The microservice architectural style structures an application as a collection of services. These services are often large, monolithic applications that are broken into smaller services. Additionally, microservices are:
- Highly maintainable and testable.
- Loosely coupled.
- Independently deployable.
- Organized around business capabilities.
- Typically owned by a small team, which enables the rapid, frequent, and reliable delivery of large, complex applications and lets organizations evolve their technology stacks.
In this article, we discuss the advantages of the microservice architecture and look at a travel booking application that illustrates how to develop applications using various microservices.
Note: If you like the discussion in this article, check out the Bee Travels session at Red Hat Summit, where we'll dive into developing and deploying microservices using Bee Travels.
Why develop with microservices?
There are many benefits to developing applications with microservices:
- They act independently. Microservices are applications that are separated into a collection of small, independently deployable services. Because microservices are designed to act independently, they are naturally consistent with agile principles that promote end-to-end team ownership.
- They simplify deployment. Each microservice is built and aligned around a feature to reduce the complexity of the application change-management process. Because each service is individually changed, tested, and deployed without affecting other services, deployment is accelerated.
- They improve application quality. Because microservices enable a "divide-and-conquer" approach, both functional and performance testing are easier with microservices than they are with monolithic applications. Microservices architecture lends itself to test-driven development, as components can be tested in isolation and combined with a full or virtualized set of microservices. This approach results in overall improvement in application quality.
