This article outlines new plug-ins and sidecar containers in Red Hat Developer Hub that provide integration between Developer Hub and Red Hat OpenShift AI. This integration lets you automatically transfer AI model metadata managed by OpenShift AI into Developer Hub’s Software Catalog.
Automating AI model metadata in Developer Hub
Red Hat Developer Hub is an internal developer platform (IDP) based on Backstage. It helps development teams and organizations increase productivity by combining parts of the development process into a single portal. Red Hat Developer Hub provides a software catalog, based on the Backstage catalog, that acts as a central library of applications, APIs, and software resources used by development teams within an organization.
With Red Hat Developer Hub software catalog as a starting point, in November of 2024 we shared our approach to mapping metadata for AI models to the software catalog, including:
- Connection information for running model instances
- Version, lifecycle, or other descriptive indicators
- Model cards
- The APIs (FastAPI, Swagger docs) for interacting with the model servers
If you revisit that post, you’ll see that:
- Model servers are stored as Components with a type of
model-server. - Models are stored as Resources with a type of
ai-model. - Details of the API that a model server provides are stored as API entities.
And with this article, we add the model cards often provided on various AI model hosting sites—stored as TechDocs and associated with the Components and Resources just mentioned.
In the November article, we constructed two GitHub repositories to illustrate the proposed mapping. We then described using the familiar Developer Hub dashboard method to import Components, Resources, and API entities defined in GitHub into the catalog.
But is a source code repository system like Git the source of truth for your AI model metadata? If you are a Red Hat OpenShift AI user, the answer is most likely no. Instead, this information is captured in OpenShift AI components like the Model Catalog, Model Registry, and even the InferenceServices that manage the Pods where your AI model servers are running.Ideally, administrators want to avoid the steps of duplicating AI model metadata already maintained in OpenShift AI into a source code repository with catalog-info.yaml files.
To solve this, Red Hat Developer Hub 1.8 introduces a new developer preview offering. This offering automatically imports information directly from Red Hat OpenShift AI’s various sources and normalizes the data into Developer Hub entities: Component, Resource, TechDoc, and API in the Developer Hub software catalog. With this addition, Developer Hub expands its role as your organization’s centralized developer portal. It provides unified views of the AI infrastructure, tooling, services, and documentation OpenShift AI provides.
Figures 1, 2, and 3 show AI-related Components, API entities with Swagger Docs, and TechDocs from model cards.
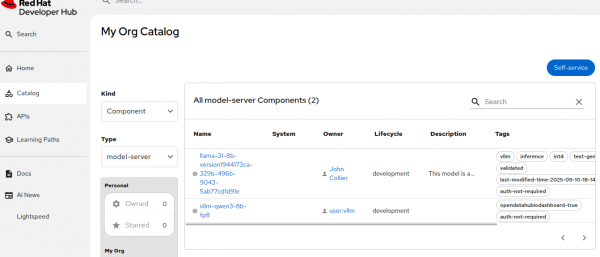
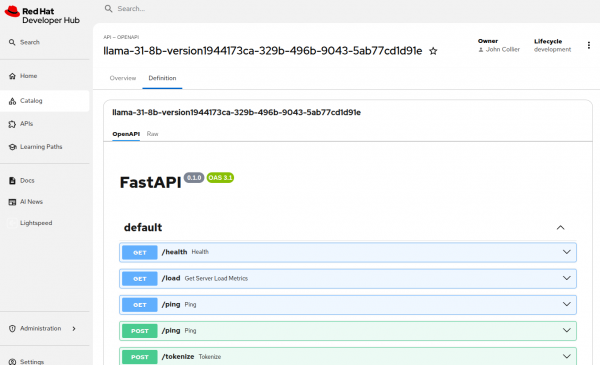
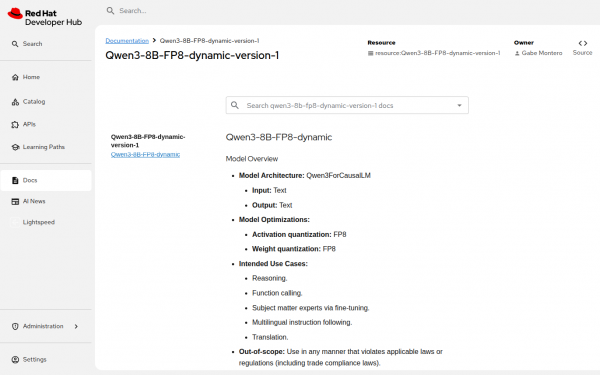
Getting started with the OpenShift AI connector for Red Hat Developer Hub
First, let's look at the system overview for the OpenShift AI Connector for Red Hat Developer Hub.
