Debugging CI/CD pipelines isn't always easy. This is especially true when a pipeline takes a long time to run, and the failing part you want to debug runs at the end of the pipeline. A feature introduced in a recent Tekton enhancement proposal (TEP) would let users stop the pipeline at any Step and debug in real time.
This article looks at debugging TaskRuns in Tekton, the open source framework that integrates with Kubernetes to create cloud-native CI/CD pipelines. You can learn more about the basics of Tekton in this article by Joel Lord.
The proposal, TEP-0042, outlines this feature with a proof of concept that describes how Tekton's composability and container support enable this functionality. For a thorough overview of these concepts, watch the talk, Russian Doll: Extending Containers with Nested Processes by Christie Wilson (Google) and Jason Hall (Red Hat).
Debugging TaskRuns: TL;DR
Debugging TaskRuns in Tekton is possible because of the composability provided by container-based pipelines it helps the user create. A Task runs as a Pod, and each Step in a Task runs in a container. With each Step running in a container, we can be sure that the delta of change in the container environment (which is not shared between Steps) is directly associated with the Step itself and nothing else. Anything else that might happen is a side effect, e.g., due to the injection of a sidecar container to the TaskRun. This makes Tekton great for debugging pipelines, as the cost to spin up a container is definitely far less than spinning up a cloud virtual machine (VM).
With this in mind, TEP-0042 would extend the TaskRun Step life cycle (responsible for orchestrating TaskRun containers to run serially) and add capabilities to pause a TaskRun Step after a failure occurs.
Modifying the life of a Step
The life of a Step currently looks something like Figure 1.

The Step starts running when e.Go() runs. This is where Tekton invokes the entry point of the Step in the TaskRun and the child process (which is the actual Step) runs. If the child process runs successfully, we write a postFile that is used as a flag to convey the same. If it fails, we write an err postFile, which conveys a similar message.
To halt this Step on failure, we must understand which parts of the Step react when the failure occurs; this is the write err postFile and exit shown in Figure 1. When a Step fails, the failure is marked by writing a <step-no>.err file to /tekton/tools/ directory in the Step container, which is shared with other containers in the Pod. This file is written by the background job in the entry point. The <step-no>.err file also lets the subsequent Steps know that there has been a failure, and eventually exits the TaskRun.
This mechanism needs to be updated to support the discovery of Step failures and the ability to stop the Steps before it exits. This requires disabling the write err postFile. Instead of exiting the Step, it will wait for a flag that would exit the Step from the suspended state. The updated flow would look something like the diagram shown in Figure 2.
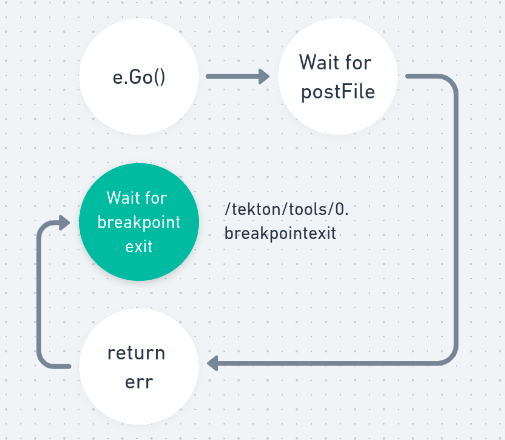
Once the Step is halted, the client can access the container environment for debugging.
Conclusion
In practice, the debugging solution is more nuanced than the overview provided here. Read the full TEP-0042 proposal for details.
This topic is also the subject of a cdCon 2021 talk: Houston, We've Got a Problem!: How to Debug your Pipeline in Tekton.
The debugging feature is expected to be available in Tekton later this year, with support across different Tekton clients, including the Red Hat OpenShift Pipelines command-line interface (tkn) and the Tekton dashboard. Get ready to debug Tekton pipelines in real time.
