Apache ActiveMQ is a highly popular message broker that features persistence, guaranteed message delivery, and high throughput. Apache ActiveMQ Artemis streamlines the classic message broker implementation for microservices architectures. This article is for developers transitioning from ActiveMQ Classic to ActiveMQ Artemis. We will show you how to get the two versions working together using Apache Camel K. Our example is based on Red Hat AMQ versions 6 and 7, and we will perform the steps on Red Hat OpenShift 4. Our code is written in Java. The integration process and techniques should be applicable to many other scenarios.
Note: See Implementing Apache ActiveMQ-style broker meshes with Apache Artemis for a discussion of the differences between Red Hat AMQ 6 and 7.
The Camel K integration workflow
Camel K is an integration framework that allows developers to exchange data easily between many common data processing tools. The demonstration in this article creates two ActiveMQ brokers, one using Red Hat AMQ 6 and the other using Red Hat AMQ 7. We then create two Camel K integrations: One to help AMQ 7 consume messages, and another to help AMQ 6 produce them. Finally, we create a third integration that functions as a message bridge between the two brokers.
Figure 1 illustrates the Camel K integration workflow.
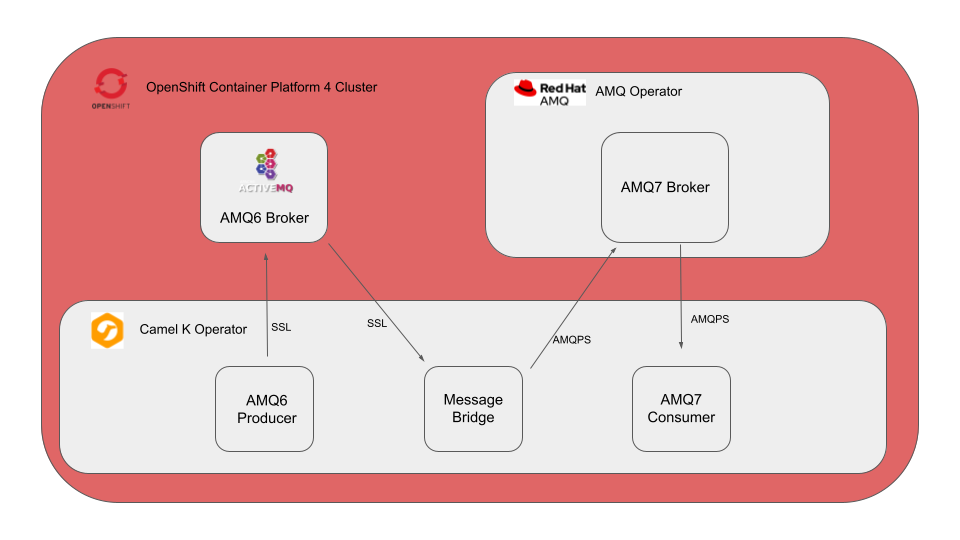
You can retrieve the files for the demonstration from the GitHub repository associated with this article.
Prerequisites
This article assumes you have a basic knowledge of the OpenShift oc command-line interface and OpenShift web console. You need a running instance of OpenShift 4 and admin access on the OpenShift cluster. You will also need to install Camel K on your local system.
Set up the cluster
Create a namespace on your OpenShift instance:
$ oc new-project camelk-sslAs the cluster administrator, install the Red Hat Camel K Operator and Red Hat AMQ 7.7 Operator on your OpenShift instance from the OpenShift OperatorHub.
