In our previous article about the Kiali toolset, we explored how Kiali acts as the "eyes" of your service mesh, providing unparalleled visibility into traffic topology, health, and metrics. We showed you how to manually inspect the graph, validate Istio configurations, and troubleshoot mTLS issues. But what if you didn't have to manually hunt for errors? What if you could just ask your cluster what’s wrong?
In this article, we will take a leap forward by installing the Kiali Model Context Protocol (Kubernetes MCP) server in Red Hat OpenShift Lightspeed. This integration allows the OpenShift Lightspeed AI assistant to interface directly with Kiali, giving the AI visibility into your service mesh to assist with troubleshooting and configuration.
Set up OpenShift Lightspeed
Before we dive into the installation, ensure you have the following prerequisites:
- OpenShift cluster (Version 4.15+ recommended).
- Red Hat OpenShift Service Mesh installed and running.
- Kiali (or the OpenShift Service Mesh console) deployed and accessible.
- OpenShift Lightspeed operator installed on your cluster.
For an enterprise-grade experience, you can integrate this toolset directly into OpenShift Lightspeed. This allows any user on the cluster to utilize Kiali's capabilities through the OpenShift Lightspeed chat interface.
Since OpenShift Lightspeed runs inside the cluster, we need to deploy the MCP server as a service rather than running it locally on your laptop.
Step 1: Create a ConfigMap for Kiali configuration
Created a mcp-osl-config.toml in a known location (e.g., ~/mcp-osl-config.toml).
toolsets = ["core","kiali"]
read_only = true
[toolset_configs.kiali]
url = "https://kiali-istio-system.apps-crc.testing/"
insecure = trueThen, upload your TOML configuration to the cluster.
oc create configmap kubernetes-mcp-config \
--from-file=~/mcp-osl-config.toml=./mcp-osl-config.toml \
-n istio-systemStep 2: Deploy the MCP server
Create a deployment that runs the server. This exposes the MCP over HTTP so OpenShift Lightspeed can connect to it.
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: kubernetes-mcp-server
namespace: istio-system
spec:
replicas: 1
selector:
matchLabels:
app: kubernetes-mcp-server
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: kubernetes-mcp-server
spec:
serviceAccountName: kubernetes-mcp-server
automountServiceAccountToken: true
containers:
- name: mcp-server
image: quay.io/containers/kubernetes_mcp_server:latest # Check for latest version
args:
- "--port=8080"
- "--config=/etc/mcp/mcp-viewer-config.toml"
ports:
- containerPort: 8080
volumeMounts:
- name: config-vol
mountPath: /etc/mcp
volumes:
- name: config-vol
configMap:
name: kubernetes-mcp-config
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: kubernetes-mcp-server
namespace: istio-system
spec:
selector:
app: kubernetes-mcp-server
ports:
- port: 8080
targetPort: 8080Step 3: Register the tool with OpenShift Lightspeed
Once the MCP server is running, OpenShift Lightspeed needs to know it exists. Depending on your version, you may need to configure the OlsConfig (OpenShift Lightspeed config) to whitelist the new tool endpoint or enable the service mesh plug-in as follows:
- Navigate to the Lightspeed Operator settings in the OpenShift console.
- Look for Tool Definitions or MCP Servers.
- Add the service URL of your new deployment (e.g., http://kubernetes-mcp-server-istio-system.apps-crc.testing/mcp).
You can also modify the YAML directly (Figure 1).
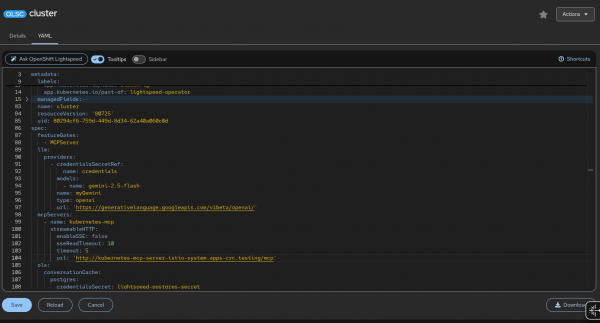
Step 4: Chat with your mesh
Now for the magic! Open the OpenShift Lightspeed chat window in the console and try this prompt (Figure 2):
User: "Analyze the traffic flow for the 'payments' service."
OpenShift Lightspeed: "I checked Kiali, and the 'payments' service is receiving traffic from 'checkout' but is experiencing a 15% error rate on the v2 workload..."
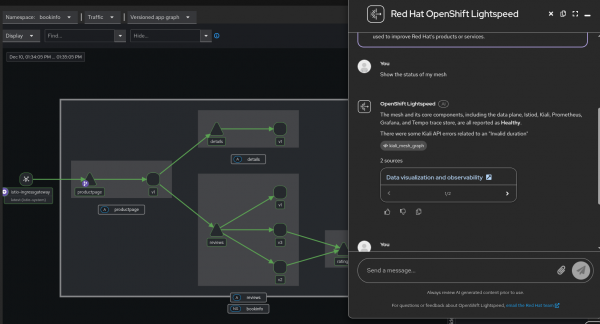
OpenShift Lightspeed returns an explanation in Figure 3.
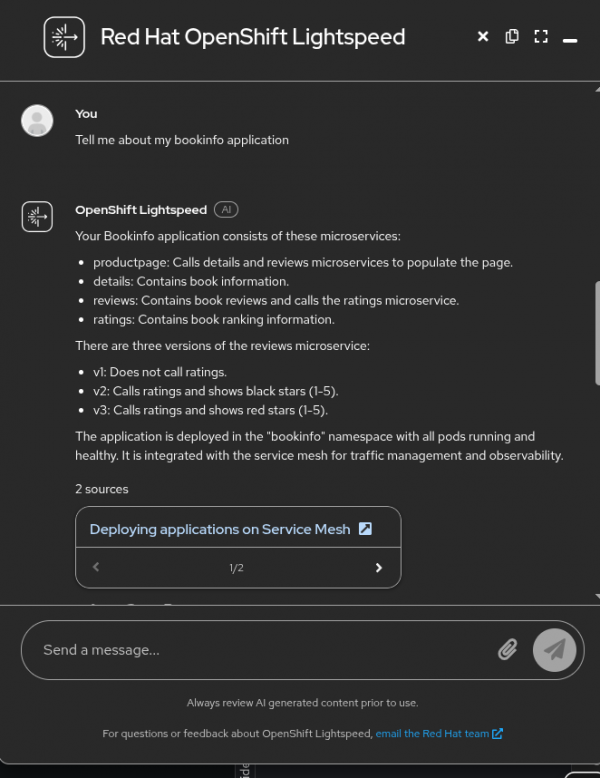
Final thoughts
By installing the Kiali MCP integration, we've transformed Kiali from a passive dashboard into an active data source for AI-driven operations. This setup reduces the "time-to-insight" for SREs and developers by combining the comprehensive Kiali toolset with the conversational power of OpenShift Lightspeed. You can watch the demo on YouTube.
