Consistent access and delivery with Data Integration
Data integration patterns help create a unified, accurate, and consistent view of enterprise data within an organization. This data is often dissimilar, living in different locations and being stored in a variety of formats.
The approaches used to achieve data integration goals will depend largely on the Quality-of-Service (QoS) and usage characteristics surrounding different sets of data. A data integration strategy helps to logically—and perhaps also physically—combine different sets of enterprise data sources to expose the data services needed by your organization.
Understanding data integration patterns and using them effectively can help organizations create an effective data integration strategy. In the sections that follow, we will detail these patterns.
Legacy data gateways for microservices
Application architecture evolution has fragmented the backend implementation into independent microservices and functions. However, there's still a gap in the way this evolution has dealt with data because evolution tends to avoid dealing with static environments.
At the same time, microservices encourage developers to create new polyglot data persistence layers that then, need to be composite to deliver business value. How can we apply the knowledge from API gateways to these new data stores?
In this discussion of legacy data, Hugo Guerrero talks about the behavior of data gateways and API gateways, the different data gateway types and their architectures, and the extended data-proxy for hybrid cloud deployments.
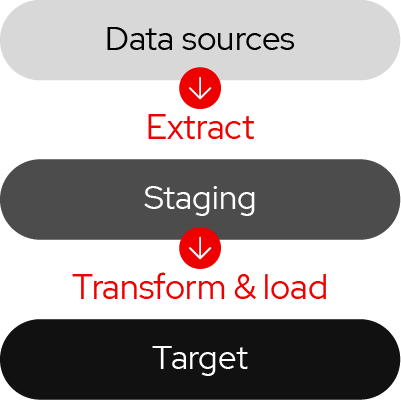
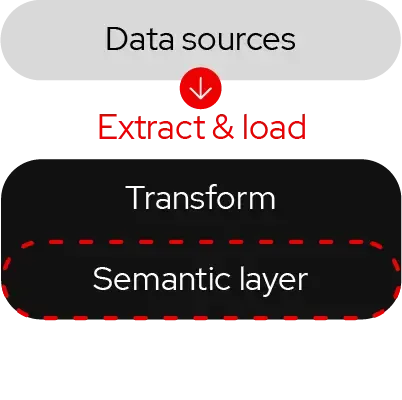
Pattern 1. Data consolidation
Data consolidation involves designing and implementing a data integration process that feeds a datastore with complete, enriched data. This approach allows for data restructuring, a reconciliation process, thorough cleansing, and additional steps for aggregation and further enrichment.
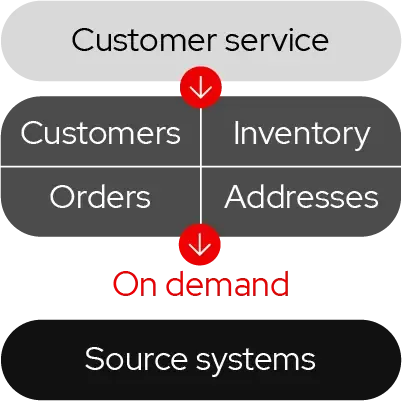
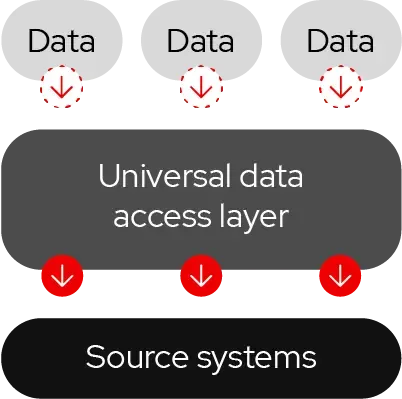
Pattern 2. Data federation
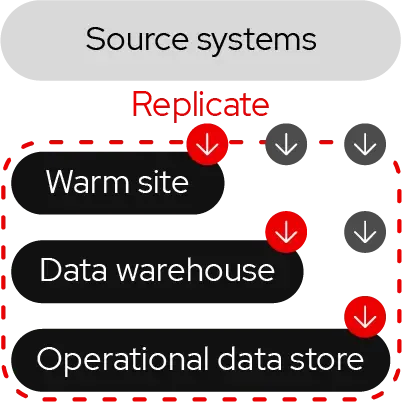
Data federation uses a pull approach where data is retrieved from the underlying source systems on-demand. This pattern provides real-time access to data. Data federation creates a virtualized view of the data with no data replication or moving of the source system data.
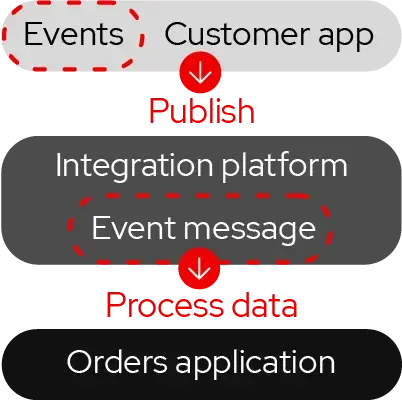
Pattern 3. Data propagation
Data propagation involves the promotion of data updates on two levels. At the application level, an event in the source application triggers processing in one or more target applications. At the datastore level, an event in the source system triggers updates in the source datastore. These change events are then replicated in near real-time to one or more target datastores.
Red Hat build of Apache Camel
Apache Camel is an open source integration framework that implements EIPs with mature and robust ready-to-use building blocks, enabling developers to rapidly create data flows and easily test and maintain them.

Data integration common practices
Change data capture
Change data capture detects data change events in a source datastore and triggers an update process in another datastore or system. CDC is usually implemented as trigger-based or log-based. In the trigger-based approach, transaction events are logged in a separate shadow table that can be replayed to copy those events to the target system on a regular basis. Log-based CDC—also known as transaction log tailing—identifies data change events by scanning transaction logs. This approach is often used as it can be applied to many data change scenarios and can support systems with extremely high transaction volumes because of the minimal amount of overhead it involves.
Battle of the in-memory data stores
Have you ever wondered what the relative differences are between two of the more popular open source, in-memory data stores, and cachés? The caché is a smaller, faster memory component inserted between the CPU and the main memory that stores its data on disks for retrieval, while in-memory data stores depend on machine memory to store retrievable data.
In this DevNation Tech Talk, the DevNation team describes those differences and more importantly, provides live demonstrations of the key capabilities that could have a major impact on your architectural

Get started with hands-on data integration
An event streaming platform using Red Hat Streams for Apache Kafka based on...
Extend capabilities with no changes to legacy apps through data integration...
Discover how an API First Approach provides the right framework to build APIs...
An accelerated path to migrating applications from Red Hat Fuse to Red Hat...
Event-driven Sentiment Analysis using Kafka, Knative and AI/ML
Expand your API Management strategy beyond RESTful APIs into event-driven...
More integration resources
Learn how integrating Red Hat Lightspeed Model Context Protocol (MCP) and Red...

Learn how to integrate ArgoCD and Red Hat Developer Hub with OpenShift GitOps.
See how to use Apache Camel to turn LLMs into reliable text-processing...
Use Red Hat Lightspeed to simplify inventory management and convert natural...
Learn how to achieve complete service mesh observability on OpenShift by...

Discover the new Camel dashboard for OpenShift to monitor a fleet of Camel...