Earlier this year, Red Hat announced the Red Hat Cache Service which is a distributed in-memory caching service that runs on Red Hat OpenShift. Red Hat Data Grid is used as the core of the cache service. The cache service is one of the things you can easily install on OpenShift through the OpenShift Service Catalog. You can find the cache service in the Red Hat OpenShift Online Pro tier. (Alternatively, you can install the Cache Service on your own Red Hat OpenShift Container Platform installation by following the installation manual.)
The Cache Service automatically calculates the amount of user storage based on the container size it’s scheduled on. Typically, it’s 512MB. What’s more interesting is that the Cache Service can operate near the full memory capacity (~97–98 %).
The automatic memory adjustment gives you a nice opportunity to try out the new Horizontal Pod Autoscaler (which now supports memory and custom metrics-based autoscaling). The autoscaler monitors the amount of memory used by the container and adds or removes Cache Service pods based on this measurement.
The demo
First, instantiate a new Cache Service from the Service Catalog. Then wait a few moments until it becomes ready.
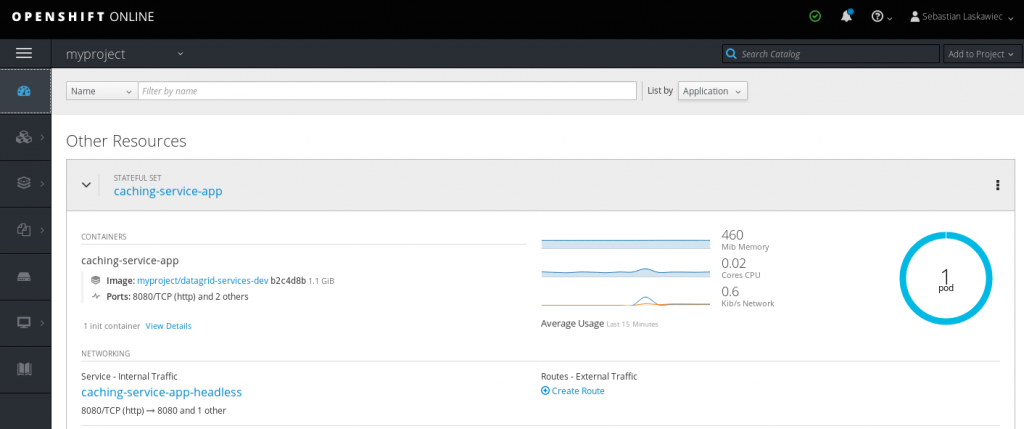
The next step is to create a Horizontal Pod Autoscaler based on the following definition:
https://gist.github.com/slaskawi/3d0b4aed6c352c4ac2f9827d3c4fd237
Once a pod hits 92% of container memory, OpenShift will spin up another one.
Next, Red Hat Data Grid will form a cluster of two (or three) nodes, which will increase the overall system’s capacity. The interesting thing to note is that the memory will not drop on pod number 0. It will remain at the same level. This is because the Cache Service uses a number of owners equal to 1 and the State Transfer minimizes data shuffling in the cluster.
Next, load some data into the Data Grid. One way to do this is to create a Red Hat Enterprise Linux (RHEL) pod inside the same project and make REST calls with the data:
https://gist.github.com/slaskawi/43667383c67f6c8d60bed2eb05ab0cfd
The above command spins up a new RHEL pod and attaches TTY to it. This way, we will be able to invoke curl commands from inside of our project:
https://gist.github.com/slaskawi/ccaafac852a228d6ec54d0f9ff421031
The above command inserts 1,000 entries into the default cache. Each of the entries is roughly 10KB. Depending on the container size, we might increase the number of iterations in the loop or tweak the command to insert data into different key prefixes.
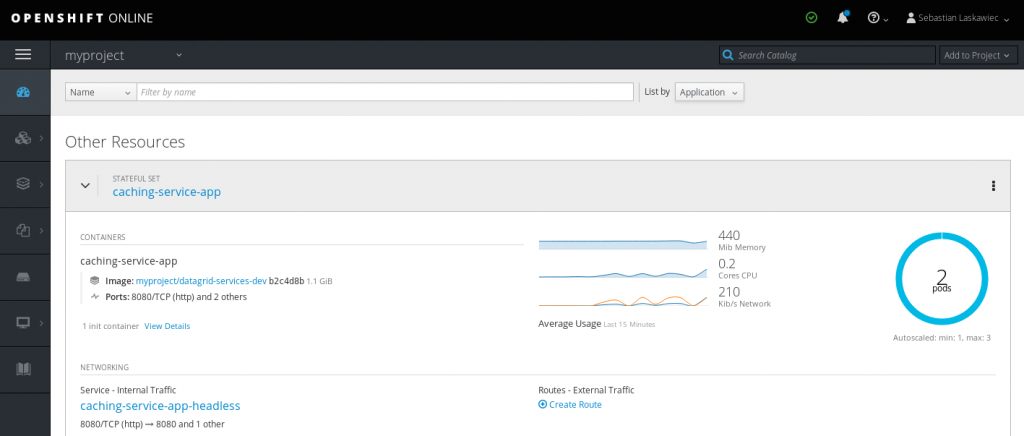
Once the container hits the scaling limit, Horizontal Pod Autoscaler will create another pod.
Conclusion
Autoscaling Red Hat Cache Service is a really nice way of increasing overall system capacity depending on the load. Since the Cache Service is based on eviction (removing the least frequently used keys when it hits the memory limit) and off-heap. It was designed to reach 97–98% of the capacity when constantly adding data. Since new data “pushes out” old entries, the container will only scale up and never scale down.
Try autoscaling Red Hat Cache Service to improve your system's overall capacity.
Last updated: March 26, 2023