Getting started with OpenShift Virtualization
Red Hat OpenShift Virtualization provides a modern platform to run and deploy new and existing virtual machine workloads.
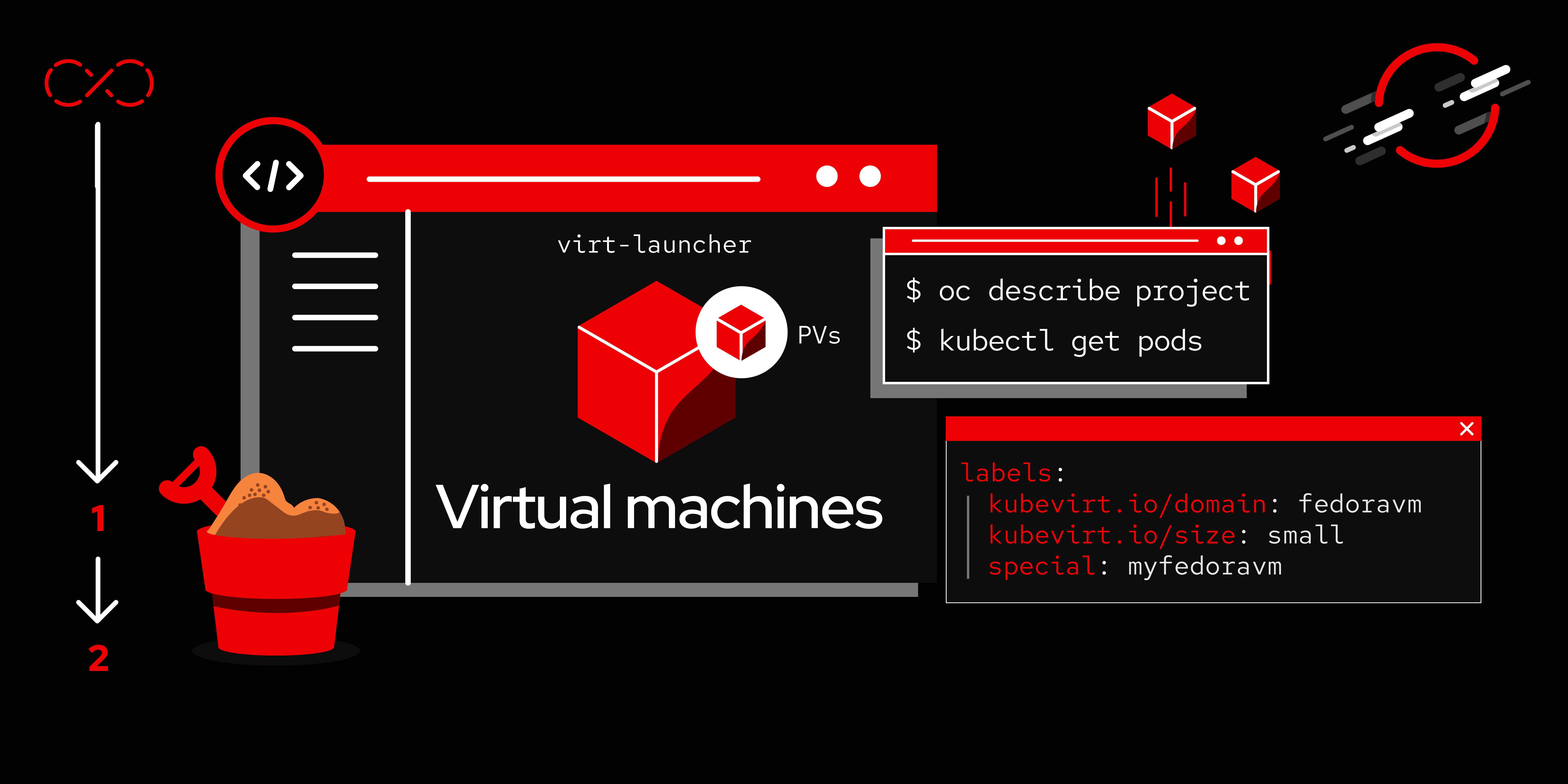
OpenShift Virtualization
OpenShift Virtualization brings virtualized workloads directly into the development, deployment, and management workflows within OpenShift. Whether you're new to OpenShift Virtualization or an experienced user, there are learning paths, articles, and other resources that will help you reach the next phase of your virtualization journey.
Virtualization and Red Hat OpenShift
OpenShift Virtualization for vSphere administrators

Explore how virtualization administrators have interacted with previous...

Discover how a containerized virtualization solution presents an entirely new...

Learn how to protect your virtual machine workloads using OpenShift...

Understand how Red Hat Service Interconnect enables a disruption free...
More OpenShift Virtualization resources


This article will help storage providers understand what should be considered...

Learn how to deploy a Redis cluster based on virtual machines powered by Red...
OpenShift virtualization and application modernization using the Developer Sandbox
Learn how to create and manage your virtual machines (VMs) using Red Hat OpenShift and the Developer Sandbox.