System overview
The Openshift AI connector for Red Hat Developer Hub consists of two dynamic plug-ins and three sidecar containers that run in the Developer Hub pod (illustrated in Figure 4).
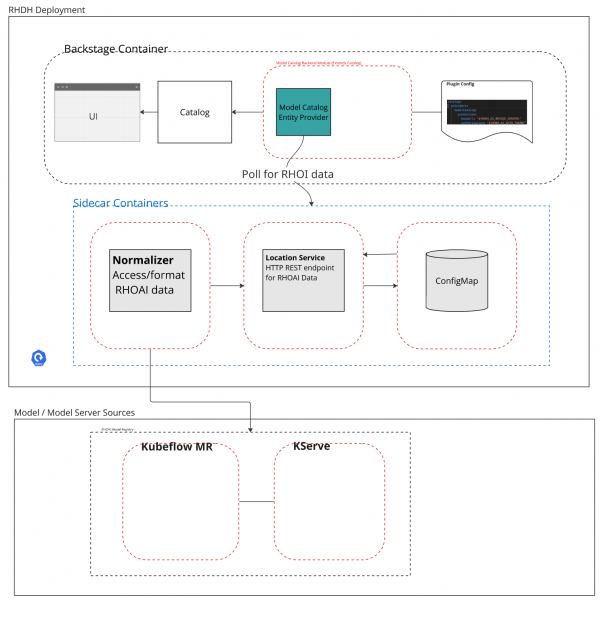
The dynamic plug-ins include:
- @red-hat-developer-hub/backstage-plugin-catalog-backend-module-model-catalog package: A Backstage Entity Provider extension that fetches the AI model metadata retrieved by the sidecar containers and creates/updates the various Component, Resource, and API entities.
- @red-hat-developer-hub/backstage-plugin-catatlog-techdoc-url-reader-backend: A Backstage URLReader extension that fetches the AI model cards retrieved by the sidecar containers and creates or updates the TechDocs for AI-related Components and Resources.
The sidecar containers include:
- A
rhoai-normalizercontainer that serves both as a KServe InferenceService Kubernetes controller (for monitoring the state of running model servers on the cluster) and as a client of the KubeFlow ModelRegistry and ModelCatalog that OpenShift AI provides. These two components are where the AI platform engineer maintains the AI model metadata. Data from those components are normalized into a format understood by the two dynamic plug-ins. - A
storagecontainer provides a REST endpoint that maintains a ConfigMap calledbac-import-modelin the Developer Hub namespace. This ConfigMap serves as a cache of the AI model metadata retrieved from OpenShift AI. Therhoai-normalizercontainer interacts with thestorageREST API to create, update, or delete AI model metadata as changes occur in OpenShift AI. - A
locationcontainer provides a REST endpoint the entity provider plug-in uses to fetch AI model metadata and model cards. Thestoragecontainer calls thelocationREST endpoint to update the available model metadata and model cards.
As the system evolves and grows, we see:
- Creating more “normalizer” types that handle other sources of AI model metadata.
- Creating more back-end storage types that are managed by a
storagecontainer that implements the same REST API as our initial ConfigMap-based offering.
Install the plug-ins and sidecar containers
Here's how to install the plug-ins and sidecars, including prerequisites and an installation overview.
Prerequisites
- Red Hat Developer Hub 1.8 or later
- Red Hat OpenShift AI:
- To have model cards from the Model Catalog imported as TechDocs, you need version 2.25 or later. You must also enable the Model Catalog dashboard and a Model Registry (they are both off by default).
- For the rest of the features, version 2.20 or later will suffice. Enabling the Model Registry and its associated dashboard allows a user to more directly customize AI model metadata.
Installation overview
- There are two dynamic plug-ins in the Red Hat Developer Hub Marketplace, @red-hat-developer-hub/backstage-plugin-catalog-backend-module-model-catalog and @red-hat-developer-hub/backstage-plugin-catalog-techdoc-url-reader-backend, which you add to your dynamic plug-in ConfigMap.
- There is a set of Kubernetes RBAC manifests you’ll apply in the namespace where your Developer Hub deployment resides, and a set of Kubernetes RBAC manifests you’ll apply where the Red Hat OpenShift AI Model Registry/Catalog deployment resides.
- The specification of the three sidecar containers will need to be added to either your Backstage CustomResource instance (if you installed using the Operator) or Deployment instance (if you installed using the Helm chart).
- Finally, you’ll update the Backstage
app-configConfigMap and enable the Catalog Entity Provider that ships with the @red-hat-developer-hub/backstage-plugin-catalog-backend-module-model-catalog dynamic plug-in.
