With the rise of generative AI, many enterprises are exploring how to bring large language models (LLMs) into secure, internal cloud-native environments. When used with KServe, vLLM, and GPU support, platforms like Red Hat OpenShift AI provide a robust approach to serving models efficiently at scale.
In this blog, I’ll walk you through a complete internal deployment workflow of the DialoGPT-small language model on OpenShift AI using Red Hat Inference Server—all without exposing any external endpoints. You’ll learn how to set up your environment, configure ServingRuntime, manage model storage with persistent volume claims (PVCs), and deploy an inference service ready for testing. The flow is illustrated in Figure 1.
Warning
This workflow is designed for internal testing and evaluation purposes only; it is not intended for production use. For production environments, follow the official product documentation and use supported configuration methods provided by Red Hat.
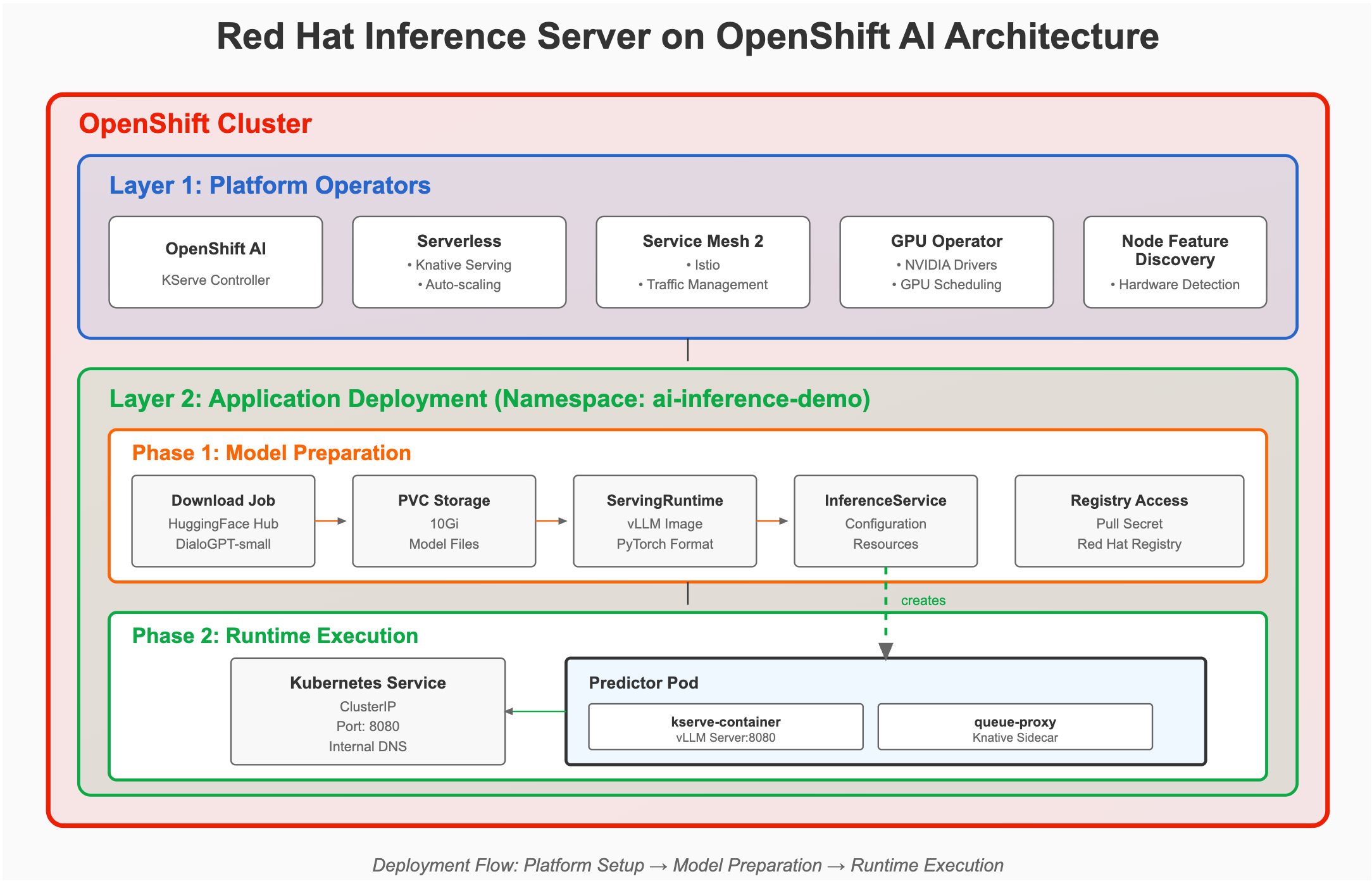
Environment verification
Ensure the following components are ready:
- KServe controller running normally
- All Knative Serving components running normally
- Istio system components running normally
DataScienceClusterstatus is Ready
Install the required operators:
- NVIDIA GPU Operator: Provides GPU support
- Red Hat OpenShift AI: Provides AI/ML platform functionality
- Red Hat OpenShift Serverless: Provides Knative Serving support
- Red Hat OpenShift Service Mesh 2: Provides Istio service mesh support
- Node Feature Discovery Operator: Automatically discovers node features
- Package Server: Manages operator packages
Verify operator status:
# Check required Operators status
oc get csv -A | grep -E "(gpu-operator|rhods|serverless|servicemesh|nfd)"
# View DataScienceCluster status
oc get datasciencecluster -ADeploy an LLM on OpenShift AI
Create and switch to the working namespace. Create a dedicated namespace for this:
oc new-project ai-inference-demoConfirm you are under the project
ai-inference-demobefore you proceed.Configure the namespace as a service mesh member:
# Add Istio injection label to namespace oc label namespace ai-inference-demo istio-injection=enabled # Check if ServiceMeshMemberRoll needs to be updated oc get servicemeshmemberroll -A # If ServiceMeshMemberRoll exists, add namespace to member list oc patch servicemeshmemberroll default -n istio-system --type='json' -p='[{"op": "add", "path": "/spec/members/-", "value": "ai-inference-demo"}]' # Verify namespace labels oc get namespace ai-inference-demo --show-labels # Enable anyuid SCC to avoid token and permission issues oc adm policy add-scc-to-user anyuid -z default -n ai-inference-demoConfigure the Red Hat registry image pull permissions:
# Create Red Hat Registry pull secret (requires valid Red Hat Customer Portal credentials) oc create secret docker-registry redhat-registry-secret \ --docker-server=registry.redhat.io \ --docker-username=YOUR_RH_USERNAME \ --docker-password='YOUR_RH_PASSWORD' \ --docker-email=YOUR_EMAIL # Link secret to default service account oc secrets link default redhat-registry-secret --for=pull oc secrets link deployer redhat-registry-secret --for=pull # Verify secret creation oc get secret redhat-registry-secretNote: Replace
YOUR_RH_USERNAME,YOUR_RH_PASSWORD, andYOUR_EMAILwith your actual Red Hat Customer Portal credentials.Note