Now, create certificates to enable secure SSL communication. Make sure you set the common name CN on the broker to your server domain name:
export CLIENT_KEYSTORE_PASSWORD=password
export CLIENT_TRUSTSTORE_PASSWORD=password
export BROKER_KEYSTORE_PASSWORD=password
export BROKER_TRUSTSTORE_PASSWORD=password
#Client Keystore
keytool -genkey -alias client -keyalg RSA -keystore client.ks -storepass $CLIENT_KEYSTORE_PASSWORD -keypass $CLIENT_KEYSTORE_PASSWORD -dname "CN=camelssl-example, O=RedHat, C=UK"
#Broker Keystore
keytool -genkey -alias broker -keyalg RSA -keystore broker.ks -storepass $BROKER_KEYSTORE_PASSWORD -keypass $BROKER_KEYSTORE_PASSWORD -dname "CN=*.apps.cluster-hhl6r.hhl6r.sandbox55.opentlc.com, O=RedHat, C=UK"
#Export Client PublicKey
keytool -export -alias client -keystore client.ks -storepass $CLIENT_KEYSTORE_PASSWORD -file client.cert
#Export Server PublicKey
keytool -export -alias broker -keystore broker.ks -storepass $BROKER_KEYSTORE_PASSWORD -file broker.cert
#Import Server PublicKey into Client Truststore
keytool -import -alias broker -keystore client.ts -file broker.cert -storepass $CLIENT_TRUSTSTORE_PASSWORD -trustcacerts -noprompt
#Import Client PublicKey into Server Truststore
keytool -import -alias client -keystore broker.ts -file client.cert -storepass $BROKER_TRUSTSTORE_PASSWORD -trustcacerts -noprompt
#Import Server PublicKey into Server Truststore (i.e.: trusts its self)
keytool -import -alias broker -keystore broker.ts -file broker.cert -storepass $BROKER_TRUSTSTORE_PASSWORD -trustcacerts -noprompt
Set up the ActiveMQ consumer (AMQ 7)
Create a secret for the broker keystore and truststore for AMQ 7:
$ oc create secret generic example-amq-secret --from-file=broker.ks --from-literal=keyStorePassword=password --from-file=client.ts=broker.ts --from-literal=trustStorePassword=passwordCreate an AMQ 7 broker using the AMQ broker operator:
apiVersion: broker.amq.io/v2alpha4
kind: ActiveMQArtemis
metadata:
name: example-amq
application: example-amq
namespace: camelk-ssl
spec:
deploymentPlan:
size: 1
image: registry.redhat.io/amq7/amq-broker:7.6
requireLogin: false
adminUser: admin
adminPassword: admin
console:
expose: true
acceptors:
- name: amqp
protocols: amqp
port: 5672
sslEnabled: true
sslSecret: example-amq-secret
verifyHost: false
expose: true
Create a new AMQ broker address. This configuration also creates a route and service for the broker:
apiVersion: broker.amq.io/v2alpha2
kind: ActiveMQArtemisAddress
metadata:
name: example-testaddress
spec:
addressName: test
queueName: test
routingType: anycast To test your AMQ 7 broker, you have to download ActiveMQ Artemis. Once the download is completed, extract it and open the /bin folder, where you will find the Apache Artemis script that is used for testing. You can produce and consume messages using the new AMQ 7 broker from your local machine; just make sure to change the URL and truststore location.
Here is a sample command to produce messages:
$ ./artemis producer --url 'amqps://example-amq7-amqp-0-svc-rte-camelk-ssl.apps.cluster-hhl6r.hhl6r.sandbox55.opentlc.com:443?jms.username=admin&jms.password=admin&transport.trustStoreLocation=/home/marslan/work/camelkssl/client.ts&transport.trustStorePassword=password&transport.verifyHost=false' --threads 1 --protocol amqp --message-count 10 --destination 'queue://test'Here is a sample command to consume messages:
$./artemis consumer --url 'amqps://example-amq7-amqp-0-svc-rte-camelk-ssl.apps.cluster-hhl6r.hhl6r.sandbox55.opentlc.com:443?jms.username=admin&jms.password=admin&transport.trustStoreLocation=/home/marslan/work/camelkssl/client.ts&transport.trustStorePassword=password&transport.verifyHost=false' --threads 1 --protocol amqp --message-count 10 --destination 'queue://test'Set up the ActiveMQ producer (AMQ 6)
Next, create a secret for the broker keystore and truststore for AMQ 6:
$ oc create secret generic example-amq6-secret --from-file=broker.ks --from-literal=keyStorePassword=password --from-file=broker.ts --from-literal=trustStorePassword=password Create an AMQ 6 broker from the command line:
$ oc new-app amq63-ssl -p APPLICATION_NAME=amq6-broker -p MQ_QUEUES=test -p MQ_TOPICS=test -p MQ_USERNAME=admin \ -p MQ_PASSWORD=admin -p ActiveMQ_SECRET=example-amq6-secret -p AMQ_TRUSTSTORE=broker.ts -p AMQ_TRUSTSTORE_PASSWORD=password \ -p AMQ_KEYSTORE=broker.ks -p AMQ_KEYSTORE_PASSWORD=password -n camelk-sslCreate a route for the broker in the OpenShift console, using the amq6-broker-tcp-ssl service.