The complete installation guide for the Developer Hub OpenShift AI connector is part of the Developer Hub 1.8 documentation. Please visit the Developer Hub 1.8 documentation for details on how to update your environment and install the OpenShift AI connector.
Updating what the OpenShift AI connector imports into Developer Hub
The default metadata imported from OpenShift AI is as follows:
- InferenceServices (Component type
model-server):- URL of the OpenShift Route (if exposed).
- URL of the Kubernetes Service.
- Authentication requirement status.
- Model Registry (Resource type
ai-model):- Model description, artifact URIs, and author/owner information.
- Model Catalog:
- Links to the model card (as Developer Hub TechDocs).
- Model license URL.
Given this, the engineers maintaining OpenShift AI might be different from the engineers maintaining Developer Hub, depending on your organization and how the OpenShift clusters are administered. If this is the case, coordination between the Developer Hub and OpenShift AI maintainers is required to set metadata in OpenShift AI so it propagates to Developer Hub. Please visit the Developer Hub 1.8 documentation to discover what is provided out of the box and how to update it.
Using the AI Model Software Catalog updates from a Developer Hub template
Now that the AI models and model servers are imported into the Developer Hub Software Catalog, what can you do with them?
Accessing REST API documentation or the model cards within Developer Hub adheres to the core Backstage tenet: providing a central location for information for development teams.
Additionally, in conjunction with the Developer Hub version 1.8 developer preview offering of the AI Model Catalog, we have updated the example AI application templates first announced in November 2024 to provide an alternative to typing in the AI model endpoint information. This alternative queries the Developer Hub Software Catalog for the Resources and Components imported using our prescribed format:
- The common
EntityPickerused by each of the sample applications can be seen here. - Associated steps that obtain the
model-serverComponent associated with anai-modelResource can be seen here. - The final use of these building blocks in each specific application will look something like this.
Here is a complete Template that pulls in the various parts from the source code repository links noted above, where we have inserted comments that start with the string # BLOG to indicate where the relevant logic resides:
apiVersion: scaffolder.backstage.io/v1beta3
kind: Template
metadata:
namespace: default
annotations:
backstage.io/managed-by-location: url:https://github.com/redhat-ai-dev/ai-lab-template/tree/ai-rolling-demo-1_9/templates/chatbot/template.yaml
backstage.io/managed-by-origin-location: url:https://github.com/redhat-ai-dev/ai-lab-template/blob/ai-rolling-demo-1_9/all.yaml
backstage.io/view-url: https://github.com/redhat-ai-dev/ai-lab-template/tree/ai-rolling-demo-1_9/templates/chatbot/template.yaml
backstage.io/edit-url: https://github.com/redhat-ai-dev/ai-lab-template/edit/ai-rolling-demo-1_9/templates/chatbot/template.yaml
backstage.io/source-location: url:https://github.com/redhat-ai-dev/ai-lab-template/tree/ai-rolling-demo-1_9/templates/chatbot/
backstage.io/techdocs-ref: dir:.
name: chatbot
title: Chatbot Application
description: Build your own Large Language Model (LLM)-enabled chat application.
Pick from the model servers available or bring your own.
tags:
- ai
- llamacpp
- vllm
- python
uid: 4cbd78eb-bc89-4966-962b-b3116e0c6a7a
etag: c2c6ed9ba1e6f27c226bc255318f3f440020e862
relations:
- type: ownedBy
targetRef: group:default/rhdh-pai
spec:
type: service
owner: rhdh-pai
parameters:
- title: Application Information
required:
- name
- owner
- argoNS
- argoInstance
- argoProject
- modelServer
ui:order:
- name
- owner
- argoNS
- argoInstance
- argoProject
- includeArgoLabel
- argoAppLabel
- modelServer
- "*"
properties:
name:
title: Name
type: string
description: Unique name of the component
ui:autofocus: true
ui:options:
rows: 5
ui:field: EntityNamePicker
maxLength: 63
owner:
title: Owner
type: string
description: Owner of the component
default: user:guest
ui:field: OwnerPicker
ui:options: {}
argoNS:
title: ArgoCD Namespace
type: string
description: The target namespace of the ArgoCD deployment
default: openshift-gitops
maxLength: 63
argoInstance:
title: ArgoCD Instance
type: string
description: The target ArgoCD instance name
default: default
maxLength: 63
argoProject:
title: ArgoCD Project
type: string
description: The target ArgoCD project name
default: default
maxLength: 63
includeArgoLabel:
title: Include ArgoCD App Label?
