Tekton is an open source project that provides standard Kubernetes-style resources and building blocks for creating CI/CD pipelines that can run on any Kubernetes. Tekton does this by introducing a number of custom resource definitions (CRD) such as Pipeline, Task, and ClusterTask to provide a language and structure for defining delivery pipelines as shown in Figure 1. Tekton also provides a set of controllers that are responsible for running pipelines in pods on demand whenever a user creates an aforementioned resource.

Figure 1: A Tekton pipeline contains a sequence of tasks.">
The use of Tekton has grown rapidly over the last year. One of the frequently requested features is the ability to share artifacts between tasks in order to cache dependencies for build tools such as Maven and NPM. Although it was possible previously to use volumes in tasks, the release of Tekton 0.10 adds support for workspaces, which makes it easier for tasks within a pipeline to share artifacts using a persistent volume.
In this article, we look at how workspaces can be used to cache Maven dependencies in Java builds in order to remove the need to download dependencies for each build.
Tekton workspaces
Workspaces in Tekton Pipelines refers to a declaration of shared volumes that a pipeline needs at runtime. They are similar to volumes except that one doesn’t provide the actual volume and only declares the intent. In a pipeline definition, a workspace can then be passed to relevant tasks as a shared volume. The result is that when the same workspace is provided to a number of tasks, they all can read and write from the exact same volume and share files and artifacts as required.
It’s worth mentioning that although a volume refers to a persistent volume for caching Maven dependencies, it can also be a ConfigMap, or a secret that is passed to a pipeline run to be mounted and shared between the tasks.
Let’s see how workspaces can be used in practice to cache Maven dependencies.
Maven task with a workspace
In order to build Maven projects in a pipeline, a Maven task should be defined. The Tekton catalog already contains a Maven task. However, we need a modified version of this task to declare a workspace for Maven's dependencies:
apiVersion: tekton.dev/v1alpha1
kind: Task
metadata:
name: mvn
spec:
workspaces:
- name: maven-repo
inputs:
params:
- name: GOALS
description: The Maven goals to run
type: array
default: ["package"]
resources:
- name: source
type: git
steps:
- name: mvn
image: gcr.io/cloud-builders/mvn
workingDir: /workspace/source
command: ["/usr/bin/mvn"]
args:
- -Dmaven.repo.local=$(workspaces.maven-repo.path)
- "$(inputs.params.GOALS)"
This task is mostly similar to the one in the Tekton catalog, with the difference being that a workspace called maven-repo is defined. This workspace states that whenever this task is to run, a volume should be provided and mounted to act as the local Maven repository. The path to this workspace is then passed to the Maven command in order to be used as the local Maven repository with -Dmaven.repo.local=$(workspaces.maven-repo.path).
The path where the workspace should be mounted can be configured; however, in this example, the default mount path is adequate.
Build a pipeline with a workspace
Now, let’s define a pipeline that uses the Maven task to build a Java application. In order to demonstrate the caching effect for Maven dependencies, the following pipeline (shown in Figure 2) runs three Maven tasks to perform the build, integrate the tasks, and generate a report for the test results, code coverage, etc.
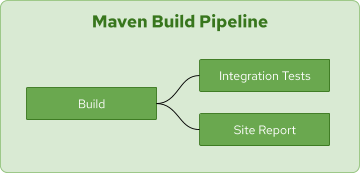
Figure 2: An example Tekton Maven build pipeline.">
The pipeline definition that represents the pipeline in Figure 2 is:
apiVersion: tekton.dev/v1alpha1
kind: Pipeline
metadata:
name: maven-build
spec:
workspaces:
- name: local-maven-repo
resources:
- name: app-git
type: git
tasks:
- name: build
taskRef:
name: mvn
resources:
inputs:
- name: source
resource: app-git
params:
- name: GOALS
value: ["package"]
workspaces:
- name: maven-repo
workspace: local-maven-repo
- name: int-test
taskRef:
name: mvn
runAfter: ["build"]
resources:
inputs:
- name: source
resource: app-git
params:
- name: GOALS
value: ["verify"]
workspaces:
- name: maven-repo
workspace: local-maven-repo
- name: gen-report
taskRef:
name: mvn
runAfter: ["build"]
resources:
inputs:
- name: source
resource: app-git
params:
- name: GOALS
value: ["site"]
workspaces:
- name: maven-repo
workspace: local-maven-repo
Notice the declaration of the pipeline's local-maven-repo workspace. It states that when this pipeline is to run, a volume should be provided and used as this workspace. This workspace is then provided to each of the tasks in this pipeline so that they all share the same workspace.
Run a Maven pipeline
The pipeline now can be run to build a Java application such as the Spring PetClinic sample application. Before starting the pipeline, a PersistentVolumeClaim (PVC) is needed for providing a workspace to cache the Maven dependencies:
apiVersion: v1
kind: PersistentVolumeClaim
metadata:
name: maven-repo-pvc
spec:
resources:
requests:
storage: 5Gi
volumeMode: Filesystem
accessModes:
- ReadWriteOnce
persistentVolumeReclaimPolicy: Retain
Now you can create a pipeline run that uses the above PVC as the pipeline's workspace:
apiVersion: tekton.dev/v1alpha1
kind: PipelineRun
metadata:
generateName: petclinic-run-
spec:
pipelineRef:
name: maven-build
resources:
- name: app-git
resourceSpec:
type: git
params:
- name: url
value: https://github.com/spring-projects/spring-petclinic
workspaces:
- name: local-maven-repo
persistentVolumeClaim:
claimName: maven-repo-pvc
Notice the mapping between the maven-repo-pvc PVC and the workspace that is declared for caching maven dependencies. As a result, this PVC is passed to the pipeline and to the respective tasks as the shared volume for caching files and artifacts.
Since it’s the first time this Maven goal runs, the pipeline run will take time to download dependencies and finish the execution:
$ tkn pr list NAME STARTED DURATION STATUS petclinic-run-6l5w7 16 minutes ago 9 minutes Succeeded
You can see here that the pipeline run took about nine minutes to complete in my environment. You can also get a breakdown of how long the execution of each task took (also see Figure 3):
$ tkn pr describe petclinic-run-6l5w7 ... Taskruns NAME TASK NAME STARTED DURATION STATUS ∙ petclinic-run-6l5w7-gen-report-s6mhf gen-report 16 minutes ago 4 minutes Succeeded ∙ petclinic-run-6l5w7-int-test-8tbkn int-test 16 minutes ago 2 minutes Succeeded ∙ petclinic-run-6l5w7-build-4gg4l build 21 minutes ago 4 minutes Succeeded

