In my previous article, How building workbenches accelerates AI/ML development, I discussed the user's experience building workbenches to accelerate AI/ML development. I also demonstrated how to select a software template and provide additional information as an input, such as namespace and cluster information to create the component. Now let’s explore how Red Hat Developer Hub and Red Hat OpenShift AI work together on top of Red Hat OpenShift.
A GitOps approach to OpenShift AI
The Software Templates are built with Helm charts, which will read from the user inputs and populate this information in a new source code creating a new repository. Thanks to Red Hat OpenShift GitOps, this source code is applied to OpenShift, building new components and ensuring that the desired state is always current. Red Hat OpenShift AI brings AI capabilities on top of OpenShift, allowing these configurations to be created and building components required to build AI applications for model serving, model training, and developing and deploying inference AI applications at scale in an enterprise environment (Figure 1).
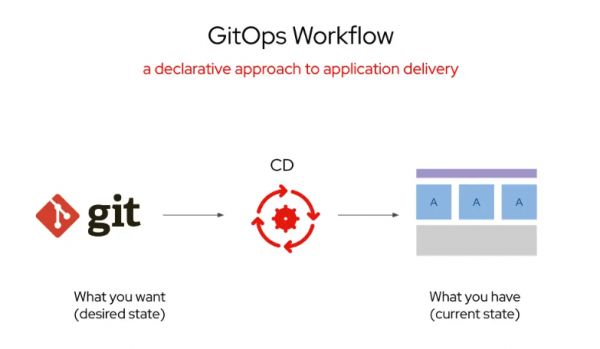
Prerequisites:
Creating a workbench
A workbench gives you an environment to build, deploy, and test AI/ML. A workbench will provide a notebook based on a specific image and a notebook optimizing with tools and libraries needed for developing and testing models (Figure 2). Learn more about creating a workbench and a notebook and explore notebooks and GitOps.
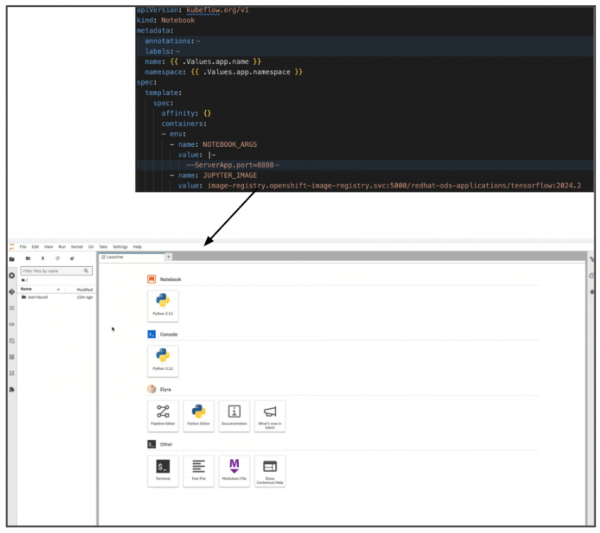
It allows you to automate training, testing, and running your model, removing the burden of manual testing and ensuring consistency.
Enable the pipeline server
To start working with data science pipelines, you need to enable the pipeline server. The pipeline server will be defined with the required storage information and a scheduler (Figure 3). Learn more about managing data science pipelines and data science pipelines and GitOps.
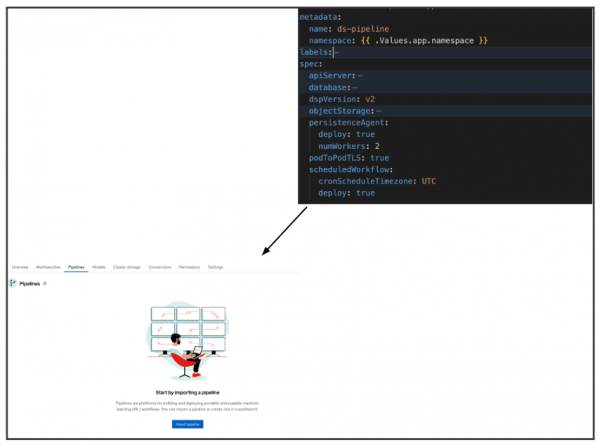
Next, you can start adding a data science pipeline into your project. Learn how to start building a pipeline or import a pipeline.
