Container technologies that are easy to maintain, extend, ship, and run are the new de facto standard for large-scale application deployments. Thanks to cluster orchestrators such as Kubernetes and Red Hat OpenShift, these runnable units are deployed to clusters to provide the desired functionality on a large scale.
To ensure the application is shipped in a healthy state, it is often up to developers to confirm that each runnable unit behaves as expected in the environment where it will be deployed. This article introduces Amun, a tool created and used by Project Thoth to inspect containerized Python applications. Running such inspections before deployment can reveal problems up and down the stack—including incompatibilities with dependencies, the operating system, or other parts of the environment.
Containerized application inspection with Amun
If you've been reading articles in this series, you might have already seen Amun mentioned in the article Resolve Python dependencies with Thoth Dependency Monkey. We introduced it there as part of Thoth's Dependency Monkey, a service for validating software packages and software stacks while respecting the resolution of different Python libraries. Amun can also be used standalone to test an application runtime environment following specifications for deployment.
Amun combines Argo Workflows with a service based on OpenShift and exposed as an API to developers who want to test their applications. The open source object storage system Ceph is used to store computed results. Amun's API accepts a specification that lists information about what to test and how.
An example is a request for Amun to test an application running a Thoth-based source-to-image (S2I) Python application or predictable stacks provided by the Thoth team. The specification also lists the Python libraries that the application requires (by specifying a lock file). All the dependencies are installed in the base container image environment together with a script to test the application. Optionally, users can specify additional input, such as RPM packages that should be installed. Users can also supply additional requests to be respected by the cluster orchestrator when deploying the application in the cluster. For instance, one might specify the features a node should provide to the application, such as a particular CPU or GPU type.
The specification is in JSON format and is accepted on the Amun API as shown in Figure 1. After validating the specification, Amun instruments OpenShift and Argo Workflows to trigger a so-called inspection of the application. At its core, the inspection consists of two steps: building and testing the containerized application. Both steps are done in the cluster.
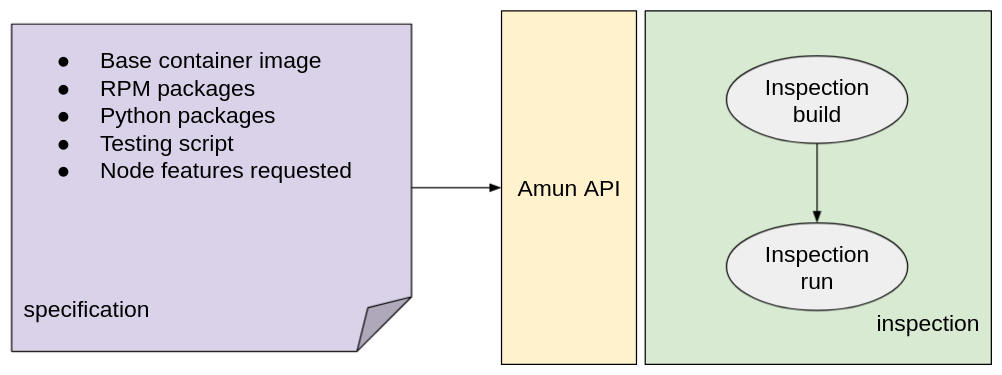
The build step happens through OpenShift. Once the build is done, the application is run in the cluster conforming to the requirements supplied in the specification. Figure 2 shows the flow of events.

The output of the inspection consists of JSON reports containing information about the application's build and run. See Thoth's amun-api repository for an example of inspection output in a JSON report.
The report captures the specification supplied, generated files (such as a Dockerfile), and logs from containers that were run during the build or application run. Reports from the application run also capture information about hardware as reported by the operating system; the actual run results computed by the supplied script; and additional aggregated metadata such as process information from the Linux kernel process control block.
The specification can ask for a given number of multiple, separate inspection runs. You can follow their progress in the Argo Workflows user interface (UI), as shown in Figure 3.

Multiple runs can be especially useful when running microbenchmarks in a cluster to eliminate possible platform or environment inference errors. The amun-api example repository includes three reports.
Amun and Dependency Monkey
Amun has many possible uses, but it was developed first as a platform for validating resolutions of dependencies made by Thoth's Dependency Monkey. In this case, Thoth's resolver uses pre-aggregated dependency data stored in Thoth's knowledge database to resolve Python application dependencies (see Figure 4). Once a valid resolution is found, Amun is instrumented to verify that the resolution leads to a healthy application. See the previously mentioned article Resolve Python dependencies with Thoth Dependency Monkey for more information. You can also watch our video tutorial on inspecting Python dependencies with Dependency Monkey.

Conclusion
Amun was successfully used to produce some of the Thoth datasets, also available on Kaggle. If you wish to use Amun to introspect the behavior of your application or to run Dependency Monkey to check the quality of your application with respect to its dependencies, feel free to reach out to the Thoth team using thoth-station/support repository or via the @ThothStation Twitter handle.
As part of Project Thoth, we are accumulating knowledge to help Python developers create healthy applications. If you would like to follow updates, please subscribe to our YouTube channel or follow us on the @ThothStation Twitter handle.
Last updated: September 20, 2023