- They're easier to scale. Teams can more efficiently scale applications by scaling individual services based on how critical they are to the overall application, throughput, memory, and CPU load.
Now that we've explored the overall concept of microservices and their advantages, let's dive into a sample application that uses them!
Microservices in action: The Bee Travels application
Bee Travels is a sample travel booking application composed of several microservices. These microservices can be run independently or together to form the full service. Users can search for and book hotels, flights, and car rentals for various destinations across the world (see Figure 1).
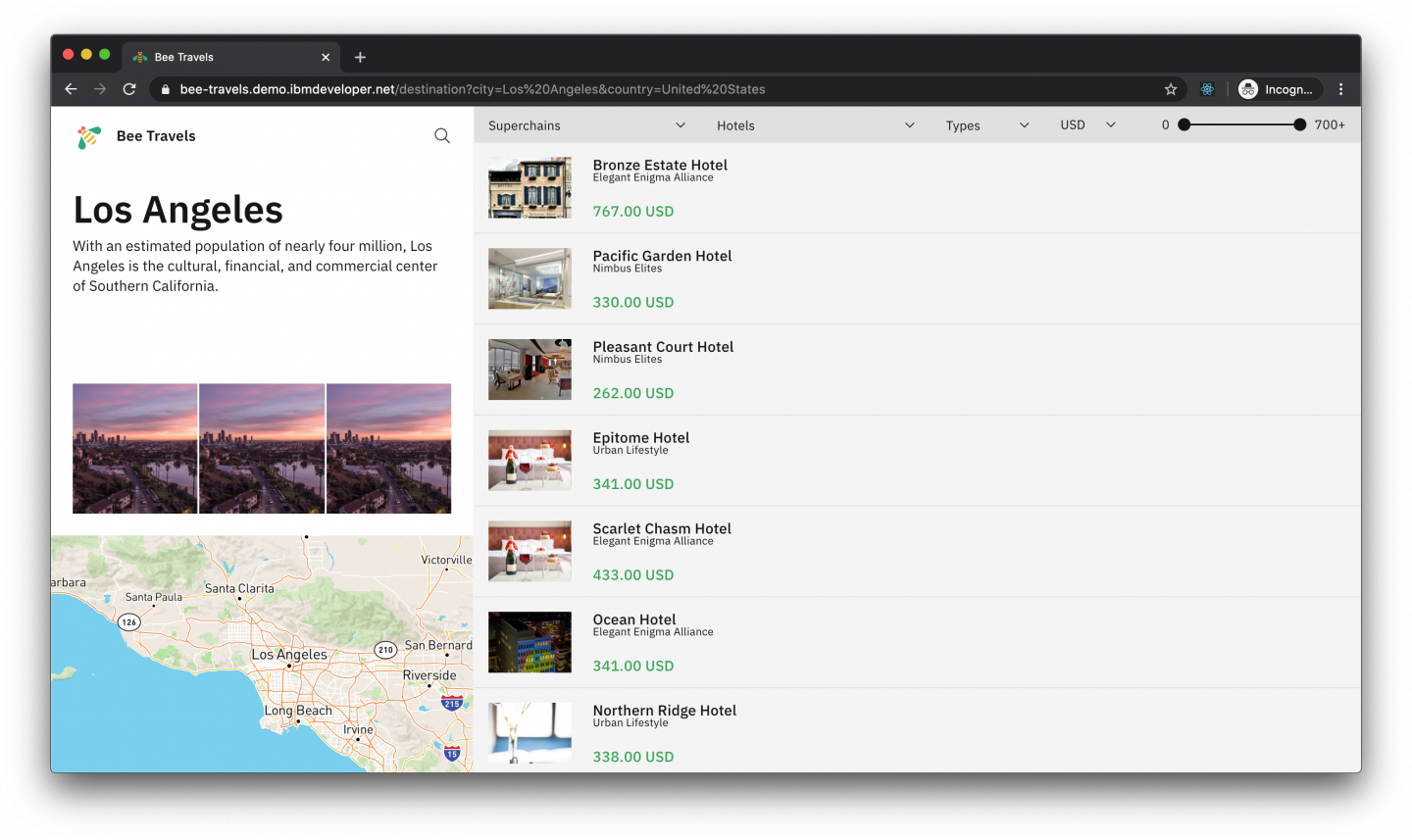
The purpose of Bee Travels is to demonstrate how to develop applications using various microservices, as well as key capabilities of Kubernetes, Red Hat OpenShift, and many other cloud-native technologies.
The project showcases best practices in the software development life cycle, spanning the full developer experience. It uses widely used open source technologies and is written in recommended coding languages including Node, Python, Rust, Go, and Java.
Bee Travels application architecture
Bee Travels is composed of the following microservices:
- UI front end
- UI back end
- Destination
- Hotel
- Car rental
- Flight
- Currency exchange
- Checkout
- Payment
The application was built in iterations, resulting in different versions of the microservices being constructed. Figure 2 is a basic architecture diagram for the containerized version 1 of Bee Travels, which includes key features such as:
- Searching for hotels, car rentals, and flights for a given destination.
- Reading data from local JSON files.
- RESTful API calls between microservices.