To test your AMQ 6 broker, you can download ActiveMQ. Once the download is completed, extract it and open the /bin folder, where you will find the ActiveMQ script that is used for testing. You can produce and consume messages using the new AMQ 6 broker from your local machine. Just make sure to change the URL and truststore location.
Enter the following command to produce messages:
$ ./activemq producer \ -Djavax.net.ssl.trustStore=/home/marslan/work/camelkssl/client.ts \ -Djavax.net.ssl.trustStorePassword=password \ -Djavax.net.ssl.keyStore=/home/marslan/work/camelkssl/client.ks \ -Djavax.net.ssl.keyStorePassword=password \ --brokerUrl ssl://test-camelk-ssl.apps.cluster-hhl6r.hhl6r.sandbox55.opentlc.com:443 \ --user admin \ --password admin \ --destination queue://test \ --messageCount 1000 \ --message HelloWorld Enter the following command to consume messages:
$ ./activemq consumer \ -Djavax.net.ssl.trustStore=/home/marslan/work/camelkssl/client.ts \ -Djavax.net.ssl.trustStorePassword=password \ -Djavax.net.ssl.keyStore=/home/marslan/work/camelkssl/client.ks \ -Djavax.net.ssl.keyStorePassword=password \ --brokerUrl ssl://test-camelk-ssl.apps.cluster-hhl6r.hhl6r.sandbox55.opentlc.com:443 \ --user admin \ --password admin \ --destination queue://test Test Camel K
Now, we will import a simple Java application and use it to ensure that Camel K is working correctly. The HelloCamelK.java program is available in the Camel K SSL Demo repository on GitHub.
Run the file with the following command (you may delete this integration after the test):
$ kamel run HelloCamelKCreate the AMQ 7 consumer
Create folders for AMQ 6 and AMQ 7:
$ mkdir amq6
$ mkdir amq7Create a new configuration directory for AMQ 7:
$ mkdir amq7/configsIn the configuration directory, create an application.properties file for the AMQ 7 integration, with the following contents:
quarkus.qpid-jms.url=amqps://example-amq7-amqp-0-svc-rte-camelk-ssl.apps.cluster-hhl6r.hhl6r.sandbox55.opentlc.com:443?transport.keyStoreLocation=/etc/ssl/example-amq-secret/broker.ks&transport.keyStorePassword=password&transport.trustStoreLocation=/etc/ssl/example-amq-secret/client.ts&transport.trustStorePassword=password&transport.verifyHost=false
quarkus.qpid-jms.username=admin
quarkus.qpid-jms.password=admin
jms.destinationType=queue
jms.destinationName=test
Within the amq7 folder, create a program named amq7consumer.java for the AMQ 7 consumer integration:
// camel-k: language=java <1>
// camel-k: dependency=mvn:org.amqphub.quarkus:quarkus-qpid-jms <2>
import org.apache.camel.builder.RouteBuilder;
public class amq7consumer extends RouteBuilder {
@Override
public void configure() throws Exception {
from("jms:{{jms.destinationType}}:{{jms.destinationName}}").to("log:info"); <3>
}
}
Let's look at a few parts of the code:
camel-k: language=javaprovides information to Camel K to run the Java file. The comment enables Camel K to sort out dependencies.camel-k: dependency=mvn:org.amqphub.quarkus:quarkus-qpid-jmssupports out-of-the-box configuration for SSL, without requiring any further customization. You can find more information in the Apache SSL documentation.- The code consumes the
jms.url,jms.destinationType, andjms.destinationNameproperties specified in theapplication.propertiesfile and prints the values to the log.