registry.redhat.io/rhaiis/vllm-cuda-rhel9:3.2.0-1752784628is the current latest version. You can find the latest version in the Red Hat Ecosystem Catalog by searching forrhaiis.Create a
ServingRuntimeas follows. AServingRuntimedefines the reusable runtime environment such as the container image, supported model formats, and resource settings that OpenShift AI uses to serve machine learning models.cat <<EOF | oc apply -f - apiVersion: serving.kserve.io/v1alpha1 kind: ServingRuntime metadata: name: red-hat-vllm-runtime namespace: ai-inference-demo spec: supportedModelFormats: - name: vllm version: "1" autoSelect: true - name: pytorch version: "1" autoSelect: true containers: - name: kserve-container image: registry.redhat.io/rhaiis/vllm-cuda-rhel9:3.2.0-1752784628 ports: - containerPort: 8080 name: http1 protocol: TCP command: ["python", "-m", "vllm.entrypoints.openai.api_server"] args: - "--model" - "/mnt/models/DialoGPT-small" - "--host" - "0.0.0.0" - "--port" - "8080" - "--served-model-name" - "DialoGPT-small" - "--max-model-len" - "1024" - "--disable-log-requests" env: - name: VLLM_CPU_KVCACHE_SPACE value: "4" - name: HF_HUB_OFFLINE value: "1" - name: TRANSFORMERS_OFFLINE value: "1" resources: requests: cpu: "1" memory: "4Gi" nvidia.com/gpu: "1" limits: cpu: "2" memory: "8Gi" nvidia.com/gpu: "1" readinessProbe: httpGet: path: /health port: 8080 initialDelaySeconds: 120 periodSeconds: 10 timeoutSeconds: 10 livenessProbe: httpGet: path: /health port: 8080 initialDelaySeconds: 180 periodSeconds: 30 timeoutSeconds: 10 EOFVerify the
ServingRuntimestatus:# Check ServingRuntime status oc get servingruntime red-hat-vllm-runtime # View detailed information oc describe servingruntime red-hat-vllm-runtimeCreate a persistent volume claim for model storage. While this example uses a PVC to store model files locally in the cluster, other storage options such as downloading directly from Hugging Face, using object storage (like S3), or mounting a
hostPathvolume are also possible depending on your environment and security needs.cat <<EOF | oc apply -f - apiVersion: v1 kind: PersistentVolumeClaim metadata: name: model-storage-pvc namespace: ai-inference-demo spec: accessModes: - ReadWriteOnce resources: requests: storage: 10Gi storageClassName: gp3-csi EOFVerify PVC creation:
oc get pvc model-storage-pvcDownload the model to the PVC:
cat <<EOF | oc apply -f - apiVersion: batch/v1 kind: Job metadata: name: dialogpt-model-downloader namespace: ai-inference-demo spec: template: spec: restartPolicy: Never containers: - name: downloader image: python:3.12-slim command: - /bin/sh - -c - | set -e export HOME=/tmp pip install --no-cache-dir --user huggingface_hub export PATH="\$HOME/.local/bin:\$PATH" mkdir -p /models/DialoGPT-small python3 -c "from huggingface_hub import hf_hub_download; files = ['config.json', 'pytorch_model.bin', 'tokenizer_config.json', 'vocab.json', 'merges.txt']; [hf_hub_download(repo_id='microsoft/DialoGPT-small', filename=f, local_dir='/models/DialoGPT-small') for f in files]" rm /models/DialoGPT-small/tokenizer.json || true ls -la /models/DialoGPT-small/ du -sh /models/DialoGPT-small/pytorch_model.bin volumeMounts: - name: model-storage mountPath: /models env: - name: HF_TOKEN value: "YOUR_HF_TOKEN_HERE" volumes: - name: model-storage persistentVolumeClaim: claimName: model-storage-pvc EOFIf you need to access private models, replace