type: boolean
description: Indicates whether to include a user provided ArgoCD Application
Label to set
default: true
modelServer:
title: Model Server
default: llama.cpp
type: string
ui:enumDisabled:
- Create a new model server
- Select an existing model server
enum:
- Create a new model server
- vLLM
- llama.cpp
- Select an existing model server
- Bring you own model server
- choose-from-the-catalog
enumNames:
- Create a new model server
- vLLM
- llama.cpp
- Select an existing model server
- Bring you own model server
- Choose from the Catalog model(s)
dependencies:
includeArgoLabel:
oneOf:
- required:
- argoAppLabel
properties:
includeArgoLabel:
const: true
argoAppLabel:
title: ArgoCD Application Label
type: string
description: Define the label RHDH will use to identify the ArgoCD Applications
default: rolling-demo
modelServer:
oneOf:
- required:
- modelEndpoint
- modelName
properties:
modelServer:
const: Bring you own model server
modelServerDescription:
type: "null"
description: Fill in the model server endpoint and model name you wish to use
with your application.
modelEndpoint:
title: Model Server Endpoint
type: string
description: The endpoint for an existing model server.
modelName:
title: Model Name
type: string
ui:help: The name of the model deployed on the model server you would like to
use.
includeModelEndpointSecret:
title: Is bearer authentication required?
type: boolean
default: false
ui:help: Create a Secret containing the authentication bearer in the preferred
targeted Namespace first.
dependencies:
includeModelEndpointSecret:
allOf:
- if:
properties:
includeModelEndpointSecret:
const: true
then:
properties:
modelEndpointSecretName:
title: Model Server Endpoint Secret Name
ui:help: Paste in the name of the Secret containing your bearer.
type: string
modelEndpointSecretKey:
title: Model Server Endpoint Secret Key
ui:help: Paste in the key of the Secret containing the bearer value.
type: string
required:
- modelEndpointSecretName
- modelEndpointSecretKey
# BLOG: define an EntityPick for selecting a Resource entity imported by the connector
- required:
- catalogModel
properties:
modelServer:
const: choose-from-the-catalog
modelServerDescription:
type: "null"
description: Select a model from the RHDH catalog you wish to use with your
application.
catalogModel:
title: Model name
type: string
ui:help: The model chosen from the model catalog.
ui:field: EntityPicker
ui:options:
allowedKinds: []
catalogFilter:
kind: resource
spec.type: ai-model
spec.dependencyOf:
exists: true
includeModelEndpointSecret:
title: Is bearer authentication required?
type: boolean
default: false
ui:help: Create a Secret containing the authentication bearer in the preferred
targeted Namespace first.
dependencies:
includeModelEndpointSecret:
allOf:
- if:
properties:
includeModelEndpointSecret:
const: true
then:
properties:
modelEndpointSecretName:
title: Model Server Endpoint Secret Name
ui:help: Paste in the name of the Secret containing your bearer.
type: string
modelEndpointSecretKey:
title: Model Server Endpoint Secret Key
ui:help: Paste in the key of the Secret containing the bearer value.
type: string
required:
- modelEndpointSecretName
- modelEndpointSecretKey
- properties:
modelServer:
const: vLLM
modelServerDescription:
type: "null"
description: A high throughput, memory efficient inference and serving engine
with GPU support for LLMs in OpenShift. If you choose vLLM,
ensure that your cluster has Nvidia GPU supported (with
compute capability 7.0 or higher). Also, it should have
enough CPU & memory resources for the model you would like
to work with. | [Learn
more](https://github.com/redhat-ai-dev/developer-images/tree/main/model-servers/vllm/0.11.0)
modelNameDeployed:
title: Model Name
description: Text Generation | Apache-2.0 | [Learn
more](https://huggingface.co/ibm-granite/granite-3.1-8b-instruct)
default: ibm-granite/granite-3.1-8b-instruct
type: string
enum:
- ibm-granite/granite-3.1-8b-instruct
- properties:
modelServer:
const: llama.cpp
modelServerDescription:
type: "null"
description: A Python binding of LLM inference in C/C++ with minimal setup. |
[Learn