The Java file is imported in the next step, where we run Camel K:
$ kamel run -n camelk-ssl --property file:./amq7/configs/application.properties --resource secret:example-amq-secret@/etc/ssl/example-amq-secret amq7/amq7consumer.java In the kamel run command:
- The
--property fileoption imports properties to Camel. - The
--resourceoption adds resources to the cluster pod. In this command, we are addingexample-amq-secretand placing its contents into the/etc/ssl/example-amq-secretfolder within the pod.
To debug Camel K, add the following option to the kamel run command:
--trait jvm.options=-Djavax.net.debug=allCreate the AMQ 6 producer
Create a new configuration directory for AMQ 6:
$ mkdir amq6/configsIn the configuration directory, create an application.properties file for the AMQ 6 integration, with the following contents:
activemq.destination.brokerURL=ssl://test-camelk-ssl.apps.cluster-hhl6r.hhl6r.sandbox55.opentlc.com:443
activemq.destination.username=admin
activemq.destination.password=admin
activemq.destination.ssl.keyStorePassword=password
activemq.destination.ssl.keyStoreLocation=/etc/ssl/example-amq6-secret/broker.ks
activemq.destination.ssl.trustStorePassword=password
activemq.destination.ssl.trustStoreLocation=/etc/ssl/example-amq6-secret/broker.ts
activemq.destination.type=queue
activemq.destination.name=test
Within the amq6 folder, create a program named amq6SSLproducer.java for the AMQ 6 producer integration:
// camel-k: dependency=camel:camel-quarkus-activemq
// camel-k: dependency=camel:camel-quarkus-timer
// camel-k: property=period=5000
public class amq6SSLProducer extends RouteBuilder {
@Override
public void configure() throws Exception {
from("timer:foo?fixedRate=true&period={{period}}").bean(this, "generateFakePerson()").to("log:info")
.to("activemq:{{activemq.destination.type}}:{{activemq.destination.name}}?connectionFactory=#pooledConnectionFactory");
}
public String generateFakePerson() {
Faker faker = new Faker();
return faker.name().fullName() + " lives on " + faker.address().streetAddress();
}
@ApplicationScoped
public ActiveMQComponent activeMq(PooledConnectionFactory pooledConnectionFactory) {
ActiveMQComponent activeMqComponent = new ActiveMQComponent();
activeMqComponent.setConnectionFactory(pooledConnectionFactory);
activeMqComponent.setCacheLevelName("CACHE_CONSUMER");
return activeMqComponent;
}
@BindToRegistry
public PooledConnectionFactory pooledConnectionFactory() throws Exception {
return new PooledConnectionFactory(sslConnectionFactory());
}
private ActiveMQSslConnectionFactory sslConnectionFactory() throws Exception {
ActiveMQSslConnectionFactory connectionFactory = new ActiveMQSslConnectionFactory();
logger.info("BrokerURL: " + destinationBrokerURL);
connectionFactory.setBrokerURL(destinationBrokerURL);
connectionFactory.setUserName(destinationUserName);
connectionFactory.setPassword(destinationPassword);
connectionFactory.setTrustStore(destinationTrustStoreLocation);
connectionFactory.setTrustStorePassword(destinationTruststorePassword);
connectionFactory.setKeyStore(destinationKeyStoreLocation);
connectionFactory.setKeyStorePassword(destinationKeystorePassword);
return connectionFactory;
}
}Run the producer using Camel K:
$ kamel run -n camelk-ssl \ --property file:./amq6/configs/application.properties \ --resource secret:example-amq6-secret@/etc/ssl/example-amq6-secret amq6/amqssl.javaCreate a message bridge between AMQ 6 and AMQ 7
Create new folders for the message bridge and its configuration:
$ mkdir message-bridge
$ mkdir message-bridge/configsIn the configuration directory, create an application.properties file for the message bridge, with the following contents:
#amq6
