Red Hat build of Apache Camel 4.8 is a highly adaptable, lightweight toolkit designed for enterprise integration, offering key advantages in flexibility and performance. Find out what's new in this release, which builds on its strong foundation with enhancements in contract-first API development, optimized OpenShift-based workflows, and improved developer tooling.
Apache Camel enhancements
Red Hat build of Apache Camel 4.8 introduces several enhancements and updates to the framework, including the productization of Kamelets, and making them a core part of Camel.
Red Hat refined and added support for the following components:
- Secret managers and vaults: AWS Secrets Manager (tech preview in Quarkus), Azure Key Vault (tech preview), GCP Secret Manager (tech preview in Quarkus), Hashicorp Vault
- All except Hashicorp Vault support automated secret refresh feature.
- JQ expression language, BeanIO data format, Quarkus Qute transformation templating
- GraphQL on Quarkus runs GraphQL queries and mutations over HTTP, like fetching book details
- Flink enables message routing to Flink tasks for data processing, such as sending a dataset to a Flink job for counting matching lines
- SMB natively connects to SMB file shares, like Windows or Samba, for reading and writing files
- New ElasticSearch REST Client handles indexing, searching, and managing documents in ElasticSearch 8.x or OpenSearch
- Azure EventHubs, Azure Storage Queue, Azure Storage Blob
- Spring RabbitMQ in Quarkus
- New Enterprise Integration Patterns
- setVariables: Set multiple variables simultaneously
- poll: A simpler alternative to the pollEnrich EIP
For the full list of supported components, check the reference guides in the product documentation.
Several improvements were also made to already supported components, such as:
- Azure ServiceBus was refactored to use a high-level client, improving robustness, failover, and reconnection.
- SQL now supports variables in SQL queries
- Kafka introduced JMSDeserializer for type-correct serialization/deserialization of JMS headers (e.g., long, int, string).
- Crypto was validated for use with SunPKCS11-NSS-FIPS provider, ensuring FIPS compliance
- Cluster leader election via the Master component, now supported with dedicated components: File cluster service, Kubernetes cluster service (tech preview) which were previously part of File and Kubernetes components
- Log EIP allows easier configuration of logger names with dynamic patterns
- Kubernetes Secrets can now reload Camel Context on Kubernetes Secrets updates.
The YAML DSL now supports setting Error handlers at the route's top level in addition to within route configurations. Both YAML and XML DSLs offer a consistent approach to defining beans, whether in routes or Kamelets. Developers can define beans using constructors, properties, builders, factory beans, scripts, and more. Additionally, custom beans in YAML and XML DSLs can now reference other beans through constructor parameters.
To simplify expressions, the Simple language introduces new functions: substring, replace, fromRouteId, and iif (ternary if).
Performance has been enhanced with micro-optimizations in Camel core. Matching predicates in the Simple language are now approximately 12% faster on average. Furthermore, buffer sizes used across multiple operations have been fine-tuned, reducing CPU cycles for string generation, input handling, and data processing.
The JUnit5 test module undergoes refactoring. Use of internal APIs is now restricted, and certain APIs have been deprecated. Future versions will introduce new, stable interfaces for configuring test behavior, context, and related functionalities, ensuring better maintainability and reliability.
Migration documentation simplified navigation for migrating from Red Hat Fuse, migrating from Camel 3, or upgrading to the latest versions of Camel 4 on Quarkus projects leveraging the automatic Update assistant between the 4.x versions. Testing documentation includes a step-by-step tutorial guiding developers on testing Camel applications. And a new Security Guide covers Camel route security, payload security, endpoint security, and configuration security.
Standardized Camel on OpenShift experience
Apache Camel offers limitless possibilities for diverse development practices and workflows. Through years of experience and recent engagements, we’ve accumulated expertise in crafting solutions for building and managing integrations in the cloud. To share these learnings, we’ve started documenting best practices and recommended setups for using Apache Camel on OpenShift.
Key highlights include:
- Integrating Camel with secret managers and vaults.
- Best practices for building and deploying Camel applications with OpenShift Pipelines and GitOps services.
- Accessing Kubernetes secrets and config maps within Camel applications.
- Observing Camel applications using OpenShift Observability and Red Hat's build of OpenTelemetry.
The best practice documentation will continue to evolve with further expansions planned for 2025.
We’ve introduced a new approach for quickly prototyping and deploying Camel applications on OpenShift. Explore our new tutorial on the no-cost Developer Sandbox for Red Hat OpenShift, which guides you through designing an integration service that retrieves user details in XML and transforms them into JSON: Try Apache Camel: From concept to deployment on OpenShift
This prototyping-focused workflow leverages Camel JBang and its new Kubernetes plug-in, which automate essential steps including assembling and running the application locally, building the container image, and deploying it to OpenShift. The process adheres to standard development practices, including the generation of Kubernetes manifest custom resources, which can later be exported to a standard Maven project for further development and phases into production.
