Tekton was originally part of the Knative project but eventually became a project of its own. It’s been around for just over a year now and is becoming the de facto standard to build continuous delivery pipelines in a Kubernetes-native fashion.
OpenShift Pipelines are built on top of Tekton and are readily available from the OperatorHub for your Red Hat OpenShift clusters. Red Hat OpenShift Container Platform 4.4 has just taken pipeline creation a step further with the Pipeline Builder. As part of the web console's Developer perspective, the Pipeline Builder makes it even easier for software developers to create their own pipelines.
Want to see how all this works? Great, let's dive in.
Steps, Tasks, Pipelines, and Resources
The goal of Tekton is to create small building blocks that are reusable, composable, and declarative, all in a cloud-native environment. It uses Steps, Tasks, Pipelines, and Resources to do this, as shown in Figure 1.

Steps
A Step is an operation performed on an input. If you are building a Node.js application, it might run some unit tests or validate that the code follows the coding standards that you have in place. Tekton will perform each step inside a container that you provide. For that Node.js application, you can run a Red Hat Universal Base Image with Node.js installed on it. Steps are the most basic unit in Tekton.
Tasks
A Task is a list of steps that are executed sequentially. Tekton runs Tasks inside a Kubernetes pod, which allows you to have a shared environment when you are designing a series of steps that are related. For example, you could mount a volume in a Task that would be shared across each step in that specific Task.
Pipelines
A Pipeline is a collection of Tasks that can be executed in parallel or sequentially. Tekton provides developers with a lot of flexibility on how and when those tasks should be executed. You could even specify conditions that a Task must meet in order to start the next one.
Resources
Most Pipelines require inputs on which to perform tasks, and can also produce outputs. In Tekton, those are known as Resources. Resources can be of many different types like Git repositories, container images, or Kubernetes clusters.
Pipeline Builder
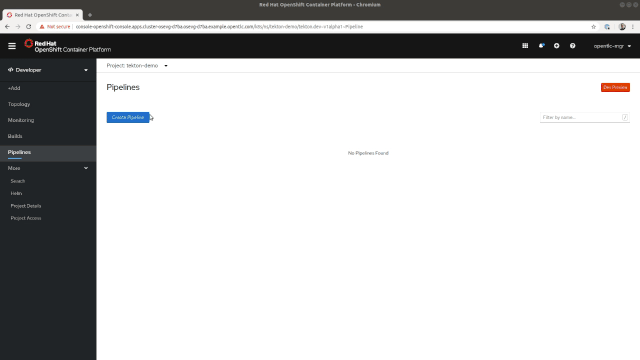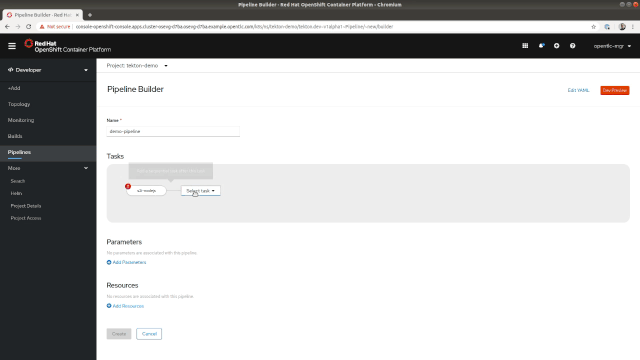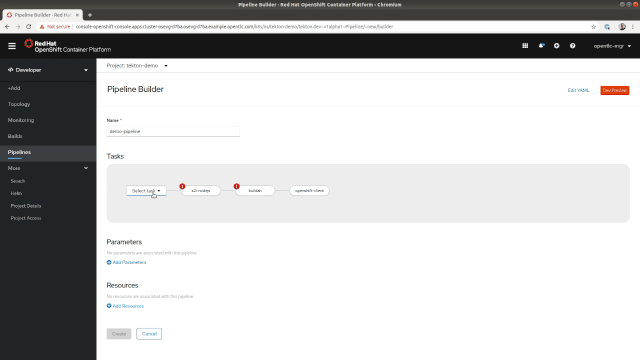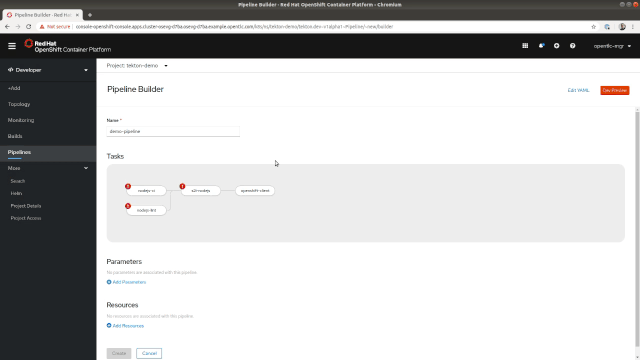
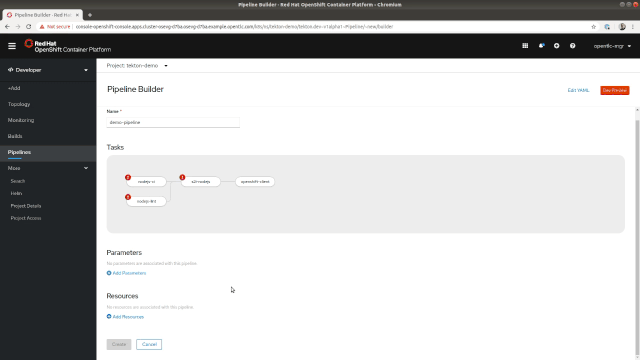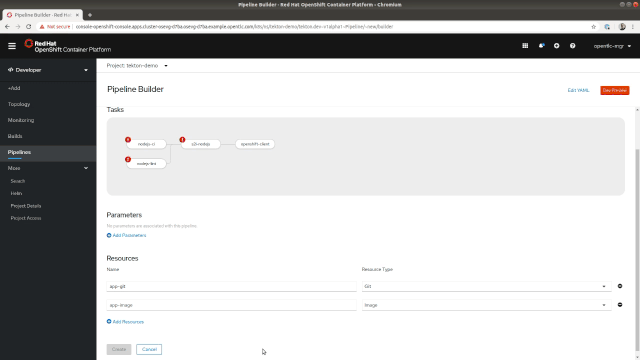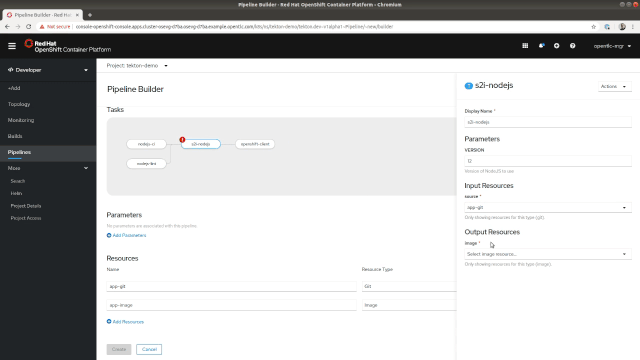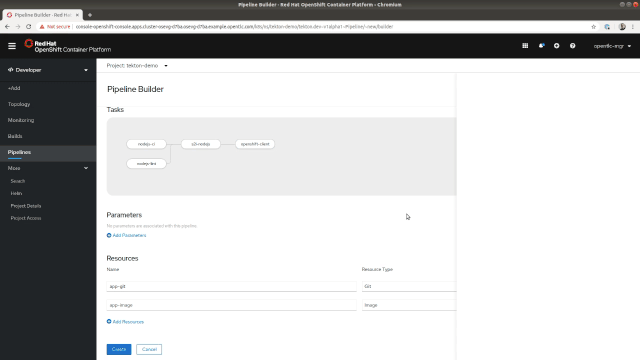
Now that we've covered some basic details of Tekton, let's dive into the Pipeline Builder, which is available on the Pipelines page in the Developer Perspective. A good interface is crucial in helping software developers easily build their own pipelines, so the Pipeline Builder's interface provides developers with a visual representation of the Pipelines that can be easily modified to suit your needs. The tasks can be arranged sequentially or in parallel as shown in Figure 2.