YOUR_HF_TOKEN_HEREwith your Hugging Face token.Monitor the model download progress. View job status:
oc get jobsView download logs:
oc logs job/dialogpt-model-downloader -f # Wait to see "Download completed!" messageVerify the model file location:
# Create debug Pod to check model files in PVC cat <<EOF | oc apply -f - apiVersion: v1 kind: Pod metadata: name: pvc-explorer namespace: ai-inference-demo spec: restartPolicy: Never containers: - name: explorer image: busybox:latest imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent command: ["sleep", "300"] volumeMounts: - name: model-storage mountPath: /data volumes: - name: model-storage persistentVolumeClaim: claimName: model-storage-pvc EOF # Check model file location - ensure PVC has downloaded LLM oc exec pvc-explorer -- ls -la /data/ oc exec pvc-explorer -- ls -la /data/DialoGPT-small/ oc exec pvc-explorer -- find /data -name "config.json" oc exec pvc-explorer -- du -h /data/DialoGPT-small/pytorch_model.bin # Verify content (required) oc exec pvc-explorer -- head -n 5 /data/DialoGPT-small/config.json oc exec pvc-explorer -- head -n 5 /data/DialoGPT-small/tokenizer_config.json # Clean up debug Pod oc delete pod pvc-explorerYou should see a
/data/DialoGPT-small/directory containing the following files:config.jsonpytorch_model.bintokenizer_config.jsonvocab.jsonmerges.txt
Create the
InferenceService:cat <<EOF | oc apply -f - apiVersion: serving.kserve.io/v1beta1 kind: InferenceService metadata: name: dialogpt-small-service namespace: ai-inference-demo annotations: sidecar.istio.io/inject: "false" # Disable Istio sidecar to avoid envoy errors serving.kserve.io/enable-service-account-token-mount: "true" # Mount token to resolve authentication failures spec: predictor: model: modelFormat: name: pytorch runtime: red-hat-vllm-runtime storageUri: pvc://model-storage-pvc resources: requests: cpu: "1" memory: "4Gi" nvidia.com/gpu: "1" limits: cpu: "2" memory: "8Gi" nvidia.com/gpu: "1" env: - name: VLLM_GPU_MEMORY_UTILIZATION value: "0.5" EOFModel information:
- Microsoft/DialoGPT-small: 117 MB, 117 M parameters
- Local storage: Loaded from PVC, fast and stable startup
- Conversational generation: Suitable for testing inference functionality
- vLLM optimized: Uses vLLM inference engine for better performance
Monitor the deployment status:
# Real-time monitor InferenceService status oc get inferenceservice dialogpt-small-service -w # View related pods oc get pods -l serving.kserve.io/inferenceservice=dialogpt-small-service # View detailed status oc describe inferenceservice dialogpt-small-service # View events oc get events --sort-by='.lastTimestamp' | head -20When you see
READY=True, it means the service has started successfully.The simplest testing method is as follows.
Important note: DialoGPT-small is a small conversational model (117 M parameters) with limited response quality. Sometimes it can generate incoherent content, which is normal behavior.
