Red Hat OpenShift 4.19, based on Kubernetes 1.32 and CRI-O 1.32, is now Generally Available (GA). This article highlights notable updates in this release for OpenShift developers.
A more cohesive OpenShift experience
The Admin and Developer perspectives have now merged into a single default view. Now you can view all tasks, from viewing topology to managing resources, from a comprehensive interface in the OpenShift console. The traditional Developer perspective can be optionally re-enabled. You can also use Favorites to bookmark and access the pages that you use the most (Figure 1).
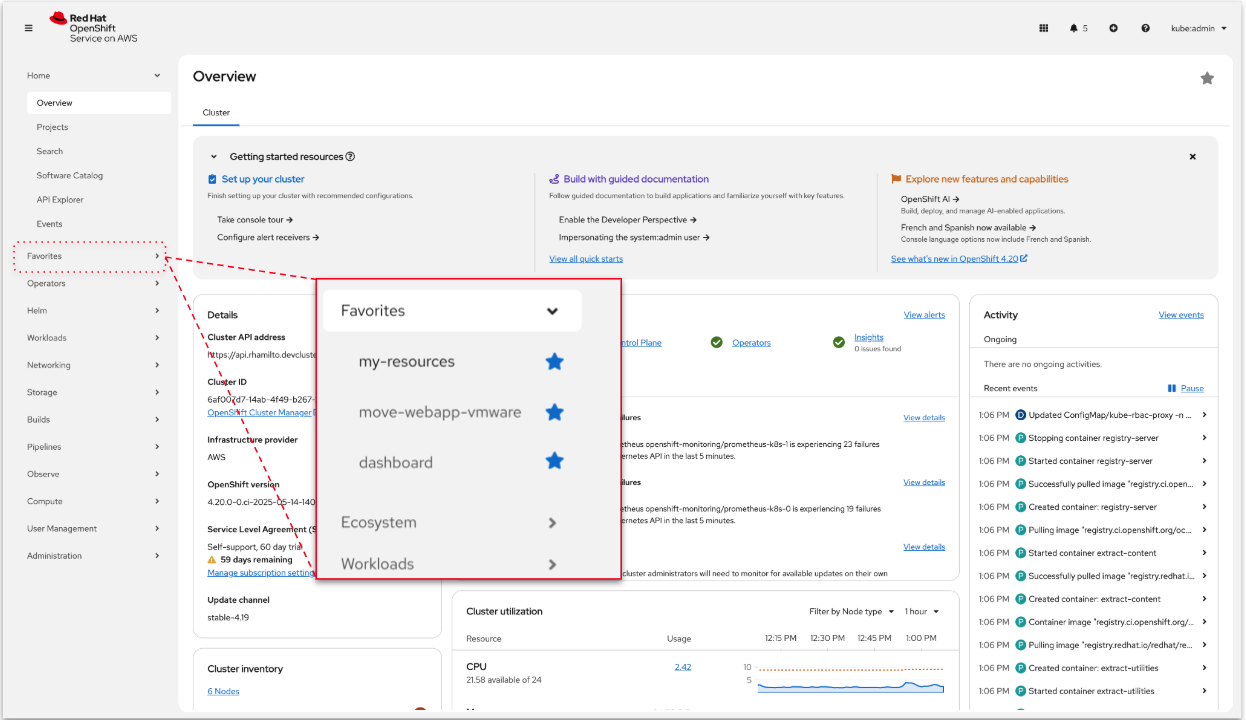
Additionally, for users with specific branding requirements, learn how to use the new Custom Logos feature for a more customized web console experience: Enable Custom Logos branding in the OpenShift web console
OpenShift Dev Spaces
Red Hat OpenShift Dev Spaces 3.21, built on Eclipse Che 7.102, now lets you configure two GitLab OAuth providers within a single instance. This feature benefits developers working with codebases hosted on both GitLab SaaS and on-premises instances.
Administrators can utilize OpenShift Template objects to replicate defined resources across all user namespaces. Additionally, ConfigMap can be used to customize VS Code settings (settings.json, extensions.json, and product.json), enabling mass customization of editor setups and ensuring consistency across developer environments. For a comprehensive list of updates, refer to the release notes.
OpenShift Toolkit extension
The OpenShift Toolkit IDE extension by Red Hat for VS Code 1.19.0 has added OpenShift Pipeline Task in the Cluster View to the Application explorer. Quarkus Tools for VS Code and IntelliJ 1.21.0 adds performance improvements for the Qute language server and support for Integer operators in Qute files.
Podman Desktop
Podman Desktop 1.19 is now available on Red Hat Enterprise Linux (RHEL) 10. It has improved Kubernetes support by adding the ability to set up port forwarding, to do namespace switching, and to browse objects, like pods, deployments, jobs, secrets, etc., directly from Podman Desktop. Configuring mirror registries is now easier to do.
Enhanced extensions
Several Red Hat-dedicated extensions have been upgraded, offering new capabilities for developers. The bootc extension has a new version that allows you to experiment with bootable containers directly from your local environment, whether you're using a Mac or Windows machine.
For OpenShift developers, you can now start MicroShift in a container for development purposes. This works similarly to Kind, letting you spin up a lightweight OpenShift environment directly from your local machine.
For those working with RHEL, there is an updated RHEL extension in the catalog that lets you to set up RHEL virtual machines (VMs) for development directly on your Mac or Windows environment.
To learn more, refer to the Podman Desktop release notes.
Red Hat Developer Hub
Red Hat Developer Hub, based on the Backstage project, provides software templates and plugins for OpenShift deployments, access to pipeline runs, viewing clusters from OCM and more. Red Hat Developer Hub 1.6, based on Backstage 1.36.1, has added high availability support for Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS), features a plug-in configuration YAML in the Extensions catalog, and allows the delegation of RBAC control to other teams. Red Hat Developer Hub Local is now available in Developer Preview.
