
Build a bootable .NET 10 application using image mode for RHEL with Podman Desktop
Use Podman Desktop to create a bootable .NET 10-based application using image

Use Podman Desktop to create a bootable .NET 10-based application using image

Learn how to build reproducible, container-native OS images on IBM Power Systems using bootc, from environment setup to capturing and exporting the image.

Kafka is a powerful event streaming platform. In this learning path, you will

Explore the latest features, updates, and fixes in Red Hat OpenShift 4.20, including multicluster support, observability, and developer experience enhancements.

Use Podman Desktop to create a bootable Flask-based application using image mode
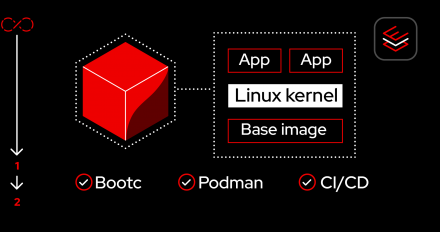
Learn how to locally build and run a bootable container (bootc) image in Podman

Learn about the deprecation of the odo CLI and how to transition to OpenShift Dev Spaces and other tools for your cloud-native development workflow.

Use Podman Desktop to create a bootable Django-based application using image

Discover how llama.cpp API remoting brings AI inference to native speed on macOS, closing the gap between API remoting and native performance.

Discover how Camel JBang's infra command simplifies local development by launching real back ends like Kafka and Artemis, eliminating complex mock setups.

Learn how to install Offline Knowledge Portal on a local system.

Enterprise-grade artificial intelligence and machine learning (AI/ML) for
This beginner's guide to Podman AI Lab walks through setting up Podman Desktop, installing the AI Lab extension, and launching your first RAG chatbot.

Discover the new features and tools in RHEL 10.

Learn how RamaLama's integration with libkrun and microVMs enhances AI model isolation, security, and resource efficiency for deployments.

The RHEL VMs extension for Podman Desktop streamlines RHEL access for Windows and Mac, bringing intuitive VM creation, management, and terminal integration.

Dive into the world of containers and Kubernetes with Podman Desktop, an open-source tool to empower your container development workflow, and seamlessly deploy applications to local and remote Kubernetes environments. For developers, operations, and those looking to simplify building and deploying containers, Podman Desktop provides an intuitive interface compatible with container engines such as Podman, Docker, Lima, and more.

Learn about the Podman AI Lab and how you can start using it today for testing and building AI-enabled applications. As an extension for Podman Desktop, the container & cloud-native tool for application developers and administrators, the AI Lab is your one-stop-shop for popular generative AI use cases like summarizers, chatbots, and RAG applications. In addition, from the model catalog, you can easily download and start AI models as local services on your machine. We'll cover this and more, and be sure to try out the Podman AI Lab today!

Podman enables developers to run Linux containers on MacOS within virtual machines, including GPU acceleration for improved AI inference performance.

Learn how Podman AI Lab and RamaLama work together to simplify local AI model execution, using containers and GPU support for faster, easier AI development.

Learn how to consolidate your workflow with the help of dev containers and Podman, enabling a seamless workflow across multiple interdependent components.

Use containers locally to simulate network latency with a distributed database cluster. Test architectures and identify issues before they occur in production.

Learn how to run RHEL 10 on Windows as a Windows Subsystem for Linux distribution using Red Hat Enterprise Linux image builder.

MINC is a new Podman Desktop extension that eases local Kubernetes development, offering a streamlined local Kubernetes experience powered by MicroShift.

Discover how you can use the Podman AI Lab extension for Podman Desktop to work