According to Gartner, despite the growing trend towards cloud migration and container adoption, a significant portion of datacenter x86 workloads will remain hypervisor-based virtualization through 2027, albeit reduced from previous years. See this e-book for more information on this topic. Managing a hybrid infrastructure that includes both hypervisor-based virtual machines and Kubernetes clusters can be a daunting task.
For platform teams, the challenge lies in efficiently managing diverse environments while optimizing existing investments. Red Hat OpenShift Virtualization offers a compelling solution by allowing organizations to run both virtual machines (VMs) and containers on a single, unified platform. This enables them to have a platform that addresses their current needs while also preparing them for future modernization and change all while enhancing the operational efficiency. By migrating virtual machines from other platforms and running them on Red Hat OpenShift, you can get the most from your existing virtualization investments while taking advantage of cloud-native architectures, streamlined operations and management, and new development approaches.
Gradual migration approach
Transitioning from traditional hypervisor solutions like VMware vSphere to OpenShift Virtualization requires a thoughtful, phased approach. Factors such as application dependencies, regulatory compliance, budget constraints, and resource availability often necessitate a phased migration approach to minimize disruption and maximize the benefits. This gradual shift allows organizations to mitigate risks and ensure continuity while migrating to OpenShift virtualization. The traffic switchover from services running on existing hypervisor platforms to OpenShift Virtualization must be disruption-free with zero downtime. Additionally, connectivity to the existing VMs in the hypervisor needs to be maintained until all components are migrated.
Ensuring seamless connectivity and zero downtime
Central to this strategy is Red Hat Service Interconnect, which simplifies connectivity across disparate environments. Offering advanced Layer 7 addressing and routing capabilities, Service Interconnect ensures seamless communication between applications across environments. This ensures that applications can seamlessly communicate across different environments, even as components are moved or updated. Service Interconnect establishes a Virtual Application Network (VAN) where multiple destinations can use the same address. It can route requests to instances of a single service running on multiple environments. If a VM is disconnected or a service is undeployed after migration, the traffic is seamlessly switched over to the service instances running at newly migrated destinations associated with same address.
This capability becomes invaluable during migrations. Imagine migrating your VMs from a hypervisor-based solution like VMware vSphere to OpenShift Virtualization. By moving a service from the hypervisor platform to OpenShift Virtualization and assigning it the same address or service name on the Service Interconnect network, traffic will be automatically distributed between the old and new environment. The anycast capability of Service Interconnect enables this. When the service running on a hypervisor enabled VM is undeployed after migration, the traffic is automatically switched over to the service running in the OpenShift Virtualization environment without any additional configurations. This ensures continuous availability and connectivity during the migration process.
Example: Migrating a sample patient portal application
Consider a patient portal application consisting of a frontend deployed on OpenShift, a database, and a payment processor running on VMware vSphere-based VMs. Through Red Hat Service Interconnect, these components are interconnected, allowing them to function as a cohesive unit despite being on different platforms, as shown in Figure 1.
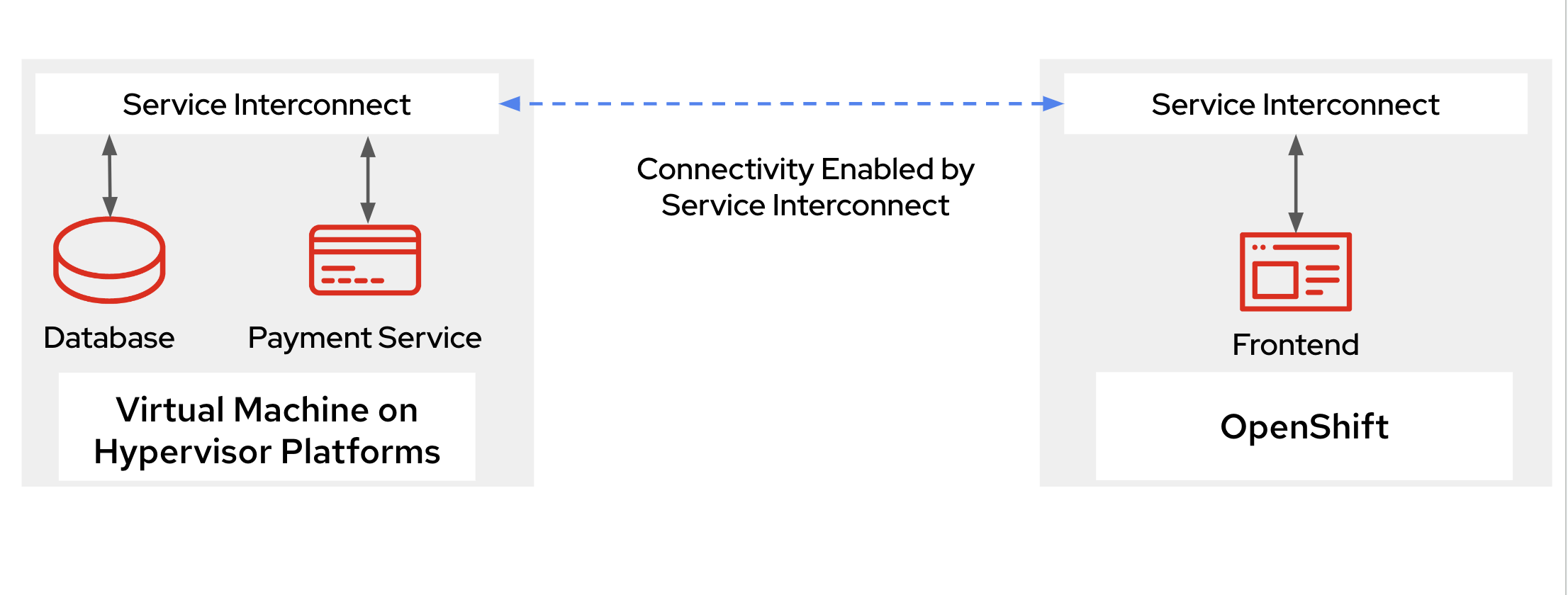
After migrating the payment processor to OpenShift Virtualization and making it a part of the Service Interconnect network, the application architecture remains resilient. If the payment service on vSphere is undeployed, Red Hat Service Interconnect automatically reroutes traffic to the VM on OpenShift Virtualization environment without any disruption, while the database continues to operate as usual. See Figure 2.