Model serving
Once your model is tested we want to make it available for testing and other applications to be consumed. Serving or deploying the model makes the model available as a service, or model runtime server, that you can access using an API. You can then access the inference endpoints for the deployed model from the dashboard and see predictions based on data inputs that you provide through API calls. Querying the model through the API is also called model inferencing.
- Single-model serving platform: Used for large models such as LLMs, uses its own runtime server and serverless deployment.
- Multi-model serving platform: Used for small/medium sized models which can use the same runtime server. Integrated with Istio.
- NVIDIA NIM model serving platform: Used for NVIDIA Inference Microservices (NIM) on the NVIDIA NIM model serving platform.
For this example, we are using a multi-model serving platform and OpenVINO as a model server runtime. For more information, consult the product documentation
For the model to be served we need to specify a serving runtime. OpenShift AI supports several runtimes and you can also build your custom runtime. Serving runtimes will provide the tools needed for the model to be served in OpenShift (Figure 4).
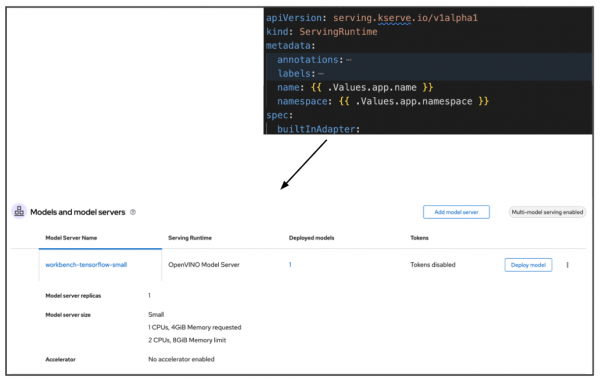
Explore more about model serving and GitOps.
Inference service
Once the model is deployed, you can access the model using an inference endpoint. The InferenceService will contain the model format, storage, and deployment mode (Figure 5).
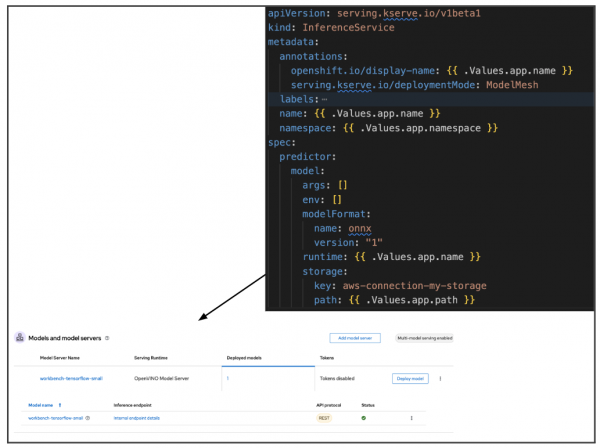
Explore inference service and GitOps further.
Additional configurations
Ensure your namespace is set up with the correct label. The following is a sample namespace configuration.
apiVersion: v1
kind: Namespace
metadata:
labels:
kubernetes.io/metadata.name: {{ .Values.app.namespace }}
modelmesh-enabled: "true"
openshift-pipelines.tekton.dev/namespace-reconcile-version: 1.16.1
name: {{ .Values.app.namespace}}You have access to S3-compatible object storage. You have created the required storage configurations.
Next steps
In this article, you learned about what happens behind the scenes with OpenShift GitOps, OpenShift AI, and OpenShift. I discussed the significance of workbenches, model serving, and namespace configurations. I also provided many resources for further learning. If you haven't already, be sure to read part 1, How building workbenches accelerates AI/ML development.
