The Eclipse Che 7.6.0 release provides a new stack for Apache Camel K integration development. This release is the first iteration to give a preview of what is possible. If you like what you see, shout it out, and more will surely come.
This article details how to test this release on a local instance deployed on minikube. The difference with a hosted instance is that we avoid the prerequisites involving Camel K installation in the cluster and specific rights for the user.
Set up the Che instance
A container host needs to be available. For instance, you can use minikube. Che requires a large amount of memory, so you need to increase what is allocated by default. For instance:
$ minikube start --memory=4096
This command provides output like this:
? minikube v1.3.1 on Fedora 31 ? Creating virtualbox VM (CPUs=4, Memory=4096MB, Disk=50000MB) ... ? Preparing Kubernetes v1.15.2 on Docker 18.09.8 ... ? Pulling images ... ? Launching Kubernetes ... ⌛ Waiting for: apiserver proxy etcd scheduler controller dns ? Done! kubectl is now configured to use "minikube"
See the official Che 7 documentation for more details. Then, download chectl from GitHub releases. You will be able to install Che on your minikube instance with the following command:
$ chectl server:start --platform minikube
This command provides output like this:
✔ Verify Kubernetes API...OK ✔ ? Looking for an already existing Che instance ✔ Verify if Che is deployed into namespace "che"...it is not ✔ ✈️ Minikube preflight checklist ✔ Verify if kubectl is installed ✔ Verify if minikube is installed ✔ Verify if minikube is running ↓ Start minikube [skipped] → Minikube is already running. ✔ Verify if minikube ingress addon is enabled ↓ Enable minikube ingress addon [skipped] → Ingress addon is already enabled. ✔ Retrieving minikube IP and domain for ingress URLs...192.168.99.123.nip.io. ❯ ? Running Helm to install Che ✔ Verify if helm is installed ✔ Check Helm Version: Found v3.0.0+ge29ce2a ✔ Create Namespace (che)...done. ✔ ? Running Helm to install Che ✔ Verify if helm is installed ✔ Check Helm Version: Found v3.0.0+ge29ce2a ✔ Create Namespace (che)...done. ✔ Check Cluster Role Binding...does not exists. ✔ Preparing Che Helm Chart...done. ✔ Updating Helm Chart dependencies...done. ✔ Deploying Che Helm Chart...done. ✔ ✅ Post installation checklist ✔ Devfile registry pod bootstrap ✔ scheduling...done. ✔ downloading images...done. ✔ starting...done. ✔ Plugin registry pod bootstrap ✔ scheduling...done. ✔ downloading images...done. ✔ starting...done. ✔ Che pod bootstrap ✔ scheduling...done. ✔ downloading images...done. ✔ starting...done. ✔ Retrieving Che Server URL...http://che-che.192.168.99.123.nip.io ✔ Che status check Command server:start has completed successfully.
For more details and options, see the official Che 7 documentation.
Create and configure a Camel K-ready workspace
To create and configure your Camel K-ready workspace, you first need to create a workspace from the Camel K stack. At the end of the previous command's log, the URL to access the Che instance is provided after "Retrieving Che Server URL..."
Open this URL in a browser. Select the Apache Camel K stack and then click the Create & Open button, which opens the page shown in Figure 1:

Wait for the workspace to be ready. This process can take several minutes, depending on your internet connection's speed.
Next, you need to inject the kubeconfig login context into the Che workspace. For that, you can return to your host and call:
$ chectl workspace:inject -k
Ensure that the injection for vscode-camelkXXX is a success. This command provides output like this:
✔ Verify if namespace che exists ✔ Verify if the workspaces is running ✔ Injecting configurations ↓ injecting kubeconfig into container che-machine-execcc7 [skipped] → the container doesn't support file injection ↓ injecting kubeconfig into container theia-idenue [skipped] → kubeconfig already exists in the target container ✔ injecting kubeconfig into container vscode-xmlcem...done. ↓ injecting kubeconfig into container vscode-apache-camelt7t [skipped] → kubeconfig already exists in the target container ✔ injecting kubeconfig into container vscode-camelkrbj...done.
