching is supported for bundle, Git, and cluster resolvers. This helps reduce redundant fetches, minimize external API calls, and improve pipeline execution reliability, especially when external services impose rate limits or are temporarily unavailable.
Fine-grained retention policies are implemented for PipelineRuns and TaskRuns to better manage cluster resources. With this update, Tekton Results implements different retention periods for PipelineRun and TaskRun based on namespace, labels, annotations, and status. The first matching policy is applied; if none match, the default retention period is used.
With builds for Red Hat OpenShift 1.7, the BuildConfig to Shipwright migration guide is available.
Red Hat OpenShift Serverless
Red Hat OpenShift Serverless 1.37 incorporates several improvements to core components following Knative's 1.17 upstream release. This includes updated default configurations for serving that make it easier to install and deploy OpenShift Serverless in your environment. We also added Eventing support for generic event sources and sinks using Apache Camel Kamelets. Multiple minor resource optimization fixes also enhance performance.
With this release, Serverless Functions - MCP Server will be available for developer preview. Serverless Functions can be used as a Model Context Protocol (MCP) server with the Serverless command-line interface (CLI) using the command function mcp.
This feature offers full-coverage of Serverless Function features via MCP and context injection via MCP "prompts.” We are also providing integration with our OpenShift Serverless functions template repository, including a Python proof of concept for experimentation. It also includes integration with popular AI tools such as Windsurf, Cursor, and Claude.
Serverless integration with OpenShift Service Mesh 3.0 will be available in technical preview.
Control plane and security
Control plane security and scalability
Red Hat OpenShift 4.21 reduces etcd database loads for high-scale environments. With a configurable event TTL, users can tune event data retention in etcd to significantly reduce etcd load and improve overall API server performance in very large Red Hat OpenShift clusters.
This version also includes integration with KMS version 2. With KMS support, you can store the encryption key for etcd secrets externally in a KMS provider.
Red Hat OpenShift core payload verification with Sigstore
In Red Hat OpenShift 4.20, we released the ImagePolicy and ClusterImagePolicy APIs for production clusters. With Red Hat OpenShift 4.21, you can validate the core payload image used during initial cluster installation and updates. Verification now takes place in parallel using the Sigstore signatures that accompany all Red Hat OpenShift images. This ensures that the payload image was released by Red Hat and will eventually extend to all Red Hat OpenShift core platform images in all namespaces.
This feature adds an additional layer of security and makes verifying Red Hat OpenShift in disconnected environments easier, because the oc-mirror utility will automatically mirror the Sigstore signatures in your offline environment and the signatures remain valid even though they come from a different registry, mitigating the need for additional storage mechanisms for image signatures.
Secrets management
Red Hat OpenShift 4.21 includes several improvements for secrets management.
Red Hat OpenShift secrets management operators are more usable and accessible, and the Red Hat OpenShift console includes tutorials and sample YAML snippets as part of each operator's installation payload. To reduce the number of false positives during vulnerability scans and minimize vulnerability exposure, all secrets management operators will now use ubi-minimal as the base image.
Trust-manager is now available and integrates seamlessly with cert-manager. Trust-manager is an add-on functionality that lets you create customized bundles of trusted certificate authorities (CAs) and distribute these to your workloads. With trust-manager you can ensure that every service knows who to trust without manual configuration, so when a CA is automatically renewed or rotated by cert-manager, the trust bundle is also automatically updated.
Red Hat OpenShift Virtualization
Changes to OpenShift Virtualization let you modernize your operations with a comprehensive lifecycle and infrastructure management capabilities.
Managing virtual machines is now smoother with an enhanced dashboard and overview, as well as the ability to execute multicluster VM operations. Create networks more easily with the VM network creation wizard (Figure 2), and troubleshoot faster with OpenShift Lightspeed information integrated into user interface flows.
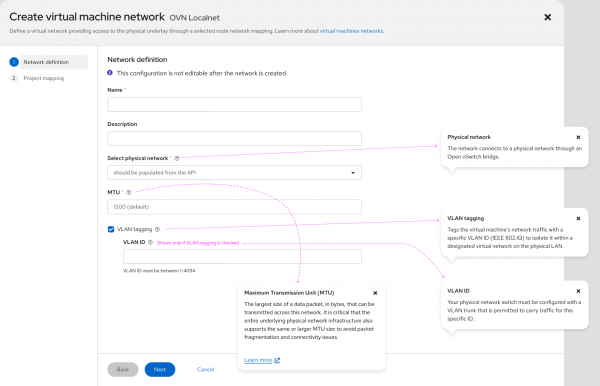
Available as developer preview, developers can optimize their infrastructure with cross-cluster live migration with the migration toolkit for virtualization and Red Hat Advanced Cluster Management for Kubernetes.
Infrastructure updates include storage-agnostic change block tracking (CBT) and the ability to insert and eject CD-ROMs. Google Cloud on bare metal has been added as a new platform, and Windows cluster support is improved. MIG vGPUs from NVIDIA can also now be added to a VM.
Get started today with Red Hat OpenShift 4.21
Get started:
- Start your OpenShift journey in the no-cost Developer Sandbox.
- Discover more ways to get started by downloading Red Hat OpenShift.
- Find resources for getting started with OpenShift.
- Explore OpenShift interactive demos
- Level up your skills with OpenShift learning paths like Foundations of OpenShift.
To find out more about Red Hat OpenShift 4.21, check out the new and improved features and fixes:
Last updated: February 9, 2026