The side panel also makes it easy to edit the settings for each one of your tasks. From there, you can add parameters or change the associated resources that will be mapped to resources once you start the Pipeline, as shown in Figure 3.
PipelineRuns
Once Pipelines are created, the final step is to execute them. The execution of a Pipeline is called a PipelineRun. OpenShift Pipelines makes it easy to trigger those Pipelines. Find the one you want to start in the Pipelines list and select Start. A dialog will appear where you specify the resources to use with this run, which will then create the Pipeline Run and start the execution.
You will then be prompted on the resources to use with this run. This selection will create the PipelineRun and start the execution. You can then follow the status of this run either from the Pipelines dashboard or by drilling down into one Task to see the details of each Step.
Figure 4: Visualization of a PipelineRun.
This visual representation also makes it easier for developers to see where their deployments failed. In the following animation, you can see the execution of a pipeline (PipelineRun) and where it failed. It also prevented this code from being deployed in production. By looking at the output logs, software developers can easily diagnose and find what caused the pipeline to fail.
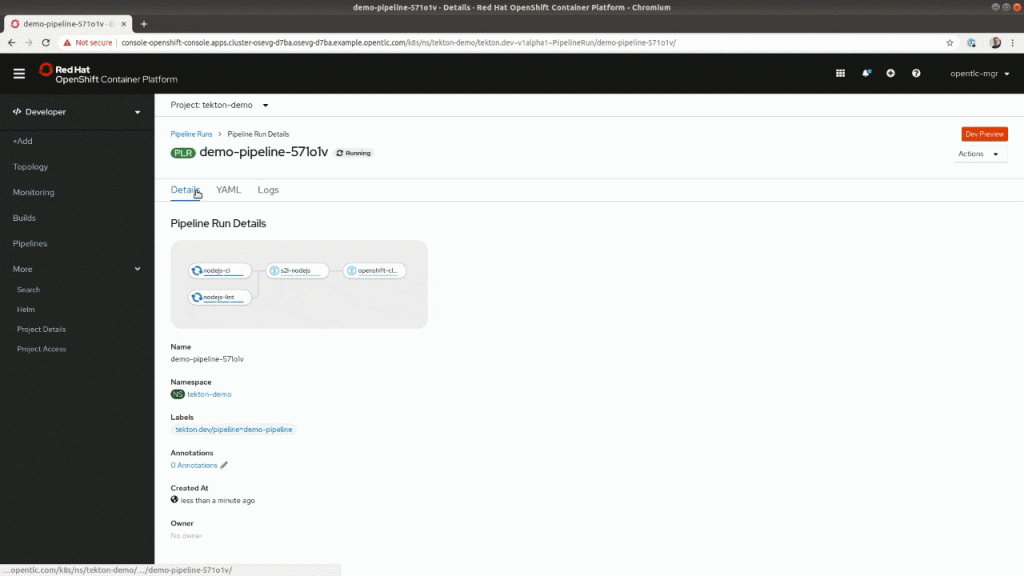
Figure 5: Accessing failure information from the PipelineRun visualization.
So, we’ve only scratched the surface of what can be accomplished with OpenShift Pipelines. We hope this new interface and the Pipeline Builder will make it much easier for software engineers to build and maintain their CI/CD deployment pipelines and let them focus on what they actually care about.
In future releases, we will continue to enhance this area. Keep an eye out for the ability to add triggers, workspace support, and much more!
Ready to get started?
Provide your feedback
Share your thoughts here and give us your feedback or ideas for improving the pipeline experience. Join our OpenShift Developer Experience Google Group to participate in discussions and learn about our Office Hours session where you can collaborate with us and provide feedback.
Learn more
Interested in learning more about application development with OpenShift? Here are some Red Hat resources that may be helpful: OpenShift Pipelines and Application development on OpenShift.
Last updated: March 30, 2023