more](https://github.com/redhat-ai-dev/developer-images/tree/main/model-servers/llamacpp_python/0.3.16)
modelNameDeployed:
title: Model Name
description: Text Generation | Apache-2.0 | [Learn
more](https://huggingface.co/ibm-granite/granite-3.1-8b-instruct)
default: ibm-granite/granite-3.1-8b-instruct
type: string
enum:
- ibm-granite/granite-3.1-8b-instruct
- title: Application Repository Information
required:
- hostType
- repoOwner
- repoName
- branch
properties:
hostType:
title: Host Type
type: string
enum:
- GitHub
- GitLab
default: GitHub
repoOwner:
title: Repository Owner
default: ai-rolling-demo
type: string
ui:help: The organization, user or project that this repo will belong to
repoName:
title: Repository Name
type: string
branch:
title: Repository Default Branch
type: string
default: main
dependencies:
hostType:
oneOf:
- required:
- githubServer
properties:
hostType:
const: GitHub
githubServer:
title: Repository Server
type: string
default: github.com
ui:help: "You can also provide the on-prem github server, example:
github-github.apps.cluster-ljg9z.sandbox219.opentlc.com"
- required:
- gitlabServer
properties:
hostType:
const: GitLab
gitlabServer:
title: Repository Server
type: string
default: gitlab.com
ui:help: "You can also provide the on-prem gitlab server, example:
gitlab-gitlab.apps.cluster-ljg9z.sandbox219.opentlc.com"
- title: Deployment Information
required:
- imageRegistry
- imageOrg
- imageName
- namespace
ui:order:
- imageRegistry
- imageOrg
- imageName
- namespace
- deployArgoCDApplicationOnRemoteCluster
- remoteClusterAPIUrl
- remoteClusterDeploymentNamespace
- rhoaiSelected
properties:
imageRegistry:
title: Image Registry
type: string
description: The image registry host
default: quay.io
ui:help: "You can also provide the on-prem registry host, example:
quay-tv2pb.apps.cluster-tv2pb.sandbox1194.opentlc.com"
imageOrg:
title: Image Organization
default: rhdhpai-rolling-demo
type: string
description: The organization, user or project that this repo will belong to
imageName:
title: Image Name
type: string
ui:autofocus: true
ui:options:
rows: 5
namespace:
title: Deployment Namespace
type: string
default: rhdh-app
ui:autofocus: true
ui:options:
rows: 5
deployArgoCDApplicationOnRemoteCluster:
title: Deploy ArgoCD Application on Remote Cluster?
type: boolean
default: false
ui:help: If you select this field, you must ensure that the Remote Cluster is
already configured on your RHDH instance.
rhoaiSelected:
title: Create Workbench for OpenShift AI
description: Deploy to OpenShift AI in your app's namespace
type: boolean
default: false
ui:help: If you select this field, you must ensure that Red Hat OpenShift AI has
been installed on your cluster.
dependencies:
deployArgoCDApplicationOnRemoteCluster:
oneOf:
- required:
- remoteClusterAPIUrl
- remoteClusterDeploymentNamespace
properties:
deployArgoCDApplicationOnRemoteCluster:
const: true
remoteClusterAPIUrl:
title: Remote Cluster API URL
type: string
ui:help: Kube API URL of remote cluster
remoteClusterDeploymentNamespace:
title: Remote Cluster Deployment Namespace
type: string
ui:help: The namespace of the remote cluster that the argoCD application will be
deployed
- properties:
deployArgoCDApplicationOnRemoteCluster:
const: false
steps:
# BLOG: define steps for fetching the model and the model server from entities imported by the connector
- id: fetch-model-from-catalog
name: Fetch Model From Catalog
action: catalog:fetch
if: ${{ parameters.modelServer === 'choose-from-the-catalog' }}
input:
entityRef: ${{ parameters.catalogModel }}
- id: fetch-model-server-from-catalog
name: Fetch Model Server From Catalog
action: catalog:fetch
if: ${{ parameters.modelServer === 'choose-from-the-catalog' }}
input:
entityRef: ${{
steps['fetch-model-from-catalog'].output.entity.spec.dependencyOf[0]
}}
- id: fetch-base
name: Fetch Base
action: fetch:template
input:
url: ./content
targetPath: source
- id: fetch-skeleton-docs
name: Fetch Skeleton Techdocs
action: fetch:template
input:
url: ../../skeleton/techdoc
targetPath: source
values:
name: ${{ parameters.name }}
appSummary: A Large Language Model (LLM)-enabled streamlit chat application. The
bot replies with AI generated responses.