Contract-first API development
The Red Hat build of Apache Camel 4.8 introduces contract-first support with OpenAPI, streamlining API-first development. By leveraging OpenAPI v3 specification files as blueprints, Camel automatically parses these contracts and maps APIs to Camel routes using the direct:operationId convention. When paired with tools like the Red Hat build of Apicurio Registry and Apicurio Studio, this creates a cohesive solution for contract-driven API design.
This release positions Camel as a cornerstone of the contract-first IDP, developer platform reference architecture, providing a set of golden paths designed to support a productive developer experience, especially for contract-driven integration scenarios. The developer platform reference manifest takes a GitOps approach for platform automation and the golden path templates are designed to streamline a contract-first development methodology.
Kaoto Integration Designer improvements
The Kaoto integration designer for Apache Camel introduces several enhancements, focusing on usability, customization, and new functionality to streamline integration workflows.
- DataMapper (tech preview) enables mapping variables and exchange body to a new XML destination format using the XSLT v2 specification, as shown in Figure 1. Future updates will expand this capability to support direct mappings between XML and JSON and will bring an upgrade to XSLT v3.
- Runtime and version selection allows users to choose their preferred runtime (Quarkus or Spring Boot) and version (4.8 or 4.4) supported by Red Hat.
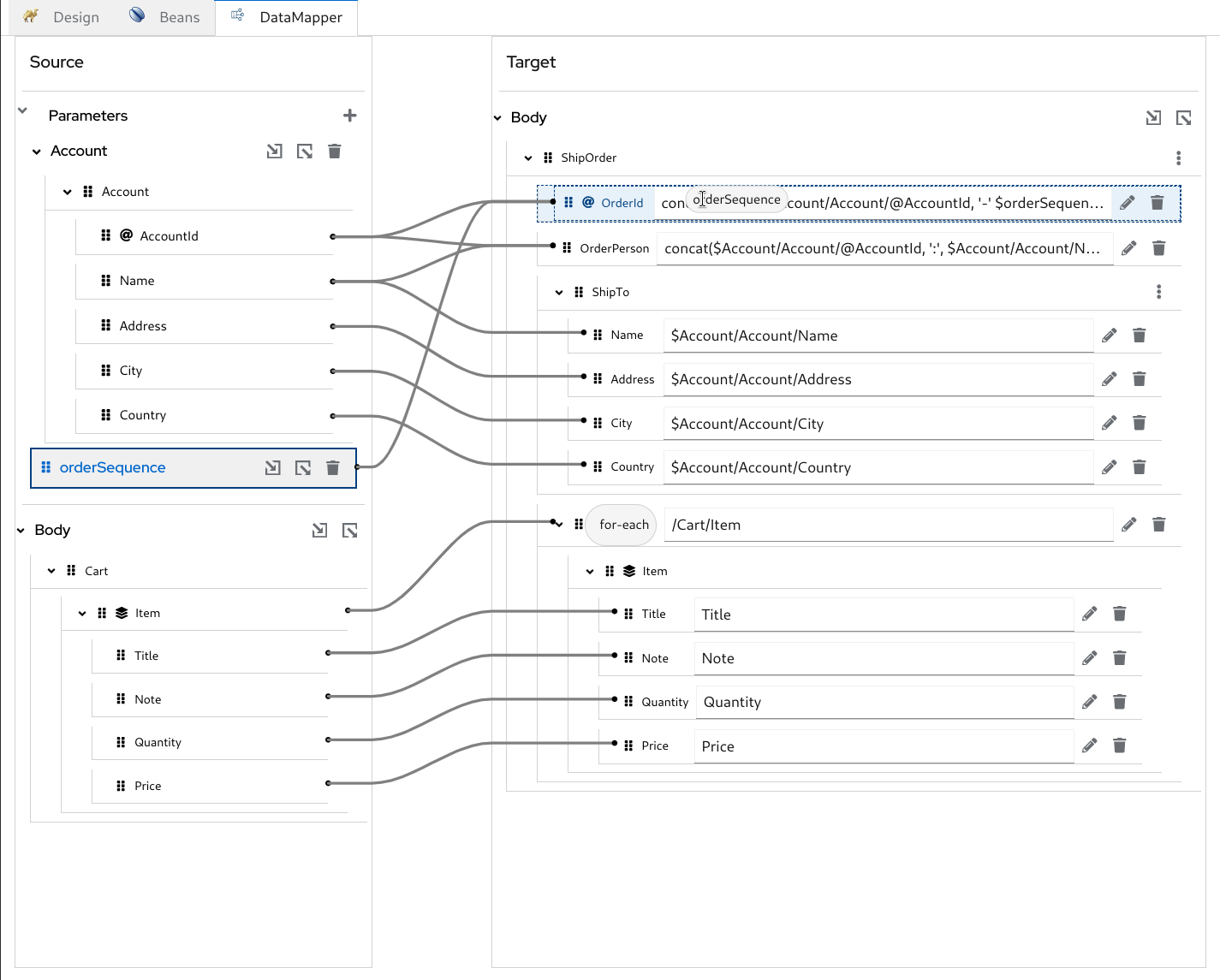
Kaoto has undergone a series of UX improvements aimed at better organization, performance, and ease of use:
- Containers for organization
- Improved step management: A new toolbar on hover/click, quick addition of next steps, warnings when replacing steps, and the ability to enable all disabled steps at once.
