Pachyderm is an open source tool for creating and running machine learning (AI/ML) pipelines. It runs on Kubernetes and provides modern developer benefits such as versioning and autoscaling. Pachyderm also integrates with the JupyterHub information sharing platform. On March 8, 2022, Red Hat announced that Pachyderm has been added to the Open Data Hub (ODH), which is a blueprint for building an AI-as-a-service platform on the Red Hat OpenShift Container Platform. In this article, you'll learn how to install Pachyderm using Open Data Hub.
To walk through the steps in this article, you'll need a Red Hat OpenShift cluster with a default StorageClass. The procedure in this article has been tested in the following environments:
- OpenShift Dedicated 4.9 on AWS with a
gp2StorageClass - An OpenShift cluster using Red Hat OpenShift Local (formerly Red Hat CodeReady Containers) with an
nfsStorageClassset up by the NFS Provisioner Operator.
The first option is used in this article. OpenShift Dedicated provides a default gp2 StorageClass, but it is not cost-free. As an alternative, with the second option you can set up a cost-free environment as follows:
- Use OpenShift Local to install an OpenShift All-in-One cluster on your laptop.
- Add an
nfsStorageClassusing the NFS Provisioner Operator, available from OperatorHub or Github.
Once you've followed those steps, you'll have essentially the same environment as OpenShift Dedicated.
This article also contains an embedded video illustrating the steps.
If you want to experiment with the Red Hat OpenShift Local test environment, please refer to the following articles:
- Configure CodeReady Containers for AI/ML development
- Create and manage local persistent volumes with CodeReady Containers
Deploy the Open Data Hub Operator
Installing an Operator is the easiest step in this procedure. Go to the OperatorHub menu option in the OpenShift console, search for the Open Data Hub Operator, and click its link (Figure 1).
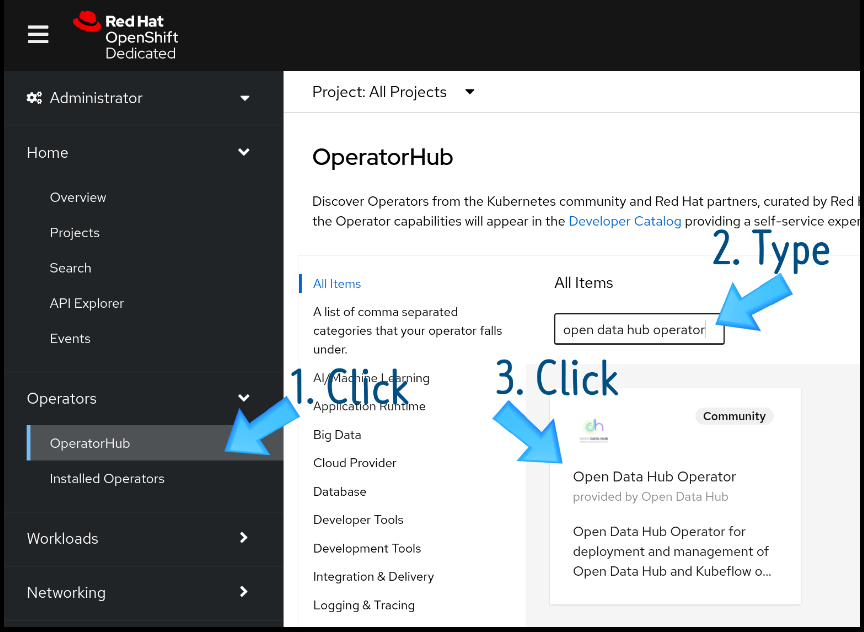
You'll be taken to the Operator page for the Open Data Hub Operator (Figure 2). Click Install.

Next, you'll see the Install Operator page (Figure 3). Keep all the defaults and click Install again.

When installation is complete, you'll see a message saying "saying "Installed operator — ready for use," as in Figure 4.

