Welcome back to this ongoing series of posts about using Large Language Models(LLMs) with Node.js. Here is what the series looks like so far:
- Experimenting with a Large Language Model powered Chatbot with Node.js
- Experimenting with Email generation and summarization with Node.js and Large Language Models
- Improving Chatbot result with Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG) and Node.js
All the posts so far have used the LLM to generate a summary response based on information we pass to it and the LLM will respond in a “natural language”. There are, however, times that we want our LLM to interact directly with some type of system, like a database. Calls to a system like this are usually in a particular format. This is where the concept of tool calling comes in. In fact, in this next post, we will tell our chatbot to “update this claims status to approved” and it will call the appropriate function to update our database with this new information.
What is Tools/Functions
This concept allows a model to respond to a given prompt by calling a tool or function. An important thing to note here is that the model doesn’t actually call the tool, rather it sees that there is a function available and then generates the arguments for that function and returns that as the response. It is then up to the application developer to then call the function with the generated arguments. Here is a simple example from the langchain.js docs that illustrates what I previously mentioned. In this case, the user asks what the weather in Hawaii is. The model knows it has a tool/function called get_weather so it generates the arguments needed to call that function.
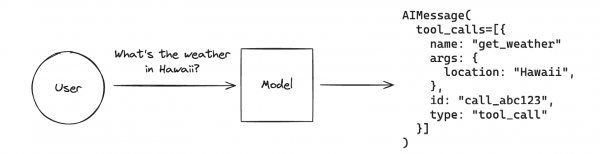
Another thing to note is that tool and function calling isn’t totally universal yet across the different LLMs, but it is supported by many of the popular LLMs
Parasol and Tools
As alluded to in a previous paragraph, we are going to update the Parasol application that we’ve been working on to include tool and function calling. The goal is to be able to write in our chatbot, Update this claims status to Approved or Denied or some status that is appropriate when managing claims. The LLM will see that we have a function called update claim status, which it will then generate arguments for. We will then write code to call the function with the provided arguments.
Create the tool
With langchain.js, creating a tool is as simple as using the tool function. It takes two parameters, the first being the actual function and the second is an object with the name, description and schema for the function.
Below is a breakdown of the various pieces of our tool. First is the actual function that will be called to update our database with the values passed in.
async ({ claimId, claimStatus }) => {
return fastify.sqlite.run('update claim set status = ? where id = ?', [claimStatus, claimId], (err, rows) => {
return `Claim Status updated to ${claimStatus} for claimId ${claimId}`;
});
}This is a pretty basic function that takes the claim Id and the claim status and uses those values to run an update statement using sqlite. We are using fastify with the sqlite plugin, that is why you see fastify.sqlite.run
The second parameter for the tool function is where we define the name and description of the function to be called as well as a schema for the function parameters. To create our schema we are using the Zod schema module. We saw this module in second post of this series
{
name: 'updateClaimStatus',
schema: z.object({
claimId: z.string(),
claimStatus: z.string()
}),
description: 'Update the claim status'
}
In this example, our function's name is updateClaimStatus with a very descriptive description. The schema is also pretty straightforward, with just two parameters, which are both strings.
All of that code is then wrapped in the tool function. You can see the the full exported function here: https://github.com/nodeshift/parasol-insurance-nodejs/blob/using-tools/ai/tools.mjs
Adding it to the Model
Adding the function to our model is pretty straightforward. Langchain.js has a “bindTools” method that is used to add them to the model. It takes a list of functions so if your application is using multiple functions, you can specify them all at once. Using the example code from earlier, the bind code might look something like this:
const llmWithTools = model.bindTools([updateClaimStatusTool]);Calling it
Once everything is set up, we can interact with our chatbot and type something like Update the claim status to approved. This will send that input to our model. The model then realizes it has a function that’s appropriate for this interaction. The initial response from our model might look like something similar:
AIMessage {
"id": "chatcmpl-604",
"content": "",
"tool_calls": [
{
"name": "updateClaimStatus",
"args": {
"claimId": "1",
"claimStatus": "approved"
},
"type": "tool_call",
"id": "call_65gvc6n6"
}
],
"invalid_tool_calls": [],
}
}This resulting langchain.js object contains the “tools_calls” property. We can see there is an entry in that array, which is an object that has the properly formatted arguments for our update claims function. At this point our function has yet to be called, this is just the model telling us that it knows about a function that relates to our query and that here are the properly formatted arguments in case we would like to use it.
We do want to use that function, so we pass those arguments to our function to actually make the call to the DB. This would look like something similar:
const toolMessage = await selectedTool.invoke(toolCall);The full code for making the function calls can be found here: https://github.com/nodeshift/parasol-insurance-nodejs/blob/using-tools/ai/chatbot-with-tools.mjs
Putting it all together
At this point, our function was called and the database was updated, but we also want our LLM to respond in a natural way. If you’ve been following the code on github, you might have noticed that we’ve been compiling an array of messages after each of the previous steps. We will then invoke our model one last time with all those messages, which will result in our LLM responding that The claim status has been updated to approved for claim ID 1.
Conclusion
Having our LLM call functions based on our interactions with a chatbot can be pretty powerful and fairly simple to set up. While this was a very simple example, you can imagine applications with more sophisticated function calls.
Stay tuned for the next post in the series which will wrap-up everything that we’ve done so far in this series.
As always if you want to learn more about what the Red Hat Node.js team is up to check these out:
https://developers.redhat.com/topics/nodejs
https://developers.redhat.com/topics/nodejs/ai
https://developers.redhat.com/blog/2024/11/20/essential-ai-tutorials-nodejs-developers
https://github.com/nodeshift/nodejs-reference-architecture
https://developers.redhat.com/e-books/developers-guide-nodejs-reference-architecture