- Canvas interactions: Autoclose sidebar on canvas click, persistent sidebar width adjustments, and smoother navigation between nodes.
- Form and layout tweaks: Enhanced property filters and quicker value lookups, direct access to expression fields, improved multi-value selectors, and better default handling
- Catalog upgrades: Paging, improved browsing performance, faster search
These updates solidify Kaoto as a powerful and user-friendly integration designer for Apache Camel, catering to diverse developer needs while enabling faster and more efficient integration design.
Rapid In-depth insights and tracing
Camel now provides more detailed service and protocol insights in traces, particularly for components that connect to remote systems. For instance, when connecting to databases or messaging systems, configurations like database drivers, connection pools, and similar elements are often managed outside of Camel. This has historically limited Camel’s ability to display the actual host:port used for connections.
To address this, Camel now detects these scenarios and attempts to retrieve such details for a variety of known connection pools, database drivers, and cloud providers, enhancing visibility and traceability.
Run camel trace --action=start to quickly start tracing.
Camel JBang CLI introduces new commands for accessing in-depth information, as described in Table 1.
Command | Description |
| Shows your custom beans with their configuration versus runtime properties to ensure they are configured correctly |
| Shows all REST endpoint and operations hosted in Camel integrations |
| Browse messages on external systems such as JMS brokers and FTP servers |
| Shows Kafka topic information such as committed offset |
It is now possible to configure logging levels for specific package names directly in the application properties, such as:
logging.level.org.apache.kafka = DEBUGAdditional tooling improvements
Taking inspiration from the Quarkus Maven plugin's automated minor version updates, the Red Hat build of Apache Camel 4.8 introduces the 4.x Update Assistant, extending this capability to Camel applications on both Quarkus and Spring Boot. Built on OpenRewrite, it provides assisted upgrades between 4.x versions, such as transitioning from 4.0 to 4.8, automating tasks like renaming classes, updating method signatures, and adapting to new Camel API changes.
HawtIO has received performance optimizations to handle a large number of MBeans efficiently. The Discovery plugin now includes paging to manage the loading of multiple pods, ensuring smooth operation even at scale. Additionally, HawtIO Online is now certified and supported on OpenShift for ppc64le (IBM Power) and s390x (IBM Z) architectures.
The Camel JBang CLI has been enhanced to allow developers to select their preferred runtime, Quarkus or Spring Boot, directly during execution:
$ camel run route.camel.yaml --runtime=quarkus$ camel run route.camel.yaml --runtime=spring-bootFor demonstrations and lightweight applications, Camel JBang now supports bundling small web apps. By including .html, .js, and .css files alongside the Camel source code, you can run the entire setup with a single command:
$ camel run *Enterprise Integration Explorer (beta)
Enterprise Integration Explorer, shown in Figure 2, is a curated catalog of integration patterns and components with links to examples. It highlights the latest supported components, suggests alternatives for deprecated ones, and offers quick access to official documentation and community resources. Note: Data format and miscellaneous components are not yet included.
