Red Hat OpenShift Serverless delivers Kubernetes-native, event-driven primitives for microservices, containers, and compatible Function-as-a-Service (FaaS) implementations. OpenShft Serverless provides out-of-the-box traffic routing and security capabilities. This offering combines Red Hat Operators, Knative, and Red Hat OpenShift. Combined, these tools allow stateless and serverless workloads to run across OpenShift deployments on private, public, hybrid, or multi-cloud environments with automated operations.
OpenShift Serverless is now generally available. It enables developers to focus purely on building next-generation applications with a wide choice of languages, frameworks, development environments, and other tools for writing and deploying business-differentiating applications.
Key features of Red Hat OpenShift Serverless include:
- Extensive choice of programming languages and runtimes for serverless applications, letting developers use preferred tools.
- Auto-scaling up and down based on requests and events, which helps shift resource consumption based on current rather than legacy needs.
- Full integration with OpenShift Pipelines, a Kubernetes-style continuous integration (CI) and continuous delivery (CD) solution that uses Tekton building blocks.
- A Red Hat Operator-based foundation, which lets administrators more safely manage and update running instances at scale, and provides a cloud-service-like experience for an application’s lifecycle.
- Continued tracking of community release cadence, including Knative 0.13 Serving, Eventing, and
kn—the official Knative CLI. As with anything we ship as a product at Red Hat, this means we have validated these components on a variety of different platforms and configurations OpenShift runs.
