In our previous article, we explored how to use the Red Hat Ansible Automation Platform's CLI to create a virtual machine (VM) in Microsoft Azure. This time, we'll take things a step further and leverage the power of the Ansible Automation Platform to automate the process. The Ansible Automation Platform is a powerful tool that enables you to manage your infrastructure more efficiently, with less manual intervention.
Follow the series:
- Part 1: How to automate VM creation on Azure with Ansible CLI
- Part 2: How to use Ansible to create a VM on Azure
- Part 3: How to use Ansible to create a VM on Azure via workflow
By using the Ansible Automation Platform, we can create a streamlined process for deploying VMs in Azure, reducing errors and saving time. In this article, we'll dive into the details of how to use the Ansible Automation Platform to create VMs in Azure.
Prerequisites
1. The operating system on your local machine must be Red Hat Enterprise Linux (RHEL).
2. Before you can complete any of the following tasks, you must create a registry service account. To log in to service account (SA), you'll need to use a container runtime such as Podman or Docker. Podman is a powerful and secure open-source tool that can be used as an alternative to Docker, with the added benefits of not requiring a daemon to run containers and having a more lightweight footprint. We recommend installing Podman. This article explains how Podman offers a more efficient container experience.
podman login registry.redhat.io
Username: {REGISTRY-SERVICE-ACCOUNT-USERNAME}
Password: {REGISTRY-SERVICE-ACCOUNT-PASSWORD}
Login Succeeded!
Once we are successful in logging into the SA, we need to create a container image by using a Dockerfile containing the following context:
FROM registry.redhat.io/ansible-automation-platform-22/ee-supported-rhel8:latest
RUN pip3 install 'ansible[azure]'
RUN ansible-galaxy collection install azure.azcollection
RUN pip3 install -r ~/.ansible/collections/ansible_collections/azure/azcollection/requirements-azure.txt
Build an image using Podman as follows:
podman build -t <image-name>.
Push the image into the container image registry. Log in to the private container image registry using the podman login command before pushing.
podman push <image-name>

3. Create an Azure Active Directory (Azure AD) account, a service principal, and give permissions in Azure.
4. Follow these instructions to generate a client secret for the service principal.
5. Click Credentials under Resources and select Microsoft Azure Resource Manager. Then, enter your subscription_id, tenant id, client id, secret, username, and password (Figure 2).

Creating and configuring the project
- Install the Ansible Automation Platform by following these instructions.
- Log in to the Ansible Automation Platform Portal in browser.
- Navigate to the Projects tab under Resources in the left pane.
- Click Add to create a new project.
- Enter a name for the project and choose Git as the source control type with the URL: https://github.com/redhat-developer-demos/ansible-automation-platform-cloud-solutions in the Source Control URL field. If you're interested in checking out the Ansible Playbooks, you can find them on Github.
- Save the changes and wait for the operation to complete successfully (Figure 3).

Creating and configuring the job template
- Go to the Templates tab under resources in the left pane, click the add button, and select Job template from the options.
- Enter a name for the job you want to create, select the Demo-Inventory or Default inventory in the Inventory section.
- In the Project section, click on the project name you previously created and select the Azure/create_vm_job_template.yml file.
Configuring the variables and execution environment
- Click on the Variables section and add the variables as follows:
---
vm_name: "Test-Ansible"
vm_size: "Standard_B1ls"
vm_image: "RedHat:RHEL:8-LVM:latest"
vm_username: "testansible"
vm_password: "my-password@1234"
rg_name: "test-ansible"
vnet_name: "test-ansible"
subnet_name: "test-ansible"
location: "centralindia"
offer: “CentOS”
publisher: “OpenLogic”
sku: “7.5”
version: ”latest”
- Select the credentials you previously created under the selected category (Figure 4).

- Select the execution environment you previously created (Figure 5).

- Save your changes by clicking the Save button.
- Click the Launch button to launch the job.
- Once the job is launched using the Ansible Automation Platform, the system will generate an output, as shown in Figure 6. The output displays the job status and the progress of the VM creation process.
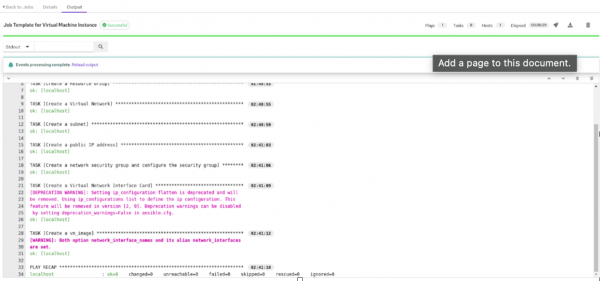
- You can check the virtual machine by navigating to the Azure portal.
What’s next?
In this article, we demonstrated how to use the Ansible Automation Platform to create a VM in Microsoft Azure. You learned how the Ansible Automation Platform can streamline the process of deploying VMs in Azure, making it more efficient and less error-prone. By using the power of automation, we can save time and free up resources to focus on other important tasks.
You can explore more of what the Ansible Automation Platform has to offer by downloading it. Additionally, there are e-books such as, Automation at the edge, Choosing an Automation Tool, and An IT executive's guide to automation. A cheat sheet is also available for WiFi automation with Ansible and SD that provides a quick reference for network automation tasks.
The final article in this 3-part series will demonstrate how to simplify the process of creating VMs in Azure by using workflow templates. Workflow templates can help standardize the process of creating VMs and reduce the amount of manual intervention required.