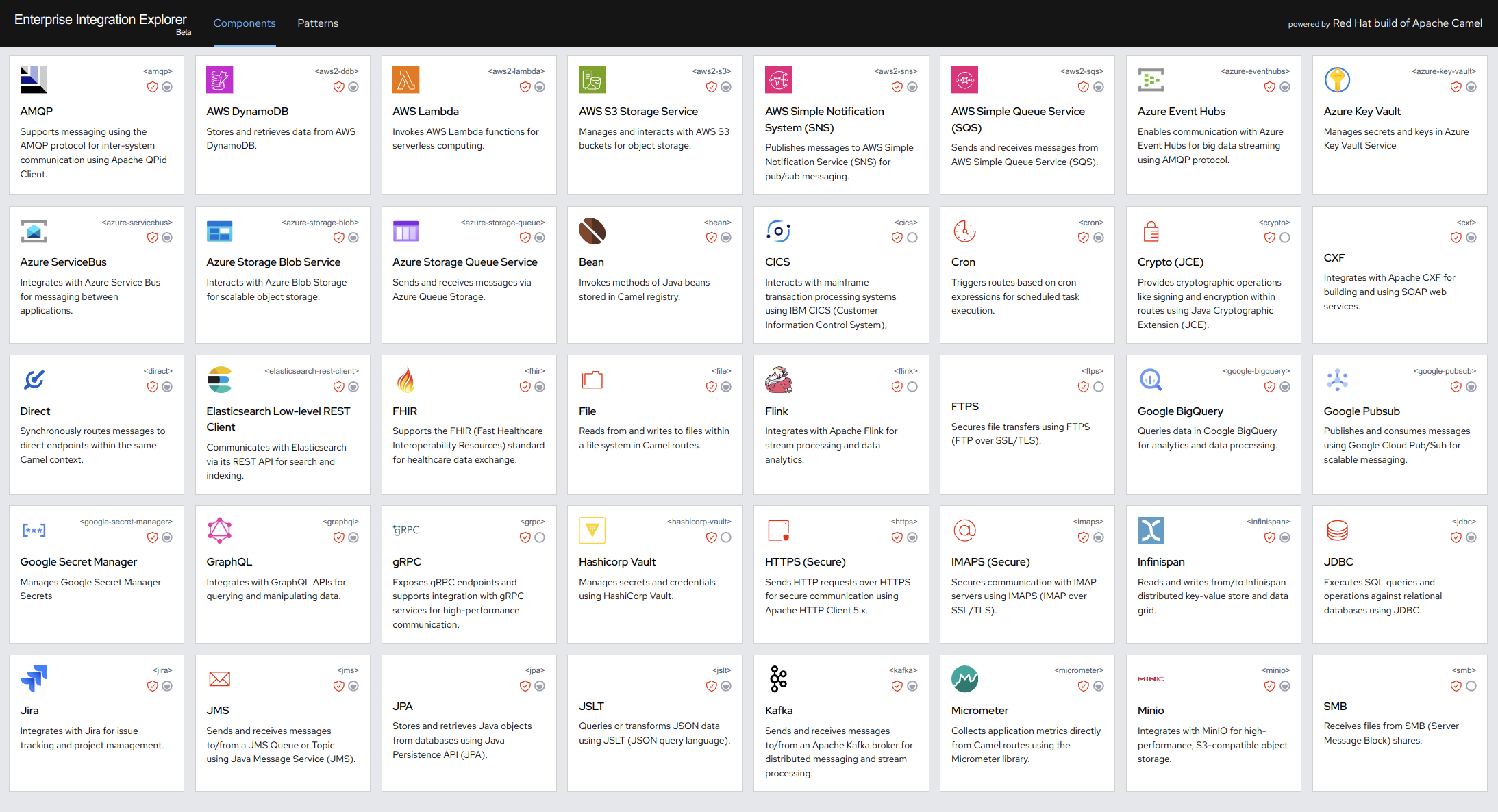
You can also share quick links to specific groups or custom lists of components/patterns via URL, such as:
- Red Hat-supported components
- AI/ML components
- Components used in the article Tutorial: Tool up your LLM with Apache Camel on OpenShift
- Routing patterns
Researching integrations in generative AI and ML applications
We added new components and capabilities for studying and experimenting with AI and machine learning integrations. These additions are part of an ongoing effort to explore and understand the potential of emerging AI technologies within the Camel ecosystem.
New Camel AI community components:
- AWS Bedrock simplifies experimentation with deploying foundation models.
- LangChain facilitates advanced generative artificial intelligence (gen AI) workflows, including chat, embeddings, tools, tokenization, and web search capabilities.
- Milvus, Qdrant, and Pinecone add integration with vector databases, embeddings and similarity-based search mechanisms
Try them out in our new tutorials and solution pattern:
- Tool up your LLM with Apache Camel on OpenShift
- Try OpenShift AI and integrate with Apache Camel
- Solution Pattern: Edge to Core Data Pipelines for AI/ML
The DJL component has been extended to cover a wider range of machine learning use cases, providing tools for researchers to explore capabilities in Computer Vision (CV), Natural Language Processing (NLP), Audio Processing and Time-Series Forecasting.
Next step
Resources
- What’s new in Apache Camel 4.8 (community)
- What’s new in Apache Camel 4.7 (community)
- What’s new in Apache Camel 4.6 (community)
- What’s new in Apache Camel 4.5 (community)
