Red Hat OpenShift Serverless recently became GA, and with it came new options for application deployment. This article introduces one of those new options, Knative Serving. I provide an overview of OpenShift Serverless and Knative Serving, then show you how to deploy a Node.js application as a Knative Serving service.
What is OpenShift Serverless?
According to the OpenShift Serverless GA release:
OpenShift Serverless enables developers to build what they want, when they want, with whatever tools and languages they need. Developers can quickly get their applications up and deployed using serverless compute, and they won't have to build and maintain larger container images to do so.
OpenShift Serverless is based on the Knative open source Kubernetes serverless project. While it has a few different parts, we will focus on deploying a serverless Node.js application as a Knative Serving service.
Knative Serving
So, what is Knative Serving? The official OpenShift documentation has a buzzword-filled section about it, but we are most interested in the ability to scale to zero.
Applications running on OpenShift and Kubernetes run inside a container or pod. An OpenShift pod needs to be up if we want users to be able to access our application. A containerized application deployed as a Knative Serving service can be off until a request comes in—that is what we mean by "scale to zero." When a request comes in, the application starts and begins receiving requests. Knative orchestrates all of this.
Getting started with Knative Serving
If you want to follow along with the example, you will need to have OpenShift Serverless installed on your OpenShift cluster. The OpenShift Serverless documentation has instructions for setting up OpenShift Serverless, and for setting up Knative Serving.
For local development, I use Red Hat CodeReady Containers (CRC) to run OpenShift locally. Note that CRC with OpenShift Serverless installed can be a little memory intensive.
Deploying the Node.js application
The example in the OpenShift documentation shows how to use a Git repository, hosted on GitHub, to deploy an application as a Knative Serving service. That's fine, but if I'm in development and coding on my laptop, I don't want to have to push my changes to GitHub just to see my application running.
Another option is to use an already built image to create a Knative Serving service. The YAML for that service might look something like this:
apiVersion: serving.knative.dev/v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: hello
namespace: default
spec:
template:
spec:
containers:
- image: docker.io/openshift/hello-openshift
env:
- name: RESPONSE
value: "Hello Serverless!"
But again, this example shows an image being hosted on Docker Hub, which brings up the same predicament as deploying from GitHub.
For local development, I prefer using the Nodeshift module. I've introduced Nodeshift elsewhere, so I won't write much about it here.
The Node.js example application
For this example, I'll use an application that I've used before, a basic REST application that is built with Express.js. As a refresher, the Express.js application has an input form that takes a name and sends it to a REST endpoint, which generates a greeting. When you pass in a name, it is appended to the greeting and sent back. To see the application running locally, enter the following command:
$ npm install && npm start
To deploy the Node.js application as a Knative service, we only have to call Nodeshift with the experimental --knative flag. The command would look something like this:
$ npx nodeshift --knative
This command archives our source code and sends it to OpenShift, where a Source-to-Image (S2I) build results in an ImageStream. This is all standard Nodeshift stuff. Once the build has completed, Nodeshift creates a Knative service, which uses the ImageStream we've just built as its input. This procedure is similar to pulling an image from Docker Hub, but in this case, the image is stored in OpenShift's internal registry.
Run the application
We could use oc commands to see that our application is running, but it's easier to understand what is happening with something more visual. Let's use the OpenShift web console's new Topology view, as shown in Figure 1.
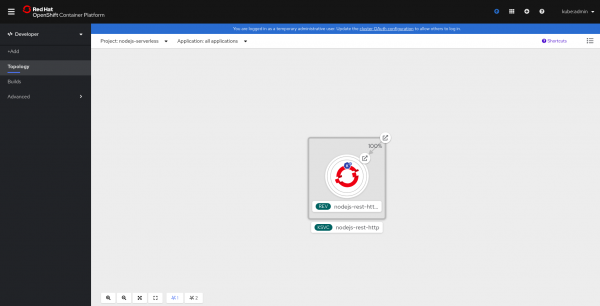
The application is deployed as a Knative service. Most likely, the blue circle (which indicates that a pod is running successfully) is not filled. Our app is currently scaled to zero and waiting for a request to come in before it starts up.
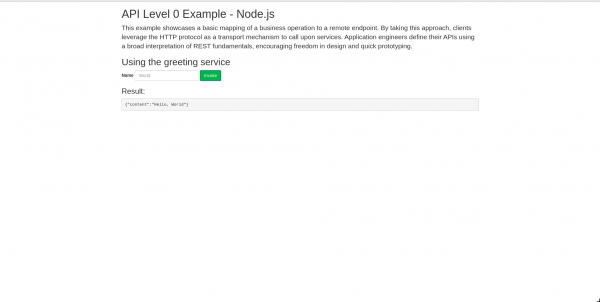
Clicking on the link icon in the top-right corner of the application opens it. This is the first time that we are accessing the app, so it takes a few seconds to load. Our application is now starting up. It's a basic Express.js application, so it starts quickly, as you can see in Figure 2.
The application in the Topology view now has that familiar blue circle, as shown in Figure 3.
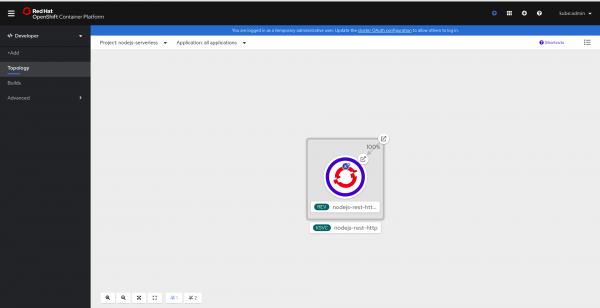
By default, after 300 seconds (5 minutes), the running pod terminates and scales back to zero. The next time that you access the application, the startup cycle will happen again.
Conclusion
In this article, I've shown you a small part of what OpenShift Serverless can do. In future articles, we'll look at more features and how they relate to Node.js. This article focused on deploying a Node.js app as a Knative Serving service, but you might have noticed that Knative and OpenShift Serverless don't care what type of application you use. In a future article, I'll discuss the things that you should consider when creating a Node.js application to be deployed as a serverless application.
Last updated: September 14, 2020