By design, Red Hat OpenShift Dev Spaces is not multi-cluster aware, and you can only have one instance per cluster. However, you can still run the product in a multi-cluster environment by deploying an instance in each cluster and using a load balancer or DNS-based routing to direct traffic to the appropriate instance based on the user’s location or other criteria. This approach can help improve performance and reliability by distributing the workload across multiple clusters and providing redundancy in case of cluster failures.
Developer Sandbox
One example of a multi-cluster architecture is workspaces.openshift.com, which is part of the Developer Sandbox. From the infrastructure perspective, the Developer Sandbox has multiple clusters of Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS. On each cluster, Red Hat OpenShift Dev Spaces is installed and configured using Argo CD. Since the user base is spread across multiple clusters, workspaces.openshift.com is used as a single entry point to the Dev Spaces instances (Figure 1).
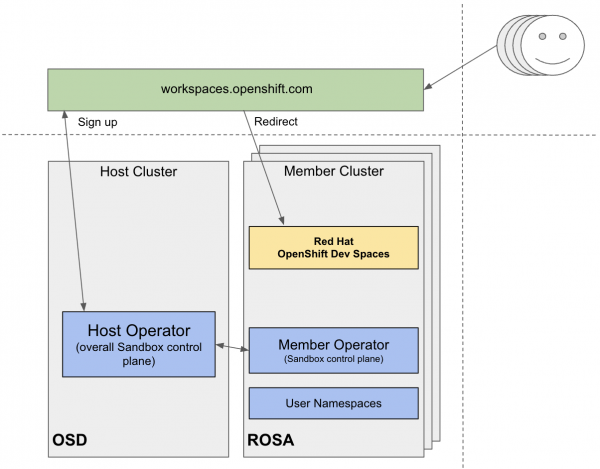
You can find implementation details about the Developer Sandbox redirector in the following GitHub repository. However, the solution for workspaces.openshift.com is Developer Sandbox-specific and can not be reused as-is in other environments. This article introduces a universal routing solution based on the OpenShift group membership.
Multicluster redirector
The devspaces-multicluster-redirector is an open-source, Quarkus-based intelligent routing service. It acts as a single gateway for developers, automatically redirecting them to the correct OpenShift Dev Spaces instance on the correct cluster based on their OpenShift group membership. Unlike the Developer Sandbox-specific solution, this redirector is designed to be a plug-and-play for any enterprise looking to scale their Red Hat OpenShift Dev Spaces across multiple OpenShift clusters.
The multicluster redirector provides an intelligent routing service that automatically redirects users to their designated OpenShift Dev Spaces instance based on their OpenShift group membership. This enables organizations to manage multiple OpenShift Dev Spaces instances and seamlessly route users to the appropriate instance. In enterprise environments with multiple OpenShift Dev Spaces deployments across different clusters, users need to be directed to the correct instance based on their team, project, or organizational unit. This redirector service solves that problem by:
- Authentication: The user is authenticated via the OpenShift OAuth Proxy sidecar.
- Identification: The user's identity and group information are passed to the Quarkus application via HTTP headers (
X-Forwarded-User,X-Forwarded-Groups). - Group lookup: The application queries the OpenShift API using the Fabric8 Kubernetes client to verify current group memberships.
- Mapping and redirection: The application checks a JSON-based mapping (stored in a ConfigMap) to find which OpenShift Dev Spaces URL corresponds to the user's group.
- Seamless handoff: The user is redirected to their designated cluster (e.g.,
team-alphagoes to Cluster A andteam-betagoes to Cluster B).
Host cluster requirement
An important requirement is that all users must be provisioned to the host cluster where the devspaces-multicluster-redirector will be physically deployed, since the OpenShift groups on this cluster are the key determination of the redirect logic.
kind: Group
apiVersion: user.openshift.io/v1
metadata:
name: team-alpha
users:
- user1
- user2
- user3Even if user1 , user2 , and user3 never actually run a workload on the host cluster, they must pass through its OAuth flow so the redirector can identify them and determine their OpenShift Dev Spaces instance based on the mapping.
Note: The host cluster may or may not have the OpenShift Dev Spaces instance installed. If the OpenShift Dev Spaces is installed on the host cluster, advancedAuthorization is expected to be used for managing the Dev Spaces access on this cluster. You can find more details about the setup in the dedicated article, How to configure granular access in OpenShift Dev Spaces.
Mapping
The mapping between OpenShift groups and OpenShift Dev Spaces URLs is stored in the devspaces-openshift-group-mapping ConfigMap. The redirector is designed to watch this file. If you add a new team or a new cluster, you simply update the ConfigMap. The application detects the change via symlink resolution and updates its routing table in real-time without a restart.
apiVersion: v1
kind: ConfigMap
metadata:
name: devspaces-openshift-group-mapping
data:
group-mapping.json: |
{
"team-alpha": "https://devspaces-alpha.example.com",
"team-beta": "https://devspaces-beta.example.com",
"contractors": "https://devspaces-external.example.com"
}Note: In a simple setup, a user belongs to only one team or group, and is redirected to their OpenShift Dev Spaces instance instantly. However, in a large enterprise, roles are rarely that static, and the user can technically belong to multiple OpenShift groups. In this case, the selection dashboard with multiple OpenShift Dev Spaces instances will be displayed (Figure 2).
Wrap up
Scaling Red Hat OpenShift Dev Spaces to thousands of users often requires a multi-cluster strategy to avoid resource contention and provide geographic proximity. The multicluster redirector bridges the gap between a fragmented multi-cluster setup and a seamless developer experience. By leveraging OpenShift groups, you can ensure that every developer lands exactly where they need to be, while your infrastructure team maintains the flexibility to scale clusters behind the scenes. The multicluster redirector will be available as an optional component starting from the Red Hat OpenShift Dev Spaces 3.27 release in March 2026. Stay tuned!
Want to try the community-supported version now? Check out the repository on GitHub and start scaling your cloud development environments.