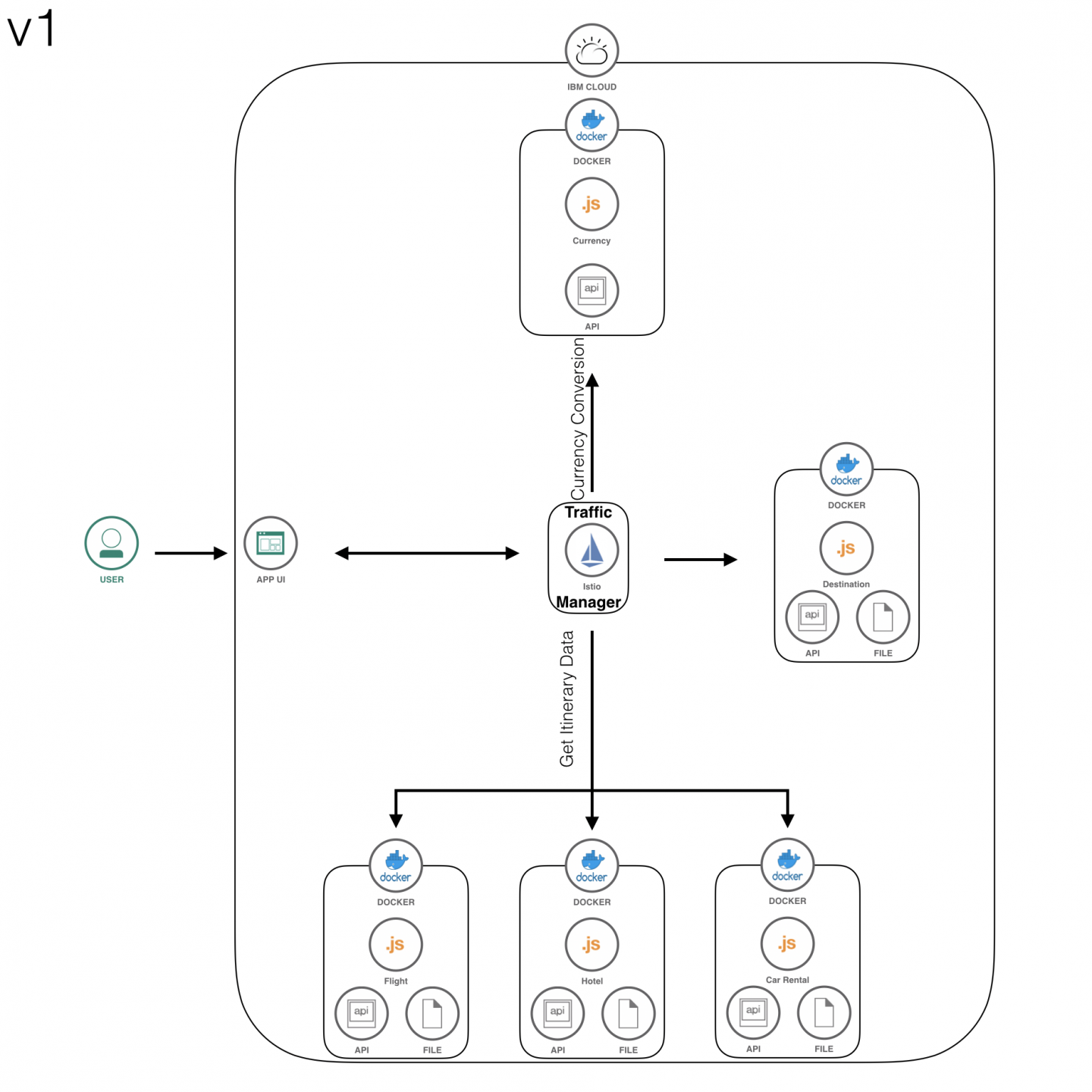
Version 2 features include reading data from databases and building out a payment structure for a travel itinerary. Version 3 will include chatbots, user accounts, recommendations, and Kafka message queues.
Given its architecture and the fact that it is a polyglot application, Bee Travels offers the flexibility to "choose your own adventure"—that is, you can decide for yourself how you want to build and deploy it. This flexibility extends to the following:
- Microservices: Whether you want to run all the microservices or only some of them is up to you. Note that certain services can be dependent on others.
- Service versions: Because Bee Travels was built with iterations of different versions of each service, you can choose which version of each service you want to run.
- Programming languages: Choose to run the microservices in one language or as a polyglot with multiple languages such as Node.js, Python, Java, Go, and Rust.
- Databases: Some services require a data source. Depending on the microservice, this can include local JSON files, MongoDB, CouchDB, Cloudant, PostgreSQL, and JanusGraph.
- Deployment: When deploying Bee Travels, you have options to use Kubernetes, Red Hat OpenShift, Red Hat OpenShift Container Platform on the LinuxONE Community Cloud, Istio, Knative, and Helm charts.
Conclusion
To learn more about Bee Travels, visit the following links:
- Learn more about the Bee Travels project at https://bee-travels.github.io, where you can play around with a live demo of the application and read through the documentation.
- Explore Bee Travels content on IBM Developer, including code patterns, articles, and videos.
- Delve into the Bee Travels repository on GitHub.
- Check out the on-demand Bee Travels session at Red Hat Summit for more about developing and deploying microservices using Bee Travels.