namespace: ${{ parameters.namespace }}
repoURL: https://${{ parameters.githubServer if parameters.hostType === 'GitHub'
else parameters.gitlabServer }}/${{ parameters.repoOwner }}/${{
parameters.repoName }}-gitops
srcRepoURL: https://${{ parameters.githubServer if parameters.hostType ===
'GitHub' else parameters.gitlabServer }}/${{ parameters.repoOwner
}}/${{ parameters.repoName }}
appContainer: ${{ 'quay.io/redhat-ai-dev/ai-template-bootstrap-app:latest' if
parameters.hostType === 'GitHub' else
'quay.io/redhat-ai-dev/chatbot:latest' }}
appPort: 8501
appRunCommand: streamlit run chatbot_ui.py
modelServiceContainer: quay.io/redhat-ai-dev/llamacpp_python:0.3.16
modelServicePort: 8001
# BLOG: logic for pulling the model server name from an annotation set on a Resourced imported by the connector
customModelName: ${{
steps['fetch-model-from-catalog'].output.entity.metadata.annotations
| pick('rhdh.modelcatalog.io/model-name') if parameters.modelServer
=== 'choose-from-the-catalog' else parameters.modelName }}
modelName: ibm-granite/granite-3.1-8b-instruct
modelSrc: https://huggingface.co/ibm-granite/granite-3.1-8b-instruct
modelServerName: ${{ parameters.modelServer }}
customModelAndModelServerSelected: ${{ true if parameters.modelServer === 'Bring
you own model server' else (true if parameters.modelServer ===
'choose-from-the-catalog' else false) }}
modelServiceSrcVLLM: https://github.com/redhat-ai-dev/developer-images/tree/main/model-servers/vllm/0.11.0
modelServiceSrcOther: https://github.com/redhat-ai-dev/developer-images/tree/main/model-servers/llamacpp_python/0.3.16
- id: fetch-skeleton
name: Fetch Skeleton
action: fetch:template
input:
url: ../../skeleton/source-repo
targetPath: source
values:
name: ${{ parameters.name }}
namespace: ${{ parameters.namespace }}
description: Secure Supply Chain Example for Chatbot Application
dockerfile: Containerfile
buildContext: .
gitopsSecretName: ${{ 'gitops-auth-secret' if parameters.hostType === 'GitHub'
else 'gitlab-auth-secret' }}
image: ${{ parameters.imageRegistry }}/${{ parameters.imageOrg }}/${{
parameters.imageName }}
tags: '["ai", "llamacpp", "vllm", "python"]'
owner: ${{ parameters.owner }}
repoSlug: ${{ parameters.imageOrg }}/${{ parameters.imageName }}
defaultBranch: ${{ parameters.branch }}
- id: fetch-github-action
name: Fetch GitHub Action
action: fetch:plain
if: ${{ parameters.hostType === 'GitHub' }}
input:
targetPath: source
url: ../../skeleton/github-action
- id: publish-github
name: Publish Repository to GitHub
action: publish:github
if: ${{ parameters.hostType === 'GitHub' }}
input:
sourcePath: source
description: This is ${{ parameters.name }}
repoUrl: ${{ parameters.githubServer }}?owner=${{ parameters.repoOwner
}}&repo=${{ parameters.repoName }}
defaultBranch: ${{ parameters.branch }}
protectDefaultBranch: true
allowAutoMerge: true
deleteBranchOnMerge: true
requiredStatusCheckContexts: []
repoVisibility: public
requiredApprovingReviewCount: 0
- id: publish-gitlab
name: Publish Repository to GitLab
action: publish:gitlab
if: ${{ parameters.hostType === 'GitLab' }}
input:
sourcePath: source
description: This is ${{ parameters.name }}
repoUrl: ${{ parameters.gitlabServer }}?owner=${{ parameters.repoOwner
}}&repo=${{ parameters.repoName }}
defaultBranch: ${{ parameters.branch }}
protectDefaultBranch: false
repoVisibility: public
- id: fetch-gitops-skeleton
name: Fetch Gitops Skeleton
action: fetch:template
input:
url: ../../skeleton/gitops-template
targetPath: gitops
values:
name: ${{ parameters.name }}
appName: ${{ parameters.name }}-gitops
description: This is GitOps manifest for ${{ parameters.name }}
namespace: ${{ parameters.remoteClusterDeploymentNamespace if
parameters.deployArgoCDApplicationOnRemoteCluster else
parameters.namespace }}
rhdhNamespace: rolling-demo-ns
repoURL: https://${{ parameters.githubServer if parameters.hostType === 'GitHub'
else parameters.gitlabServer }}/${{ parameters.repoOwner }}/${{
parameters.repoName }}-gitops
srcRepoURL: https://${{ parameters.githubServer if parameters.hostType ===
'GitHub' else parameters.gitlabServer }}/${{ parameters.repoOwner
}}/${{ parameters.repoName }}
argoComponentOverlays: ./components/${{ parameters.name }}/overlays
owner: ${{ parameters.owner }}