After you install Open Data Hub Operator, you need to create a new project that we'll call opendatahub, where all required components—Jupyterhub, Ceph Nano, and Pachyderm—will be deployed
$ oc new-project opendatahub
Create a KfDef to deploy Pachyderm, JuypterHub, and Ceph Nano
Pachyderm supports any storage option compatible with AWS S3 object storage. Open Data Hub provides two of these storage options:
- Full automation: Deploy Ceph Nano on Open Data Hub, which creates a secret for Pachyderm.
- Partial automation: Manually create a secret for the credentials to access S3 or another S3-compatible object storage, such as MinIO.
Full automation using Ceph Nano
Open Data Hub provides a full automation YAML configuration using a Kubernetes Job named pachyderm-deployer. Here's an excerpt of the configuration:
# Ceph Nano
- kustomizeConfig:
repoRef:
name: manifests
path: ceph/object-storage/scc
name: ceph-nano-scc
- kustomizeConfig:
repoRef:
name: manifests
path: ceph/object-storage/nano
name: ceph-nano
# Pachyderm operator
- kustomizeConfig:
parameters:
- name: namespace
value: openshift-operators
repoRef:
name: manifests
path: odhpachyderm/operator
name: odhpachyderm-operator
# Pachyderm deployer
- kustomizeConfig:
repoRef:
name: manifests
path: odhpachyderm/deployer
name: odhpachyderm-deployer
The configuration contains a script that makes sure Ceph Nano is in a ready state, and then creates an S3 bucket in Ceph Nano. After that, the script creates a secret for the S3 bucket credentials, which Pachyderm will use to gain access to the S3 bucket.
To use full automation on Kubernetes, you need a KfDef custom resource (CR). A manifest for this KfDef can be found in my GitHub repository. Create the KfDef on OpenShift through the following command:
$ oc create -f https://bit.ly/3wHwt59
Partial automation using S3 or other compatible storage (MinIO)
If you want to go the partial automation route, the only difference from using Ceph Nano is that you need to create a secret before creating the KfDef, then pass that information to pachyderm-deployer in the KfDef. The relevant line can be found in context in the YAML file.
An oc command that creates a secret for AWS S3 looks like this:
$ oc create secret generic pachyderm-aws-secret \
--from-literal=access-id=XXX \
--from-literal=access-secret=XXX \
--from-literal=region=us-east-2 \
--from-literal=bucket=pachyderm
An oc command that creates a secret for MinIO looks like this:
$ oc create secret generic pachyderm-minio-secret \
--from-literal=access-id=XXX \
--from-literal=access-secret=XXX \
--from-literal=custom-endpoint=${minio_ip}
--from-literal=region=us-east-2 \
--from-literal=bucket=pachyderm
The following excerpt from a KfDef manifest shows how to use the secret with S3. The example uses pachyderm-aws-secret for the secret:
# Pachyderm Operator
- kustomizeConfig:
parameters:
- name: namespace
value: openshift-operators
repoRef:
name: manifests
path: odhpachyderm/operator
name: odhpachyderm-operator
# Pachyderm Deployer
- kustomizeConfig:
parameters:
- name: storage_secret #<=== Must set this
value: pachyderm-aws-secret #<=== Use your Secret Name
repoRef:
name: manifests
path: odhpachyderm/deployer
name: odhpachyderm-deployer
Once you've created the secret, you can create the KfDef through the following command:
$ oc create -f https://bit.ly/3NkV31I
After you create the KfDef, OpenShift creates several pods in the opendatahub project. Four pods are created for Pachyderm:
$ oc get pod
etcd-0 1/1 Running 0 12m
postgres-0 1/1 Running 0 12m
pachd-874f5958c-7w98p 1/1 Running 0 11m
pg-bouncer-7587d49769-gwn8f 1/1 Running 0 11m
Even more pods might be devoted to Pachyderm if you are using Red Hat OpenShift Local. If resources on your cluster are tight, it could take some time to create the pods.
Now you can try Pachyderm on your cluster.
Video demo
The following video illustrates the steps outlined so far.
Troubleshooting
If you are running this example on your laptop, you might see some errors with the JupyterHub pods, jupyterhub and jupyterhub-db, due to a lack of resources (Figure 5).

traefix-proxy pods might show some errors, but you can ignore them. When jupyterhub and jupyterhub-db are recovered, traefix-proxy will be automatically healed.
If you see these errors, start a rollout of the DeploymentConfigs for jupyterhub and jupyterhub-db as shown in Figures 6 and 7.


Start a rollout for jupyterhub-db in the same way.
If these steps don't solve the problem, roll out jupyterhub-db first, wait until it is ready, then roll out jupyterhub. Then enjoy experimenting with what Pachyderm has to offer!