We have also engaged with several partners in the Serverless space and have an ongoing collaboration in place with Microsoft around Azure Functions and KEDA, and we should have a blog post covering more details about that coming up soon. TriggerMesh has a certified operator for OpenShift, and most recently Serverless.com also decided to partner with us to enable the Serverless Framework to work with OpenShift Serverless and Knative. These partnerships demonstrate how the serverless space is maturing gradually and with a thriving ecosystem.
While new installations should receive the generally available version, older installations can upgrade smoothly. Administrators with existing deployments of OpenShift Serverless that are using the Technology Preview will need to reconfigure the OLM Subscription Update Channel to receive the update, as shown in Figure 1.
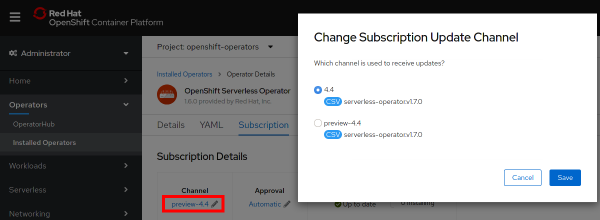
The subscription update channel should be updated to match the OpenShift Container Platform Version of either 4.4 or 4.3.
Knative Services as first-class citizens
OpenShift 4.4 makes it easier than ever to deploy applications using OpenShift Serverless by providing you a simplified way to deploy Knative Services within the Developer perspective of the OpenShift Web Console.
Now, you can select a Knative Service Resource Type when adding a new application into the project, instantly allowing any application to benefit from the power that is OpenShift Serverless—including the ability to scale to zero when idle, as shown in Figure 2.
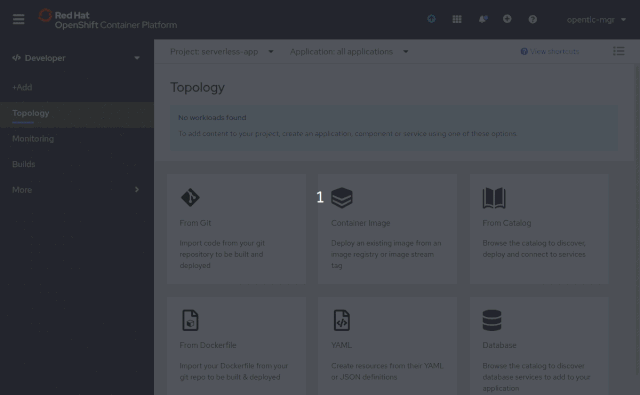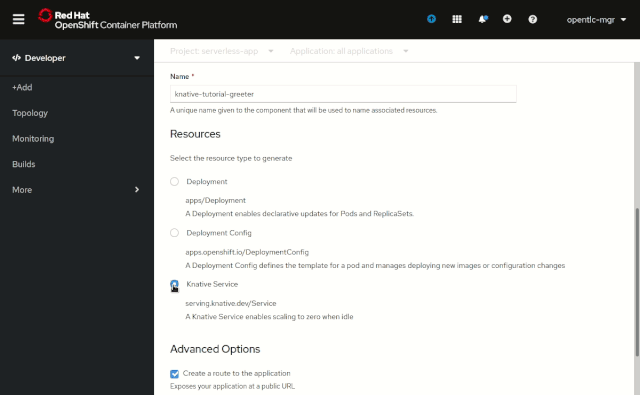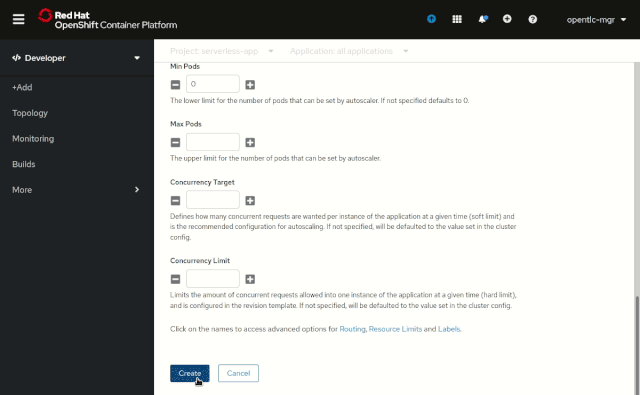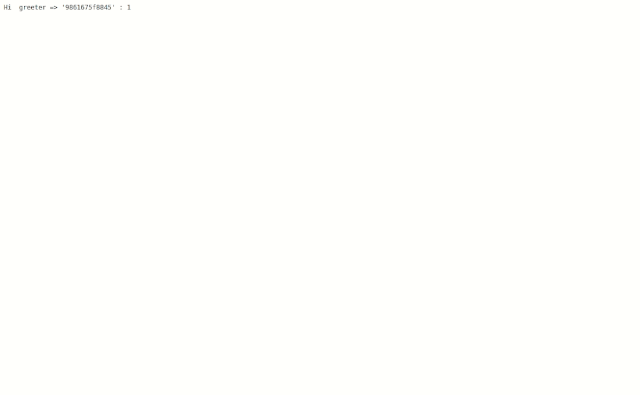
Simplified installation experience with Kourier