# Set variables PREDICTOR_POD=$(oc get pods -l serving.kserve.io/inferenceservice=dialogpt-small-service -o jsonpath='{.items[0].metadata.name}') # Basic health check echo "=== Health Check ===" oc exec $PREDICTOR_POD -c kserve-container -- curl -s localhost:8080/health # Conversation test 1: Simple greeting echo -e "\n=== I ask: Hello, how are you? ===" oc exec $PREDICTOR_POD -c kserve-container -- curl -s -X POST localhost:8080/v1/chat/completions \ -H "Content-Type: application/json" \ -d '{ "model": "DialoGPT-small", "messages": [{"role": "user", "content": "Hello, how are you?"}], "max_tokens": 30, "temperature": 0.7 }' # Conversation test 2: Ask for name echo -e "\n=== I ask: What is your name? ===" oc exec $PREDICTOR_POD -c kserve-container -- curl -s -X POST localhost:8080/v1/chat/completions \ -H "Content-Type: application/json" \ -d '{ "model": "DialoGPT-small", "messages": [{"role": "user", "content": "What is your name?"}], "max_tokens": 20, "temperature": 0.8 }' # Conversation test 3: Simple question echo -e "\n=== I ask: Hi ===" oc exec $PREDICTOR_POD -c kserve-container -- curl -s -X POST localhost:8080/v1/chat/completions \ -H "Content-Type: application/json" \ -d '{ "model": "DialoGPT-small", "messages": [{"role": "user", "content": "Hi"}], "max_tokens": 10, "temperature": 0.5 }'Performance and monitoring check. To view resource usage:
# View Pod resource usage (requires metrics-server support) oc adm top pod -l serving.kserve.io/inferenceservice=dialogpt-small-service # If the above command doesn't work, use alternative methods: # View Pod resource configuration and limits PREDICTOR_POD=$(oc get pods -l serving.kserve.io/inferenceservice=dialogpt-small-service -o jsonpath='{.items[0].metadata.name}') oc describe pod $PREDICTOR_POD | grep -A10 -B5 "Limits\|Requests" # View Pod status and runtime oc get pod $PREDICTOR_POD -o wide # View node resource usage oc adm top nodes # If metrics-server is not available, view basic Pod information oc get pod $PREDICTOR_POD -o jsonpath='{.status.containerStatuses[*].restartCount}' echo " (restart count)"Service status check:
# Check InferenceService overall status oc get inferenceservice dialogpt-small-service -o yaml | grep -A20 status # View all related resource status oc get pods,svc,inferenceservice -l serving.kserve.io/inferenceservice=dialogpt-small-service # View recent cluster events oc get events --sort-by='.lastTimestamp' | head -20 # Check service endpoints oc get endpoints dialogpt-small-service-predictor
Troubleshooting common issues
Inference service cannot be accessed:
# Check service status
oc get svc | grep dialogpt-small-service
# Check endpoints
oc get endpoints dialogpt-small-service-predictor
# Check pods status
oc get pods -l serving.kserve.io/inferenceservice=dialogpt-small-serviceModel loading failed:
# View pod events
oc describe pod $PREDICTOR_POD
# Check model files
oc exec $PREDICTOR_POD -c kserve-container -- ls -la /mnt/models/DialoGPT-small/
# View vLLM startup logs
oc logs $PREDICTOR_POD -c kserve-container | grep -i errorMemory or GPU resource insufficient:
# Check node resources
oc describe nodes | grep -A5 -B5 "Allocated resources"
# Reduce resource requirements
oc patch inferenceservice dialogpt-small-service --type='merge' -p='{
"spec": {
"predictor": {
"model": {
"resources": {
"requests": {"cpu": "500m", "memory": "2Gi"},
"limits": {"cpu": "1", "memory": "4Gi"}
}
}
}
}
}'Resource cleanup
If you want to clear your environment after the tests, delete the resources with the following commands:
# Delete test Pod
oc delete pod inference-test-client
# Delete InferenceService
oc delete inferenceservice dialogpt-small-service
# Delete ServingRuntime
oc delete servingruntime red-hat-vllm-runtime
# Delete download Job
oc delete job dialogpt-model-downloader
# Delete PVC (Note: this will delete all downloaded models)
oc delete pvc model-storage-pvc
# Delete Pull Secret
oc delete secret redhat-registry-secret
# Delete entire project
oc delete project ai-inference-demoSummary
This guide provides a complete Red Hat Inference Server deployment and internal testing process. Its advantages include the following:
- Security-focused: All testing is done internally within the cluster, no need to expose external endpoints
- Efficient: Uses PVC local storage for fast model loading
- Flexible: Supports multiple testing methods and interaction approaches
- Observable: Provides detailed monitoring and log viewing methods
Use cases:
- Development and testing environment verification
- Internal API integration testing
- Model performance evaluation
- AI service deployment in security-compliant environments
Following this guide, you can completely deploy and test Red Hat Inference Server without creating external routes.
Explore the Red Hat AI Inference Server product page and our guided demo for more information or check out our technical documentation for detailed configurations.
