In Red Hat Developer Hub, any user (from data scientists to MLOps engineers) can build, train, and deploy AI applications with ready-to-use workbenches from a pre-defined template, using Red Hat OpenShift AI. Platform AI engineers can extend self-service by creating workbenches and other components for any team, using software templates via role-based access control (RBAC).
Red Hat OpenShift AI is a flexible, scalable artificial intelligence and machine learning (AI/ML) platform that enables enterprises to create and deliver AI-enabled applications at scale across hybrid cloud environments. Built using open source technologies, OpenShift AI provides trusted, operationally consistent capabilities for teams to experiment, serve models, and deliver innovative apps.
In this article, I will demonstrate how to get started utilizing each platform and component.
Why you should build a workbench
Building a workbench allows you to access a new environment to build, train, and test your model running on Red Hat OpenShift to provide a single enterprise-ready AI application platform. A workbench can have dedicated storage for your model connected to diverse storage options as well as different notebooks from Jupyter Notebook and TensorFlow. These include many libraries, such as CUDA and PyTorch libraries.
Bringing a new workbench with its configurations offers many possibilities and flexibility for end users to decide which tools to use to build AI applications.
Learn more about workbenches.
Where Developer Hub comes in
Red Hat Developer Hub (RHDH) is a developer portal that enables teams to work efficiently and seamlessly with containers and cloud technologies while integrating best practices and scaling them across any organization. Developers and platform engineering teams are part of many successful stories to bring modernization and new application capabilities.
OpenShift GitOps enables customers to build and integrate declarative Git-driven CD workflows directly into their application development platform. Red Hat Developer Hub uses the power of GitOps to create and maintain the virtual machines (VMs) definition in the Kubernetes cluster.
Key features of Red Hat OpenShift GitOps
Red Hat OpenShift GitOps helps you automate the following tasks:
- Ensuring that clusters have similar states for configuration, monitoring, and storage.
- Applying or reverting configuration changes to multiple Red Hat OpenShift Container Platform clusters.
- Associating templated configuration with different environments.
- Promoting applications across clusters, from staging to production.
Building my environment with RHDH
In this example, RHDH provides workbenches of different sizes based on resource consumption needed and extra configurations to enable pipelines and model serving. Additionally, RHDH provides different workbenches to use notebooks from CUDA, PyTorch, TensorFlow, and many others.
Access Red Hat Developer Hub and select the category Workbench from there according to your organization setup (Figure 1).
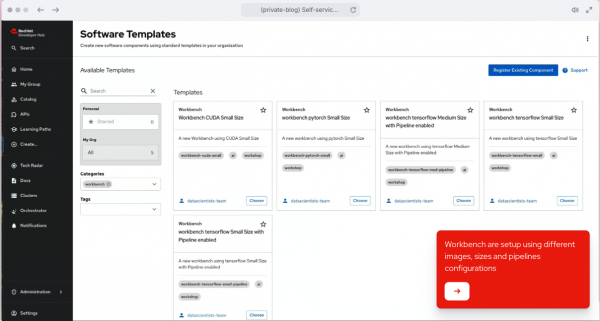
After selecting a template, I choose an environment to work with and a namespace name (Figure 2).
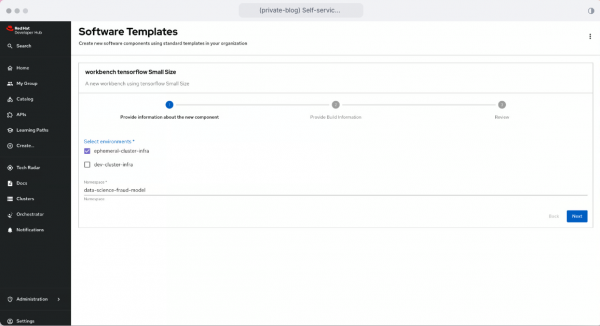
- The component will be created in RHDH through Argo CD and applied to an OpenShift cluster. This means everything will be automatically available in OpenShift AI. The user can access the workbench with a button from the created component (Figure 3).
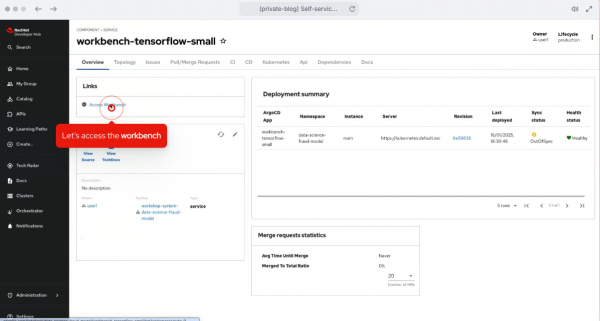
Now that I have created the workbench, I can access the Jupyter Notebook and start building, training, and testing the model (Figure 4).
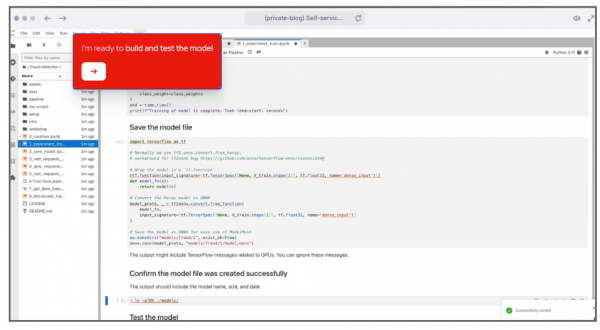
Red Hat OpenShift AI provides teams with the tools necessary to build AI applications, thanks to integrated workbenches that provide flexibility in building and training models and MLOps (Figure 5).

Explore OpenShift AI
End users such as data scientists and MLOps engineers can build, train, and deploy AI applications with workbenches from a template like the one I demonstrated in Red Hat Developer Hub. You can utilize Red Hat OpenShift AI to accelerate AI/ML development. Try our demo for a more interactive experience.
Stay tuned for the next article where we'll go behind the scenes of Red Hat OpenShift GitOps, Red Hat OpenShift AI, and Red Hat OpenShift.
Last updated: April 22, 2025