As mentioned in Announcing OpenShift Serverless 1.5.0 Tech Preview – A sneak peek of our GA, the most recent versions of OpenShift Serverless use Kourier. By using Kourier, we can bring the list of requirements to get Serverless installed in OpenShift down even smaller than our Technology Preview releases. This factor allows for lower resource consumption and faster running application cold starts. We also avoid impacting non-serverless workloads running on the same namespace.
Overall these improvements in combination with fixes we implemented in OpenShift 4.3.5 speed up the time to create an application from a pre-built container between 40–50%, depending on the container image size.
Figure 3 shows the results before using Kourier.
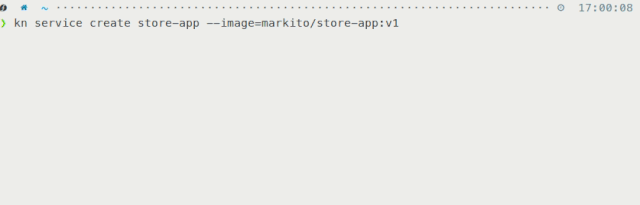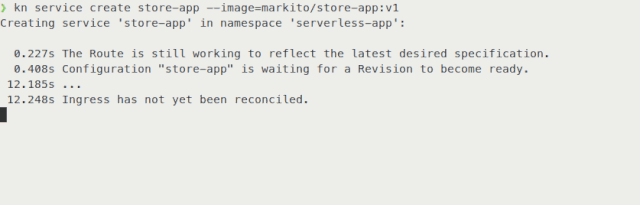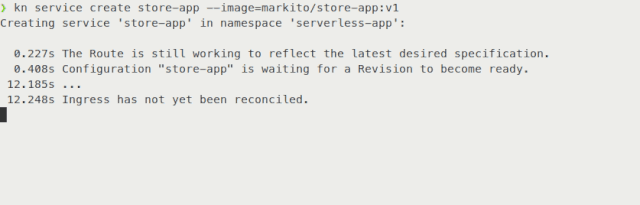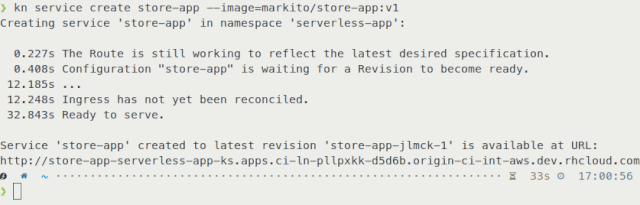
Figure 4 shows the create time after adding Kourier:
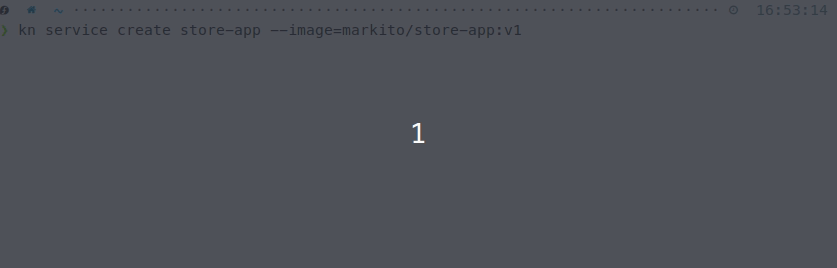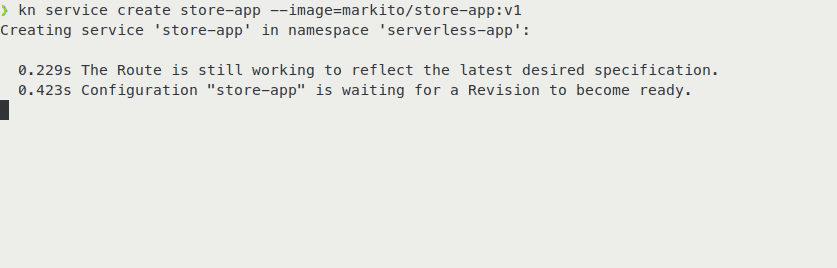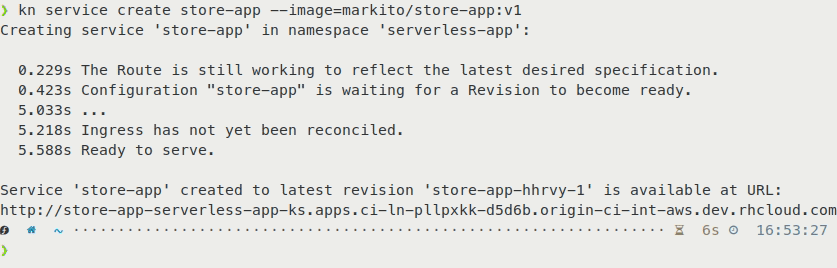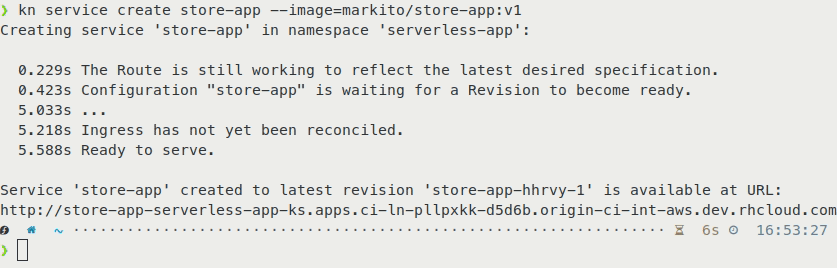
Automatic TLS/SSL
OpenShift Serverless now allows for automatic creation and deployment of TLS/SSL for a Knative Service's given route. This means that you can continue focusing on developing your application instead of running and managing it. As a result, Serverless can handle the complexities of managing the deployment while still maintaining the security developers expect from Red Hat OpenShift.
OpenShift Serverless command-line interface (CLI)
The OpenShift Serverless command-line interface (CLI) kn is now available via the OpenShift Console's Command Line Tools section, as shown in Figure 5.
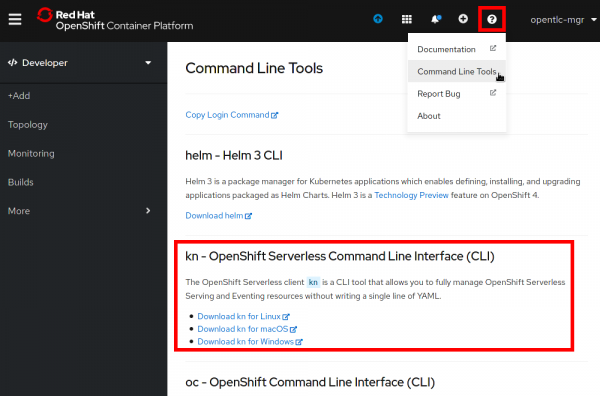
When using this interface to download the serverless CLI, enterprise customers have access to a Red Hat-notarized version of kn. MacOS, Windows, or Linux users can have more confidence that this distributed CLI has been checked for malicious components.