For an in-depth review of all of the latest features, including updates for plug-ins and templates, see What's new in Red Hat Developer Hub 1.6 and the latest release notes.
Read about how to empower your documentation processes through smart automation and Developer Hub integration: Build an AI agent to automate TechDocs in Red Hat Developer Hub.
OpenShift Lightspeed
OpenShift Lightspeed, available as an operator that integrates its chat user interface (UI) in the OpenShift Web console, is now GA. This generative AI-based chat assistant allows you to ask OpenShift-related questions and inspect your pod resources. It is compatible with multiple large language models (LLMs), including IBM watsonx, Azure OpenAI, OpenAI, Red Hat OpenShift AI, and Red Hat Enterprise Linux AI (RHEL AI). OpenShift Lightspeed also works in disconnected mode, where RHEL AI and OpenShift AI are used as the LLM provider.
Cluster interaction, in Technology Preview, provides information and recommendations about the state of your cluster. Bring your own (BYO) knowledge is also in Technology Preview, where you can add your learnings and documentation about your environment.
To discover what else is new with Red Hat OpenShift Lightspeed, see the release notes.
OpenShift Virtualization
Red Hat OpenShift Virtualization is an operator included with all Red Hat OpenShift editions that lets you run and manage virtual machine (VM) workloads alongside container workloads. OpenShift Virtualization is now in Technology Preview on Microsoft Azure Red Hat OpenShift and Red Hat OpenShift Dedicated.
Based on customer feedback, OpenShift 4.19 introduces the capability to migrate multiple virtual machines simultaneously between different storage classes (Figure 2). Previously, this functionality was limited to single VMs.
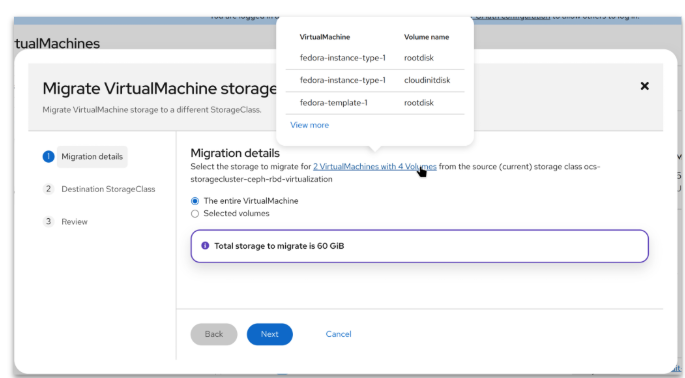
For a more detailed description of the latest release, see the release notes.
For VMware administrators interested in migrating your VMs to OpenShift, download the OpenShift Virtualization for VMware administrators cheat sheet.
OpenShift Pipelines 1.18 (Tekton 0.68)
OpenShift Pipelines is a cloud-native continuous integration and continuous delivery (CI/CD) solution based on Kubernetes that automates deployments using Tekton building blocks across multiple platforms by removing the hidden implementation details and provides an integrated user experience with the OpenShift Container Platform web console.
OpenShift Pipelines-as-Code (PaC) in Release 1.18 introduces enhancements such as the tkn pac info globbing command for testing pattern matching in PipelineRun definitions using sample data or within the working directory. Additionally, the on-comment annotation now allows triggering PipelineRuns on GitHub commit pushes based on specific comments, providing more granular control over when pipelines are executed.
Tekton Results is now GA. Tekton Cache, in Technology Preview, optimizes the image build time.
OpenShift GitOps 1.17 (Argo CD 3.0 and Argo Rollouts 1.8.0)
Red Hat OpenShift GitOps provides a declarative way to implement continuous delivery of applications across clusters and development lifecycles. Argo Rollouts can now be viewed in the OpenShift console. The Argo CD Agent, in Technology Preview, enables a distributed, agent-based architecture for managing applications across multiple Kubernetes clusters.

You can find more information in the release notes.
Read this blog post to learn how to get started with OpenShift GitOps, from installation to provisioning a sample application: Getting Started with OpenShift GitOps.
OpenShift Serverless 1.36 based on Knative 1.16
Red Hat OpenShift Serverless provides autoscaling and networking for containerized microservices and functions. The kn event plug-in, which lets you build and send events, and Eventing Transport encryption, which transports encryption for Knative eventing, are both now GA.
Several other resources are available in Technology Preview, like IntegrationSource and IntegrationSink, which are Knative eventing custom resources that support Kamelets from the Apache Camel project.
To learn more, see the OpenShift Serverless 1.36 release notes.
OpenShift Service Mesh 3.1 based on Istio 1.26 and Kiali 2.11
Red Hat OpenShift Service Mesh creates a central point of control in an application. OpenShift Service Mesh 3.1 will be generally available shortly after the OpenShift 4.19 release. It provides end-to-end Gateway API support to service mesh, including CustomResourceDefinitions (CRDs). There is also a Technology Preview of Istio ambient mode, which uses less resources and doesn't require sidecar proxies.
You can find more information in the release notes.
Get started today with Red Hat OpenShift 4.19
To find out more about Red Hat OpenShift 4.19, including a list of new features and fixes, read the blog post Red Hat OpenShift 4.19 accelerates virtualization and enterprise AI innovation or check out the release notes.
Ready to try Red Hat OpenShift?
- Start your OpenShift journey: Start your Developer Sandbox.
- Explore resources for getting started with OpenShift.
- Discover more ways to try OpenShift: Red Hat OpenShift download
- Check out the interactive learning content.
- Visit the Red Hat OpenShift product page.
- Stay up-to-date with the Red Hat Developer community on our YouTube channel.
