The ongoing quest for greater and greater automation of building, testing, and deployment has recently inspired several new features in Argo CD, Kubernetes, Red Hat OpenShift, and other tools. This article shows how to improve feature testing by automating builds and the creation of Kubernetes environments.
Red Hat OpenShift GitOps includes an opinionated deployment of Argo CD that provides a way to manage continuous development or delivery cluster-wide, or even in a multi-tenant cluster configuration. This Operator also provides many toolsets that can help you fit your GitOps workflows into your CI/CD (continuous integration/continuous delivery) processes. One of these tools is called ApplicationSets.
ApplicationSets mass-produces Argo CD applications and deploys them onto a cluster or multiple clusters. ApplicationSets accomplishes this task by using generators. Generators vary from use case to use case and depend on things like the Git repository structure, configuration files, key/value lists, and cluster names.
Generators take these inputs and mass-produce Argo CD applications in the manner of a factory. To find out more about ApplicationSets, read this guide and take a look at the official documentation.
The pull request generator in OpenShift GitOps 1.4
The latest release of OpenShift GitOps offers the powerful pull request generator, one of the newest generators. Whenever there is a pull request in the GitHub repository associated with this generator, it creates an Argo CD application reflecting the changes in the pull request. This automation is especially useful to help you check how the change looks in your environment before merging the change into the parent branch.
Let's take a look at an example:
apiVersion: argoproj.io/v1alpha1
kind: ApplicationSet
metadata:
name: bgd-pr-testing
namespace: argocd
spec:
generators:
- pullRequest:
github:
owner: christianh814
repo: bgd
labels:
- preview
requeueAfterSeconds: 300
template:
metadata:
name: 'bgd-{{branch}}-{{number}}'
spec:
source:
repoURL: 'https://github.com/christianh814/bgd'
targetRevision: '{{head_sha}}'
path: app/overlays/default/
project: default
syncPolicy:
automated:
prune: true
selfHeal: true
syncOptions:
- CreateNamespace=true
destination:
server: https://kubernetes.default.svc
namespace: 'bgd-{{branch}}-{{number}}'
The .spec.generators.pullRequest property contains the information needed for the generator to work in the GitHub repository. The generator invokes the GitHub API to target the specified account or organization and the specified repository. The optional labels property allows you to tell the generator to create applications only for pull requests specifying the labels in that property (preview in this example).
The requeueAfterSeconds option tells how many seconds to wait before checking whether another pull request has been submitted. The default is 30 minutes.
The generator has access to the following variables in GitHub:
number: The ID of the pull requestbranch: The name of the branch of the pull request headhead_sha: The SHA of the head of the pull request
The variables appear in the YAML between {{ }} braces and are used in the .spec.template section of the file to create a tailored Argo CD application.
With this YAML file in place, any time someone makes a pull request with the label preview to the repository, Argo CD creates a corresponding application on your cluster. You can then test the application to see how the change in the pull request affects your application as a whole.
Feature branching
The pull request generator is convenient for feature branches, a popular development pattern in source code repositories. Developers create and test new features independently from the stable branch by creating a new branch, which can be merged when the feature is validated. Argo CD and the pull request generator can generate a new Kubernetes environment from a template like the one in the previous section.
To show the versatility of the generator, we'll run BGD, an example web application that just shows a color (blue by default). We'll create a new application by switching the color.
Deploy the Argo application in your cluster, pointing to the application's manifests:
$ kubectl apply -f \
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/christianh814/bgd/main/manifests/applications/bgd-app.yaml
Verify that the application has been deployed to the bgd namespace, which represents our main branch:
$ kubectl get apps -n argocd
NAME SYNC STATUS HEALTH STATUS
bgd Synced Healthy
$ kubectl get pods -n bgd
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
bgd-788cb756f7-6lths 1/1 Running 0 10s
$ kubectl describe pod bgd-788cb756f7-6lths -n bgd | grep COLOR
COLOR: blue
Now deploy the ApplicationSet using the pull request generator listed in the previous section:
$ kubectl apply -f \
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/christianh814/bgd/main/manifests/applicationsets/bgd-pr-appset.yaml
$ kubectl get appsets -n argocd
NAME AGE
bgd-pr-testing 51s
To change the color from blue to green, you need to change the COLOR environment variable. Because this application was managed through Kustomize, you can just create a pull request that changes this YAML file to specify green instead of blue:
- op: replace
path: /spec/template/spec/containers/0/env/0/value
value: green
Create a new feature branch containing this change and open a pull request. The pull request generator will create a new Argo CD application representing the feature branch, assigning a name following the property's value in the template: 'bgd-{{branch}}-{{number}}'.
You can test your change before merging it into the main branch as follows:
$ kubectl get apps -n argocd
NAME SYNC STATUS HEALTH STATUS
bgd Synced Healthy
bgd-green-1 Synced Healthy
$ kubectl get pods -n bgd-green-1
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
bgd-55ff677658-zlccd 1/1 Running 0 5s
$ kubectl describe pod bgd-55ff677658-zlccd -n bgd-green-1 | grep COLOR
COLOR: green
Automate builds in a CI/CD pipeline
The method shown in this article to generate an environment for each new feature is very powerful and can allow both continuous testing and continuous delivery. We'll take the next step by automating the builds in a CI/CD pipeline that can be implemented with Red Hat OpenShift Pipelines together with OpenShift GitOps. OpenShift Pipelines is built around Tekton, a Kubernetes-native CI/CD implementation that integrates with many DevOps tools, including Argo CD.