In Figure 6, we use kn to deploy a service in a single command, instantiating our application on OpenShift with a URL to access it within a few seconds.
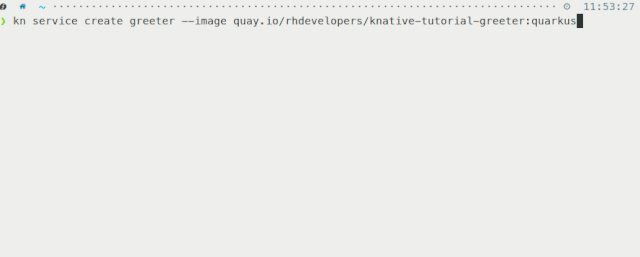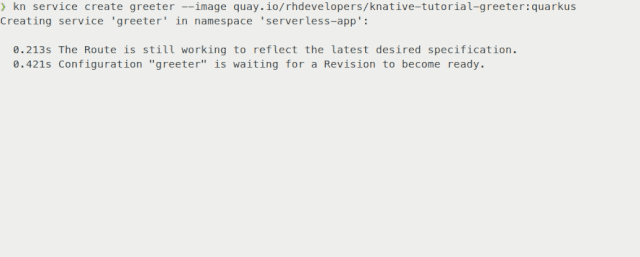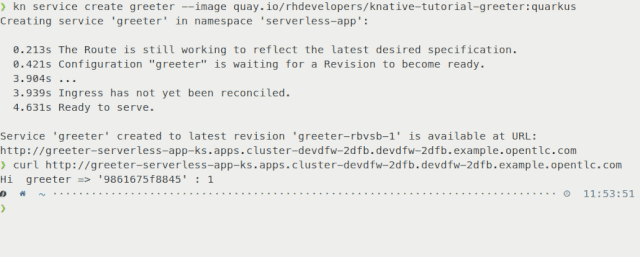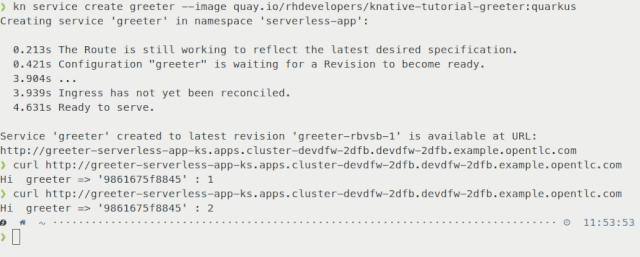
This tool allows you to fully manage both Serverless Serving and Eventing resources without the need to edit or view any YAML configurations.
Developer Topology enhancements
Let's take a look at the Topology view enhancements to make managing OpenShift Knative Services easier.
Knative Service-centric visualizations
Knative Services are represented as a rectangle containing all of the revisions within the Topology view, as shown in Figure 7.
You can quickly see the current traffic distribution percentages for a Knative Service. It is also possible to group Knative Services within an application group, which allows for quick and organized visual management of what is happening within a given grouping.
Collapsing OpenShift Knative Services
Speaking of application grouping, OpenShift 4.4 brings the ability to collapse Knative Services within an application group. This makes it easier to manage and view your services when more complex applications are deployed within a project.
Knative Service details
OpenShift 4.4 also provides improved side panel content for Knative Services. The Resources tab within the side panel now shows the components that the service is composed of, specifically: Pods, Revisions, and Routes. You can also use these components for quick and easy access to individual pod logs.
This view shows the traffic distribution percentages and even allows for a rapid configuration change. As a result, you can quickly notice the live traffic distribution for the given Knative Service via the number of pods that are running for a given revision, as shown in Figure 8.