Now, install Camel K. In the right column, click My Workspace to expand the panel. Then, expand the Plugins -> vscode-camelkXXX tree. Click New terminal, then type:
$ kamel install
The result is shown in Figure 2:

Deploy and automatically redeploy a Camel K integration
The official Camel K examples are populated by default. You can open, for instance, hello.xml. Notice that the integration simply logs "Hello World!!!" every three seconds.
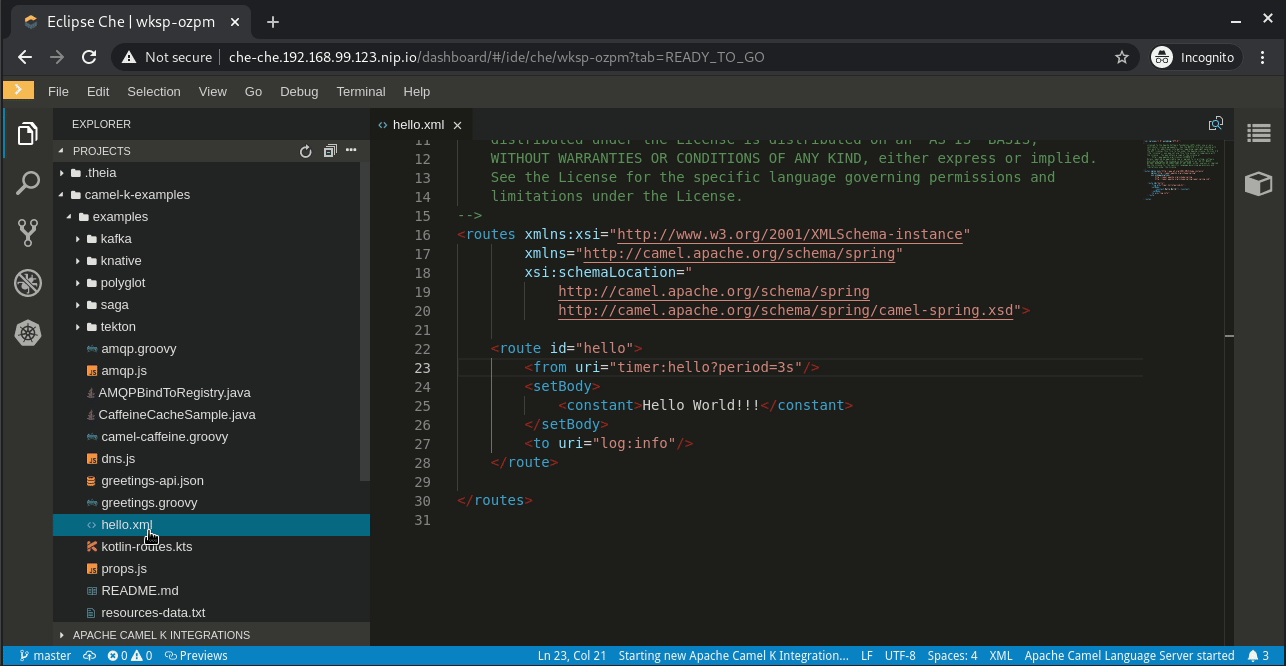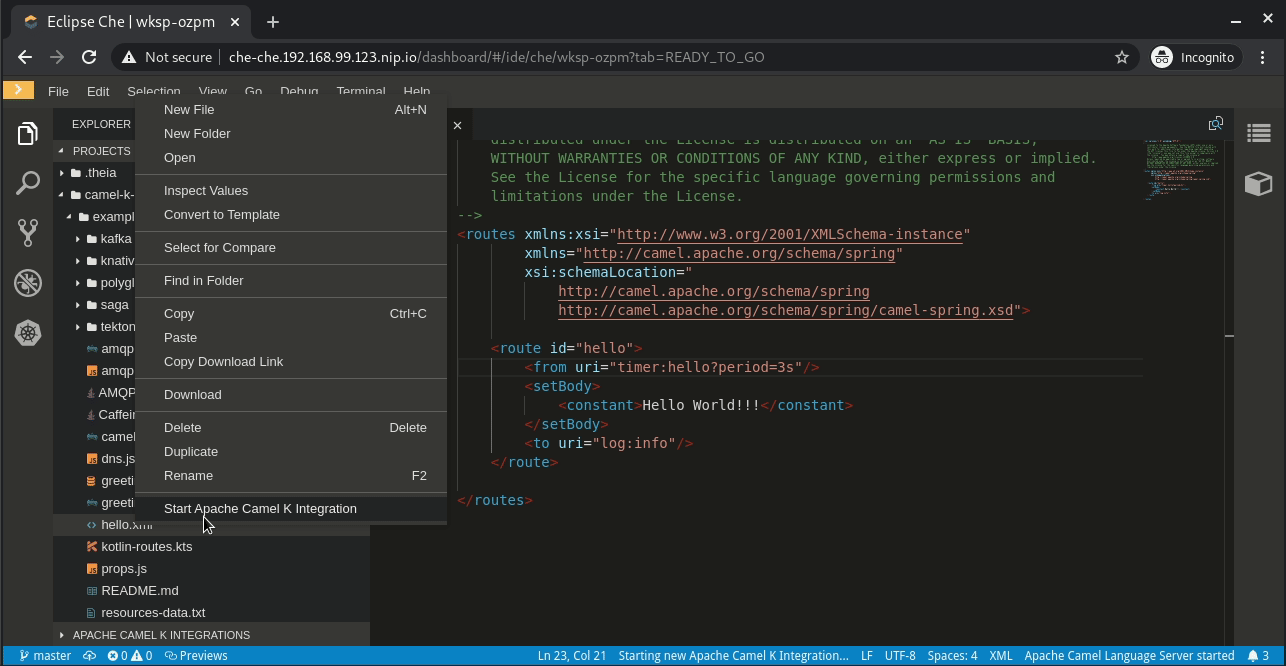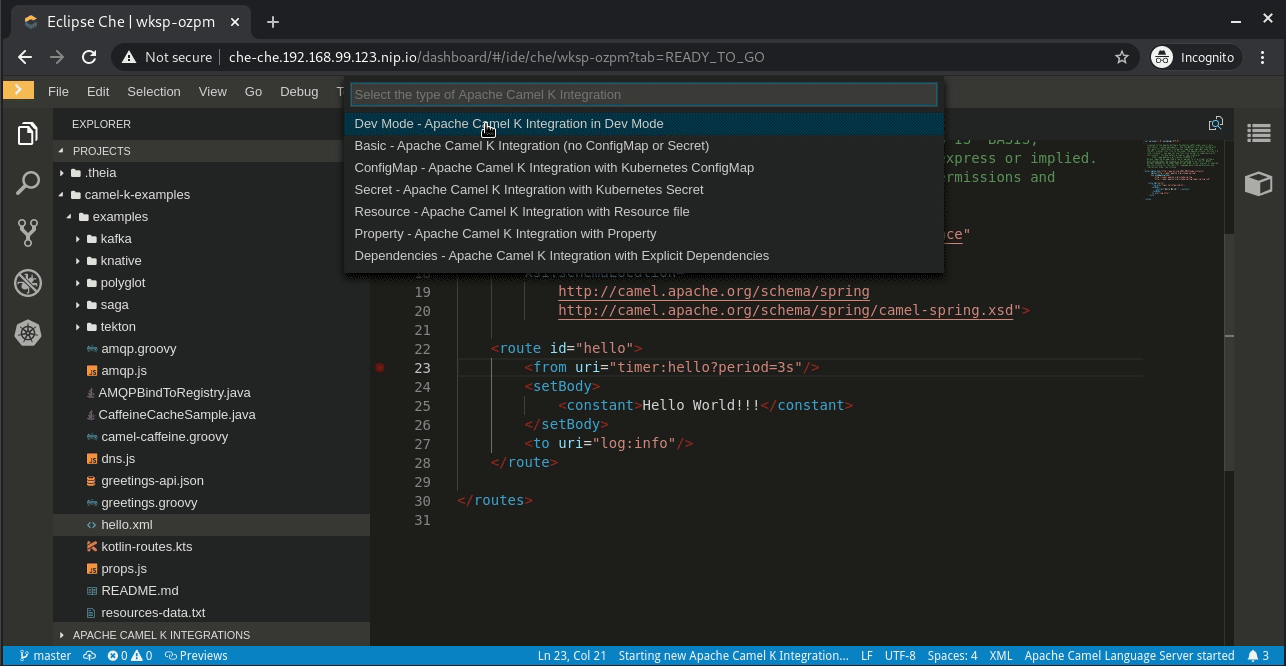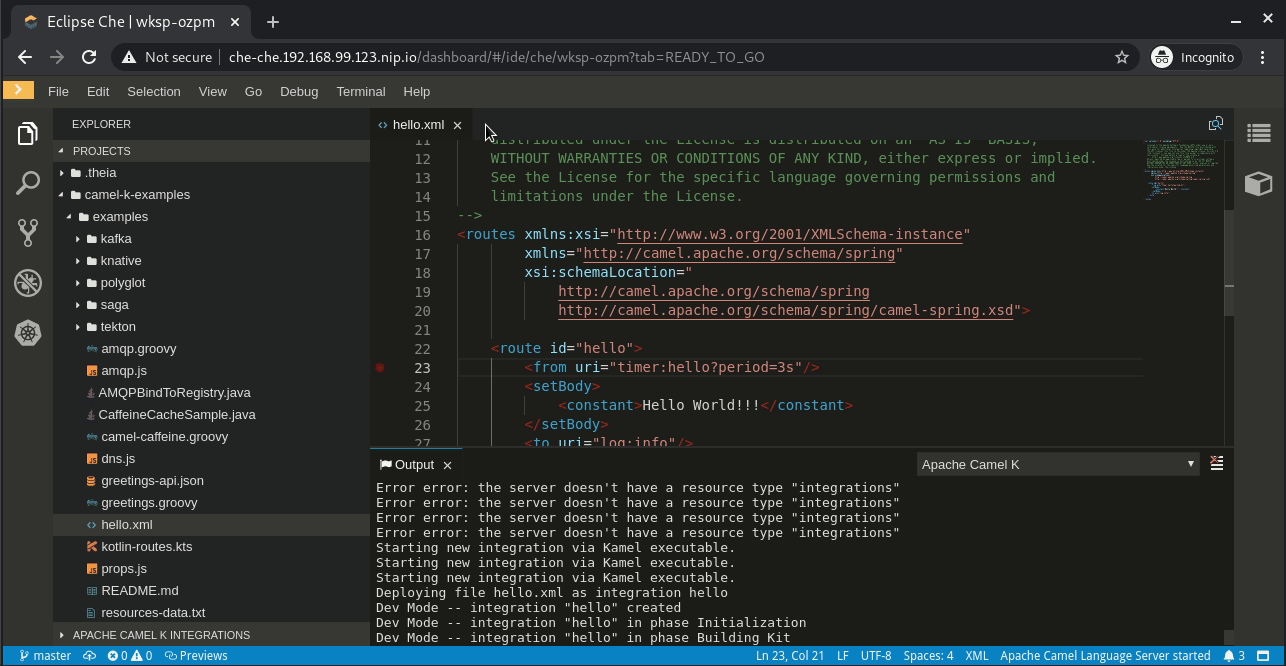
Right-click on this example in the Projects panel. Select Start Apache Camel K integration and then Dev mode - Apache Camel integration in Dev mode, as shown in Figure 3:
Wait several seconds (or minutes) for the first deployment. Again, how long this takes depends on your internet connection's speed.
When ready, go to the Output panel. Select Apache Camel K output, which should display "Hello World!!!" logged every three seconds, as shown in Figure 4:

Modify the hello.xml file's content. For instance, you might change the constant to "Hello World from Che!!!" The integration is automatically redeployed in a few milliseconds, as you can see in Figure 5:

Because the Che workspace reuses the VS Code extension, you can use all of the Tooling for Apache Camel K VS Code extension's features. See our previous article on how to create an integration sending a Telegram to take this example further.
Known limitations
There are two major known limitations. The login for the Camel K instance needs to be redone on each workspace startup, and on a remote cluster, special rights need to be given so you can install and access the Camel K instance.
Last updated: June 29, 2020