activemq.source.brokerURL=ssl://test-camelk-ssl.apps.cluster-hhl6r.hhl6r.sandbox55.opentlc.com:443
activemq.source.username=admin
activemq.source.password=admin
activemq.source.ssl.keyStorePassword=password
activemq.source.ssl.keyStoreLocation=/etc/ssl/example-amq6-secret/broker.ks
activemq.source.ssl.trustStorePassword=password
activemq.source.ssl.trustStoreLocation=/etc/ssl/example-amq6-secret/broker.ts
activemq.source.type=queue
activemq.source.name=test
#amq7
quarkus.qpid-jms.url=amqps://example-amq7-amqp-0-svc-rte-camelk-ssl.apps.cluster-hhl6r.hhl6r.sandbox55.opentlc.com:443?transport.keyStoreLocation=/etc/ssl/example-amq-secret/broker.ks&transport.keyStorePassword=password&transport.trustStoreLocation=/etc/ssl/example-amq-secret/client.ts&transport.trustStorePassword=password&transport.verifyHost=false
quarkus.qpid-jms.username=admin
quarkus.qpid-jms.password=admin
jms.destinationType=queue
jms.destinationName=testIn the message-bridge folder, create a program named sixToSevenBridge.java, with the following contents:
@Override
public void configure() throws Exception {
from("activeMQSource:{{activemq.source.type}}:{{activemq.source.name}}").to("log:info")
.to("jms:{{jms.destinationType}}:{{jms.destinationName}}?connectionFactory=artemisConnectionFactory");
}
@BindToRegistry("artemisConnectionFactory")
public JmsConnectionFactory connectionFactory() throws Exception {
return new JmsConnectionFactory(destinationBrokerURL);
}
@BindToRegistry("activeMQSource")
public ActiveMQComponent activeMQSource() throws Exception{
ActiveMQComponent activeMqComponent = new ActiveMQComponent();
activeMqComponent.setConnectionFactory(pooledConnectionFactorySource());
activeMqComponent.setCacheLevelName("CACHE_CONSUMER");
return activeMqComponent;
}
@BindToRegistry("pooledConnectionFactorySource")
public PooledConnectionFactory pooledConnectionFactorySource() throws Exception {
return new PooledConnectionFactory(sslConnectionFactorySource());
}
private ActiveMQSslConnectionFactory sslConnectionFactorySource() throws Exception {
ActiveMQSslConnectionFactory connectionFactory = new ActiveMQSslConnectionFactory();
System.out.println("BrokerURL: " + sourceBrokerURL);
connectionFactory.setBrokerURL(sourceBrokerURL);
connectionFactory.setUserName(sourceUserName);
connectionFactory.setPassword(sourcePassword);
connectionFactory.setTrustStore(sourceTrustStoreLocation);
connectionFactory.setTrustStorePassword(sourceTruststorePassword);
connectionFactory.setKeyStore(sourceKeyStoreLocation);
connectionFactory.setKeyStorePassword(sourceKeystorePassword);
return connectionFactory;
}
Run the message bridge:
$ kamel run -n camelk-ssl \ --property file:./message-bridge/configs/application.properties message-bridge/sixToSevenBridge.java \ --resource secret:example-amq6-secret@/etc/ssl/example-amq6-secret \ --resource secret:example-amq-secret@/etc/ssl/example-amq-secret View the logs to see whether the message bridge worked:
$ oc logs -f {AMQ7 consumer pod} Clean up
Uninstall the operators using the OpenShift command line:
$ oc delete project camelk-sslConclusion
This article showed you how to use Camel K to connect different versions of the ActiveMQ message broker using Red Hat AMQ on OpenShift 4. Camel K is a highly effective integration framework that runs natively on Kubernetes. This article showcased just a few of its capabilities. Camel K allows you to build and containerize applications easily and quickly. Its integrations use very lightweight pods, thus consuming fewer resources.
Get more information from the Camel K documentation. You might also enjoy the article Six reasons to love Camel K and our series of related Camel K learning courses.
Last updated: October 8, 2024