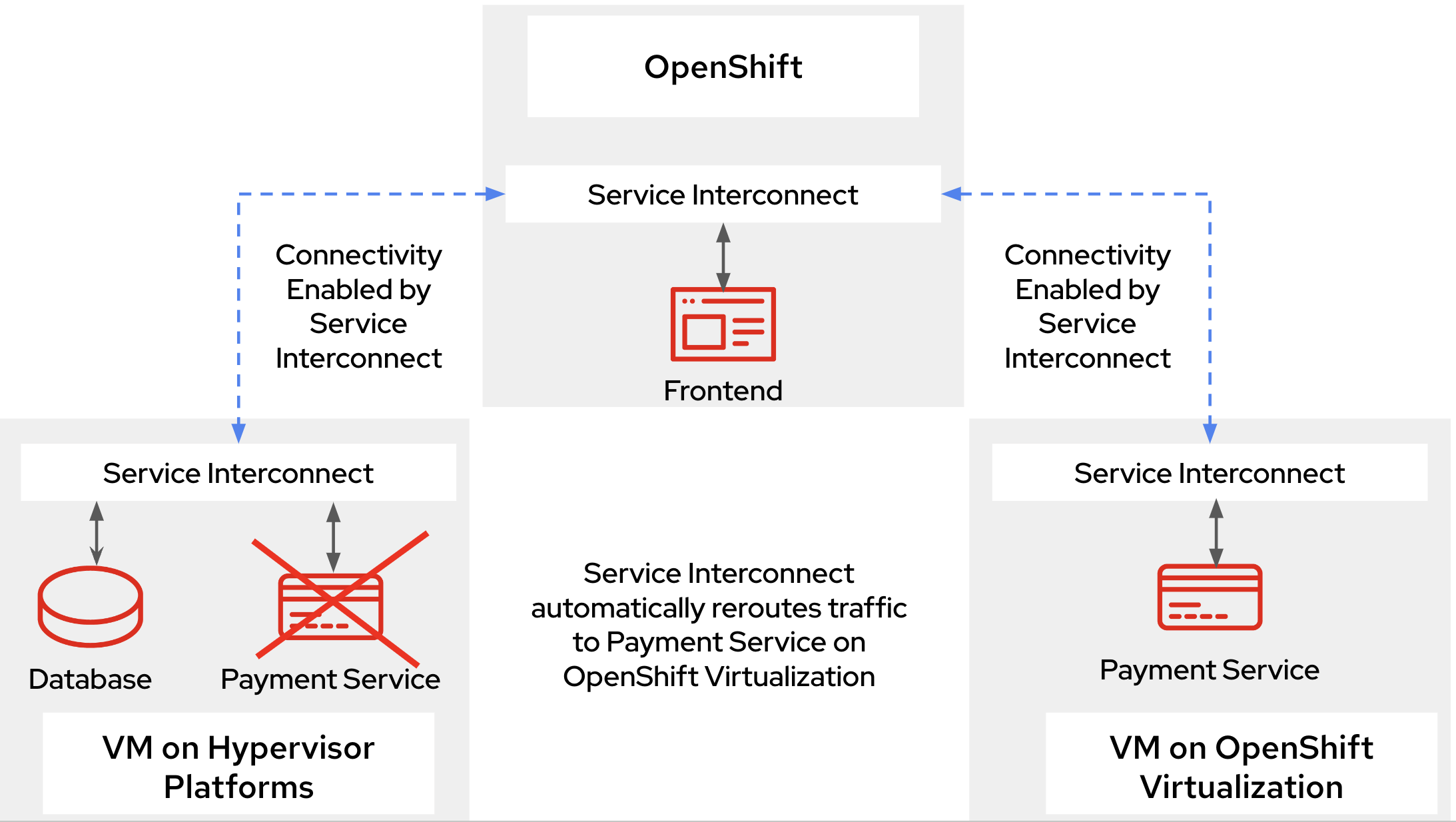
Eventually, when ready, the same approach can be used to migrate the database to OpenShift virtualization in a similar manner to complete the migration and completely move out from the hypervisor based platform such as Vsphere. This video showcases a demo of this scenario. If you are interested to try this out yourselves here is a link to the instructions on how to set things up.
Conclusion
Red Hat's integrated approach with OpenShift Virtualization and Service Interconnect exemplifies a practical solution for gradually migrating VMs from hypervisor platforms such as vSphere to OpenShift virtualization. Service Interconnect plays a pivotal role by ensuring continuous service availability and connectivity during migrations. By leveraging Service Interconnect alongside OpenShift Virtualization, organizations can navigate hybrid cloud environments with confidence, ultimately achieving greater agility and operational efficiency.
