Note
This tutorial provides a way to quickly try Red Hat AI Inference Server and learn the deployment workflow. This is not a production-grade deployment; it is intended for quick exploration on a personal machine with a local GPU.
With the growing demand for running lightweight language models on personal GPUs, developers often struggle to test Red Hat AI Inference Server in a quick and simple way. This tutorial demonstrates how to containerize and run a small LLM using Red Hat AI Inference Server with minimal setup—ideal for developers looking to validate models locally before scaling to OpenShift.
This post demonstrates how to deploy the lightweight AI model Llama-3.2-1B using Red Hat AI Inference Server containerization. The deployment workflow is shown in Figure 1.
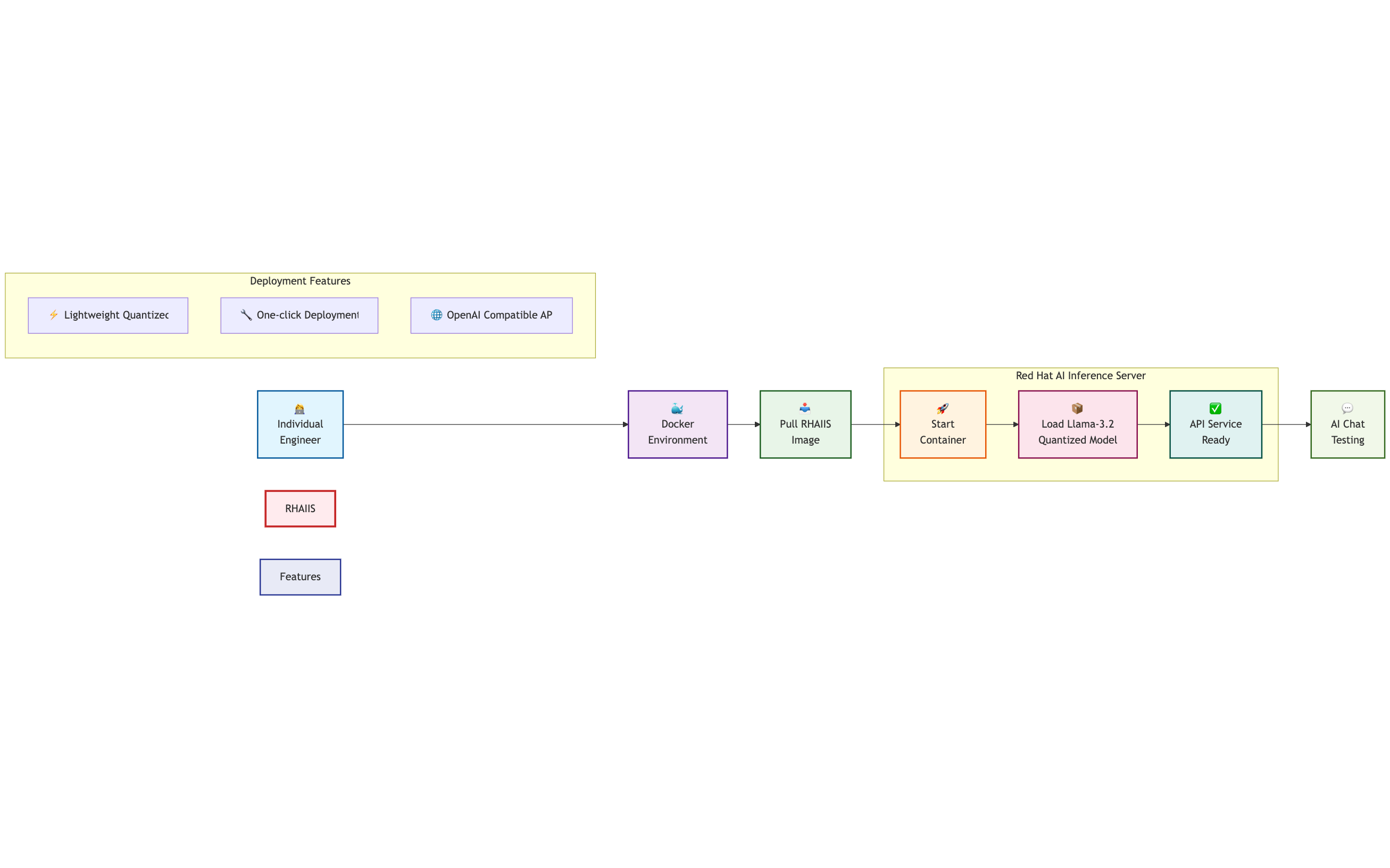
Prerequisites
Account requirements:
Red Hat account: You will need a valid subscription or a free Developer account. This account lets you access the Red Hat AI Inference Server container images.
Hugging Face account (optional): This account lets you obtain an access token if you need to download private models. Register for an account. You can find all Red Hat-verified large language models (LLMs) on the Red Hat AI Hugging Face page.
Hardware requirements:
- A computer with a GPU. For more details, see the Red Hat AI Inference Server documentation.
Tutorial
Log in to the Red Hat container registry, you need to authenticate to access the Red Hat AI Inference Server container images:
podman login registry.redhat.ioPull the latest image. You can find the latest Red Hat AI Inference Server image in the Red Hat Ecosystem Catalog; search for
rhaiis.podman pull registry.redhat.io/rhaiis/vllm-cuda-rhel9:3The size of this image is around 15 GB.