Figure 3: Viewing your pipeline run results in Red Hat OpenShift Container Platform.">
Re-run the pipeline once more by applying (through kubectl create) the pipelinerun YAML once more and observe the execution time:
$ tkn pr list NAME STARTED DURATION STATUS petclinic-run-qb64z 7 minutes ago 4 minutes Succeeded petclinic-run-6l5w7 40 minutes ago 9 minutes Succeeded
Notice the significant reduction in the execution time to about four minutes in my environment. The breakdown of task execution time can show the effect more accurately:
$ tkn pr describe petclinic-run-qb64z ... Taskruns NAME TASK NAME STARTED DURATION STATUS ∙ petclinic-run-qb64z-int-test-ppwgc int-test 4 minutes ago 2 minutes Succeeded ∙ petclinic-run-qb64z-gen-report-mhhmj gen-report 4 minutes ago 2 minutes Succeeded ∙ petclinic-run-qb64z-build-ck7cp build 5 minutes ago 1 minute Succeeded
The test task run wasn't affected much because it uses most of the same dependencies that were downloaded in the build task run even in the first pipeline run, as you can see in Figures 4 and 5.

Figure 4: Comparing the pipeline details for the two runs.">

Figure 5: Viewing the pipeline run overview.">
Conclusion
Workspace support in Tekton 0.10 simplifies sharing files and artifacts between tasks in a pipeline, such as passing a JAR file from one task to another, or caching build dependencies as demonstrated in this article. Nevertheless, that’s just the beginning of what Tekton can do, and the Tekton community is developing improvements for the workspace user experience by bringing support to TektonCD CLI.
Try it out
All files used in this article are available in the following GitHub repository:
https://github.com/siamaksade/tekton-pipelines-maven-demo. To use them, download and install CodeReady Containers and TektonCD CLI on your workstation, and then install the OpenShift Pipelines Operator from the canary operator channel to enable Tekton Pipelines 0.10 on the platform.
Thereafter, run the following commands to create the pipeline:
$ oc create -f pvc.yaml $ oc create -f maven-task.yaml $ oc create -f maven-pipeline.yaml $ oc create -f maven-pipelinerun.yamlLast updated: October 31, 2023