As an example, to automate feature branch testing by creating a pull request for each change, build a Tekton pipeline like the one shown in Figure 1 containing the following Tasks:
git-clone: A ClusterTask that downloads the application source codecreate-image: A ClusterTask that creates a new container image containing the featureupdate-manifests: A Task that uses Kustomize to update the Kubernetes manifests controlled by Argo CDcreate-pr: A Task that creates a pull request using the GitHub command-line interface (CLI)
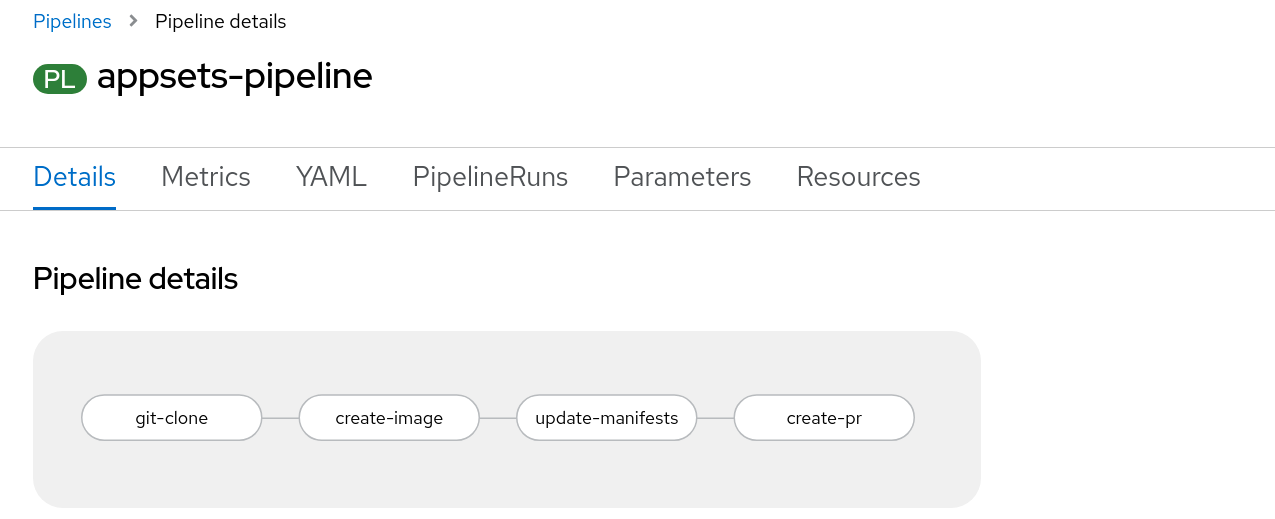
For each change to the application, a new feature branch is created together with a pull request, and Argo CD's pull request generator creates a new environment to test the pull request.
Here's an example for the update-manifests Task:
apiVersion: tekton.dev/v1beta1
kind: Task
metadata:
annotations:
tekton.dev/pipelines.minVersion: 0.12.1
tekton.dev/tags: git
name: update-manifests
labels:
app.kubernetes.io/version: '0.2'
operator.tekton.dev/provider-type: community
spec:
description: >-
This Task can be used to update image digest in a Git repo using kustomize and push changes into a feature branch.
It requires a secret with credentials for accessing the git repo.
params:
- name: GIT_REPOSITORY
type: string
- name: FEATURE
type: string
default: feature
- name: CURRENT_IMAGE
type: string
- name: NEW_IMAGE
type: string
- name: NEW_DIGEST
type: string
- name: KUSTOMIZATION_PATH
type: string
results:
- description: The commit SHA
name: commit
steps:
- image: 'docker.io/alpine/git:v2.26.2'
name: git-clone
resources: {}
script: >
rm -rf git-update-digest-workdir
git clone $(params.GIT_REPOSITORY)
git-update-digest-workdir
workingDir: $(workspaces.workspace.path)
- image: 'quay.io/wpernath/kustomize-ubi:latest'
name: update-digest
resources: {}
script: >
cd git-update-digest-workdir/$(params.KUSTOMIZATION_PATH)
kustomize edit set image
$(params.CURRENT_IMAGE)=$(params.NEW_IMAGE)@$(params.NEW_DIGEST)
echo "##########################"
echo "### kustomization.yaml ###"
echo "##########################"
cat kustomization.yaml
workingDir: $(workspaces.workspace.path)
- image: 'docker.io/alpine/git:v2.26.2'
name: git-commit
resources: {}
script: |
cd git-update-digest-workdir
git config user.email "tektonbot@redhat.com"
git config user.name "My Tekton Bot"
git status
feature=$(params.FEATURE)
if [ "$feature" = "feature" ];
feature="$feature-$RANDOM"
fi
git checkout -b $feature
git add $(params.KUSTOMIZATION_PATH)/kustomization.yaml
git commit -m "[ci] Image digest updated"
git push
RESULT_SHA="$(git rev-parse HEAD | tr -d '\n')"
EXIT_CODE="$?"
if [ "$EXIT_CODE" != 0 ]
then
exit $EXIT_CODE
fi
# Make sure we don't add a trailing newline to the result!
echo -n "$RESULT_SHA" > $(results.commit.path)
workingDir: $(workspaces.workspace.path)
workspaces:
- description: The workspace.
name: workspace
Conclusion
This article introduced a way to use Argo CD ApplicationSets and Tekton to create a CI/CD system that includes feature branch testing. You can use OpenShift Pipelines to compose and define the level of automation you want when creating new features with feature branches and feature environments. All these tools are available "out of the box" (i.e., "batteries included") with the OpenShift Container Platform.
Interested in more Argo CD goodness with a GitOps twist? Make sure to tune in to GitOps Guide To The Galaxy, which streams on YouTube and Twitch every other Thursday at 3:00 p.m U.S. Eastern time. You can also get some free hands-on training with Argo CD and Tekton at the interactive portal.
Last updated: October 31, 2023