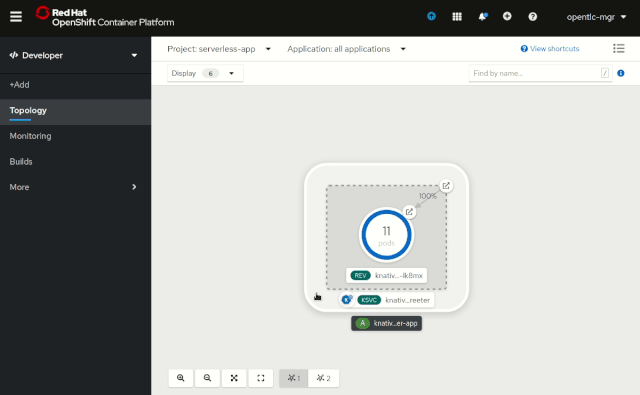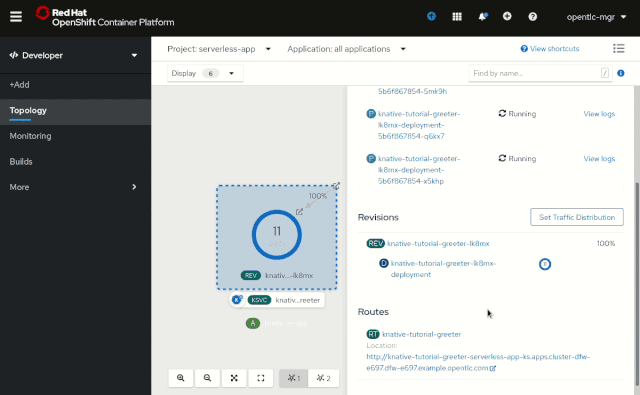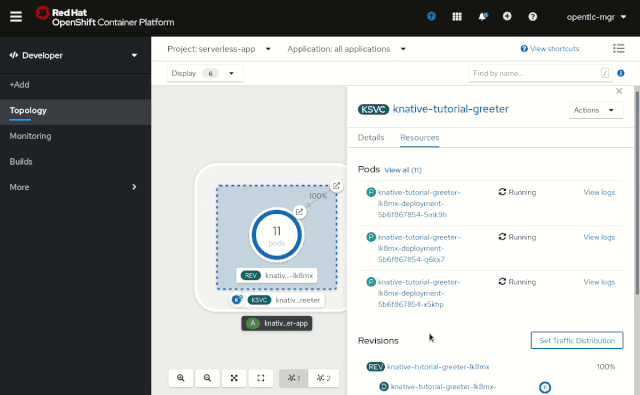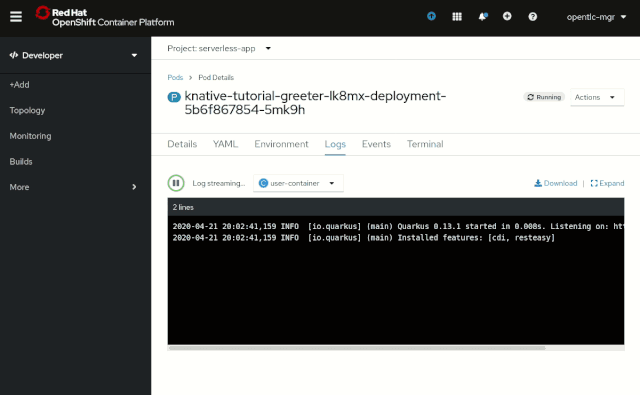
A deeper view into Revisions
The Developer Topology view, for now, includes a much deeper view into individual Serverless Revisions. Now, you can quickly see all pods for a revision and view their logs if needed. This view also allows for easy access to the Revision’s Deployments and Configurations, as well as a sub-route that points directly to the given revision, as shown in Figure 9.
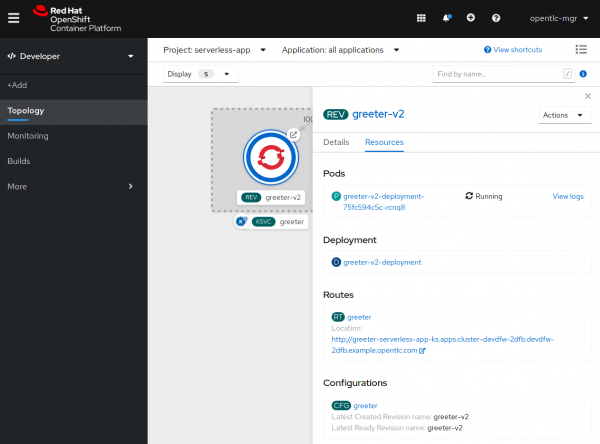
We hope these features help you successfully create and manage serverless applications. In future releases, we’ll provide even more functionality in the developer experience. Keep an eye out for the ability to create event sources, and more!
Ready to get started?
Provide your feedback
Let us know what you think about the serverless experience. Keep the feedback coming, your feedback allows us to help you. Also, you can join our OpenShift Developer Experience Google Group to participate in discussions and learn about our Office Hours session, where you can collaborate with us and provide feedback.
Learn more
Learn more about OpenShift application development with these Red Hat resources:
Last updated: March 30, 2023