Set your HF token if the model you are downloading is private. Better choose a small model for testing.
#Set the Hugging Face Token (if needed) export HF_TOKEN=your_HuggingFace_TokenCreate a local directory for model caching
mkdir -p rhaiis-cache chmod g+rwX rhaiis-cacheThe following command generates a Container Device Interface (CDI) configuration file for NVIDIA GPUs.
sudo nvidia-ctk cdi generate --output=/etc/cdi/nvidia.yamlNow, let's test Llama 3.2 1B. This command starts a GPU-enabled container, loads the Llama 3.2 model, and launches the OpenAI-compatible API on port 8000. Start the container:
podman run -d --device nvidia.com/gpu=all -p 8000:8000 -v ~/rhaiis-cache:/opt/app-root/src/.cache:Z --shm-size=4g --name rhaiis-llama --restart unless-stopped -e HUGGING_FACE_HUB_TOKEN=$HF_TOKEN -e CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=0 -e NVIDIA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=all -e NVIDIA_DRIVER_CAPABILITIES=compute,utility -e HF_HUB_OFFLINE=0 registry.redhat.io/rhaiis/vllm-cuda-rhel9:latest --model RedHatAI/Llama-3.2-1B-Instruct-quantized.w8a8 --host 0.0.0.0 --port 8000 --max-model-len 1024 --max-num-seqs 8 --tensor-parallel-size 1 --enforce-eager --disable-custom-all-reduceTo change the LLM, modify the content behind
--model.While this tutorial uses Docker for simplicity, you can also use Podman as a drop-in replacement if your system does not support Docker. Here are explanations for each parameter:
podman run -d \ # Run container in detached (background) mode --device nvidia.com/gpu=all \ # Attach all available NVIDIA GPUs via CDI -p 8000:8000 \ # Map host port 8000 to container port 8000 for API access -v ~/rhaiis-cache:/opt/app-root/src/.cache:Z \ # Mount cache directory to store/download models & weights --shm-size=4g \ # Allocate 4GB shared memory (needed for large model inference) --name rhaiis-llama \ # Assign container name "rhaiis-llama" --restart unless-stopped \ # Auto-restart unless container is manually stopped -e HUGGING_FACE_HUB_TOKEN=$HF_TOKEN \ # Provide Hugging Face token for private model downloads -e CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=0 \ # Restrict container to use only GPU 0 -e NVIDIA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=all \ # Make all GPUs visible to container (overridden by CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES) -e NVIDIA_DRIVER_CAPABILITIES=compute,utility \ # Enable compute (CUDA) and utility (nvidia-smi) driver functions -e HF_HUB_OFFLINE=0 \ # Enable Hugging Face online mode (allow auto model download) registry.redhat.io/rhaiis/vllm-cuda-rhel9:latest \ # Container image (Red Hat AI Inference Server with vLLM) --model RedHatAI/Llama-3.2-1B-Instruct-quantized.w8a8 \ # Model to load (quantized Llama 3.2 1B Instruct) --host 0.0.0.0 \ # Bind API server to all interfaces (not just localhost) --port 8000 \ # Serve API on port 8000 --max-model-len 1024 \ # Maximum token length for a single request --max-num-seqs 8 \ # Maximum concurrent requests (batch size) --tensor-parallel-size 1 \ # Tensor parallelism factor (1 = no parallel split) --enforce-eager \ # Force eager execution (disable graph optimizations for stability) --disable-custom-all-reduce # Disable custom all-reduce ops (avoid distributed sync issues)Test the LLM conversation:
curl -X POST http://localhost:8000/v1/chat/completions \ -H "Content-Type: application/json" \ -d '{ "model": "RedHatAI/Llama-3.2-1B-Instruct-quantized.w8a8", "messages": [{"role": "user", "content": "Hello, how are you?"}], "max_tokens": 100 }'
If you see the following output, your LLM has been deployed successfully:
{"id":"chatcmpl-32b8543d39824253bd8b07e1a10dc4d3","object":"chat.completion","created":1757411067,"model":"RedHatAI/Llama-3.2-1B-Instruct-quantized.w8a8","choices":[{"index":0,"message":{"role":"assistant","content":"I'm doing well, thank you for asking. I'm a large language model, so I don't have feelings or emotions like humans do, but I'm here to help you with any questions or topics you'd like to discuss. How about you? How's your day going so far?","refusal":null,"annotations":null,"audio":null,"function_call":null,"tool_calls":[],"reasoning_content":null},"logprobs":null,"finish_reason":"stop","stop_reason":null}],"service_tier":null,"system_fingerprint":null,"usage":{"prompt_tokens":41,"total_tokens":101,"completion_tokens":60,"prompt_tokens_details":null},"prompt_logprobs":null,"kv_transfer_params":null}Conclusion
In this tutorial, you learned how to deploy a small language model using Red Hat AI Inference Server in a containerized environment with minimal hardware requirements. This quick-start approach helps validate local setups, explore FP8 quantized models, and test vLLM-based APIs on your own machine. To take the next step, consider exploring.