argoNS: ${{ parameters.argoNS }}
argoProject: ${{ parameters.argoProject }}
secretRef: ${{ parameters.hostType === 'GitLab' }}
gitSecret: gitlab-auth-secret
gitSecretKey: password
webhookSecret: pipelines-secret
webhookSecretKey: webhook.secret
defaultBranch: main
initContainer: quay.io/redhat-ai-dev/granite-3.1-8b-instruct-gguf:latest
modelInitCommand: "['/usr/bin/install', '/model/model.file', '/shared/']"
modelPath: /model/model.file
appContainer: ${{ 'quay.io/redhat-ai-dev/ai-template-bootstrap-app:latest' if
parameters.hostType === 'GitHub' else
'quay.io/redhat-ai-dev/chatbot:latest' }}
appPort: 8501
modelServiceContainer: quay.io/redhat-ai-dev/llamacpp_python:0.3.16
modelServicePort: 8001
vllmSelected: ${{ parameters.modelServer === 'vLLM' }}
vllmModelServiceContainer: quay.io/redhat-ai-dev/vllm-openai-ubi9:v0.11.0
# BLOG: logic for getting the model name from the annotation set on the Resource entity imported by the collector
modelName: ${{ parameters.modelName if parameters.modelServer === 'Bring you own
model server' else
(steps['fetch-model-from-catalog'].output.entity.metadata.annotations
| pick('rhdh.modelcatalog.io/model-name') if parameters.modelServer
=== 'choose-from-the-catalog' else
'ibm-granite/granite-3.1-8b-instruct') }}
modelSrc: https://huggingface.co/ibm-granite/granite-3.1-8b-instruct
maxModelLength: 4096
existingModelServer: ${{ true if parameters.modelServer === 'Bring you own model
server' else (true if parameters.modelServer ===
'choose-from-the-catalog' else false) }}
# BLOG: logic for getting the model server URL from the annotation set on the Component entity imported by the collector
modelEndpoint: ${{
(steps['fetch-model-server-from-catalog'].output.entity.metadata.annotations
| pick('rhdh.modelcatalog.io/internal-service-url')) if
parameters.modelServer === 'choose-from-the-catalog' else
parameters.modelEndpoint }}
modelEndpointSecretName: ${{ parameters.modelEndpointSecretName }}
modelEndpointSecretKey: ${{ parameters.modelEndpointSecretKey }}
includeModelEndpointSecret: ${{ parameters.includeModelEndpointSecret }}
rhoaiSelected: ${{ parameters.rhoaiSelected }}
dbRequired: false
supportApp: true
modelServerName: ${{ parameters.modelServer }}
modelServiceSrcVLLM: https://github.com/redhat-ai-dev/developer-images/tree/main/model-servers/vllm/0.11.0
modelServiceSrcOther: https://github.com/redhat-ai-dev/developer-images/tree/main/model-servers/llamacpp_python/0.3.16
imageRegistry: ${{ parameters.imageRegistry }}
imageOrg: ${{ parameters.imageOrg }}
imageName: ${{ parameters.imageName }}
deployOnRemoteCluster: ${{ parameters.deployArgoCDApplicationOnRemoteCluster }}
remoteClusterAPIUri: ${{ parameters.remoteClusterAPIUrl }}
remoteClusterDeploymentNamespace: ${{ parameters.remoteClusterDeploymentNamespace }}
customModelServer: ${{ parameters.modelServer }}
customModelName: ${{ parameters.modelName }}
- id: cleanupDatabaseResources
action: fs:delete
name: Cleanup Unused Database Resources
if: true
input:
files:
- gitops/components/http/base/deployment-database.yaml
- gitops/components/http/base/service-database.yaml
- gitops/components/http/base/database-config.yaml
- id: cleanupRhoaiResources
action: fs:delete
name: Cleanup Unused RHOAI Resources
if: ${{ not parameters.rhoaiSelected }}
input:
files:
- gitops/components/http/base/rhoai
- id: cleanupvLLMResources
action: fs:delete
name: Cleanup Unused vLLM Resources
if: ${{ parameters.modelServer !== 'vLLM' }}
input:
files:
- gitops/components/http/base/pvc.yaml
- id: cleanupModelServerResources
action: fs:delete
name: Cleanup Unused Model Server Resources
if: ${{ true if parameters.modelServer === 'Bring you own model server' else
(true if parameters.modelServer === 'choose-from-the-catalog' else
false) }}
input:
files:
- gitops/components/http/base/deployment-model-server.yaml
- gitops/components/http/base/service-model-server.yaml
- id: cleanupApplicationResources
action: fs:delete
name: Cleanup Unused Application Resources
if: false
input:
files:
- gitops/components/http/base/deployment.yaml
- gitops/components/http/base/service.yaml
- gitops/components/http/base/route.yaml
- action: fs:rename
id: renameComponentDir
name: Rename Component Directory
input:
files:
- from: gitops/components/http
to: gitops/components/${{ parameters.name }}
overwrite: true
- id: publish-github-gitops
name: Publish GitOps Repository to Github
action: publish:github
if: ${{ parameters.hostType === 'GitHub' }}
input:
sourcePath: gitops
description: This is GitOps repository for ${{ parameters.name }}
repoUrl: ${{ parameters.githubServer }}?owner=${{ parameters.repoOwner
}}&repo=${{ parameters.repoName }}-gitops
defaultBranch: main
protectDefaultBranch: false
repoVisibility: public
- id: publish-gitlab-gitops
name: Publish GitOps Repository to GitLab
action: publish:gitlab
if: ${{ parameters.hostType === 'GitLab' }}
input:
sourcePath: gitops
description: This is GitOps repository for ${{ parameters.name }}
repoUrl: ${{ parameters.gitlabServer }}?owner=${{ parameters.repoOwner
}}&repo=${{ parameters.repoName }}-gitops
defaultBranch: main
protectDefaultBranch: false
repoVisibility: public
- id: wait-for-github-repository
name: Waiting for Repository Availability
action: debug:wait
input:
seconds: 3
- id: register
name: Register
action: catalog:register
input:
repoContentsUrl: ${{ steps['publish-github'].output.repoContentsUrl if
steps['publish-github'].output else
steps['publish-gitlab'].output.repoContentsUrl }}
catalogInfoPath: /catalog-info.yaml
- id: register-gitops
name: Register Gitops
action: catalog:register
input:
repoContentsUrl: ${{ steps['publish-github-gitops'].output.repoContentsUrl if
steps['publish-github-gitops'].output else
steps['publish-gitlab-gitops'].output.repoContentsUrl }}
catalogInfoPath: /catalog-info.yaml
- id: create-argocd-resources
name: Create ArgoCD Resources
action: argocd:create-resources
input:
appName: ${{ parameters.name }}-app-of-apps
argoInstance: ${{ parameters.argoInstance }}
namespace: ${{ parameters.argoNS }}
labelValue: rolling-demo
repoUrl: https://${{ parameters.githubServer if parameters.hostType === 'GitHub'
else parameters.gitlabServer }}/${{ parameters.repoOwner }}/${{
parameters.repoName }}-gitops.git
path: ./app-of-apps
- id: trigger-build-pr
name: PR to Trigger Pipeline Build
action: publish:github:pull-request
if: ${{ parameters.hostType === 'GitHub' }}
input:
repoUrl: ${{ parameters.githubServer }}?owner=${{ parameters.repoOwner
}}&repo=${{ parameters.repoName }}
branchName: trigger-pipeline
commitMessage: trigger pipeline build
description: pr to trigger pipeline build
title: trigger pipeline build
sourcePath: source
targetBranchName: ${{ parameters.branch }}
- id: trigger_gh_workflow
name: Trigger GitHub workflow
action: github:actions:dispatch
if: ${{ parameters.hostType === 'GitHub' }}
input:
repoUrl: ${{ parameters.githubServer }}?owner=${{ parameters.repoOwner
}}&repo=${{ parameters.repoName }}
branchOrTagName: ${{ parameters.branch }}
workflowId: automerge.yml
workflowInputs:
pr_url: ${{ steps['trigger-build-pr'].output.remoteUrl }}
output:
links:
- title: Source Repository
url: ${{ steps['publish-github'].output.remoteUrl if
steps['publish-github'].output else
steps['publish-gitlab'].output.remoteUrl }}
- title: GitOps Repository
url: ${{ steps['publish-github-gitops'].output.remoteUrl if
steps['publish-github-gitops'].output else
steps['publish-gitlab-gitops'].output.remoteUrl }}
- title: Open Component in Catalog
icon: catalog
entityRef: ${{ steps['register'].output.entityRef }}
- title: Open GitOps Resource in Catalog
icon: catalog
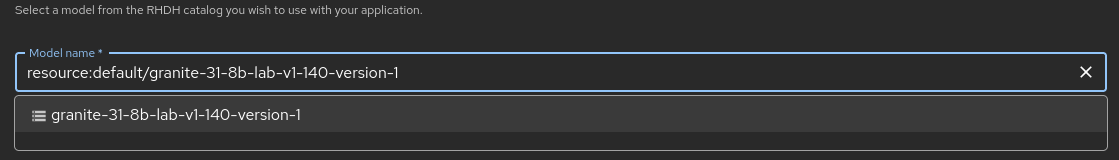
entityRef: ${{ steps['register-gitops'].output.entityRef }}These changes simplify the task of looking up AI model connection information for AI application developers who use Developer Hub and these templates. Figure 5 shows the simple yet powerful drop-down.
Conclusion
Building on the prior blog post’s definition of a model catalog structure for AI models and model servers, we believe this developer preview shows the value provided by the OpenShift AI connector’s integration between Red Hat Developer Hub and Red Hat OpenShift AI. Metadata is pulled from the source of truth from within the OpenShift AI platform. It is then imported in a way that’s familiar to existing Red Hat Developer Hub or Backstage users and allows easy integration with other Developer Hub features.
Explore more topics:
Last updated: January 23, 2026