Integrating Azure DevOps with Red Hat Developer Hub brings together two powerful platforms to create a seamless, end-to-end CI/CD experience. Azure DevOps offers robust capabilities for source control, build automation, and deployment. Meanwhile, Red Hat Developer Hub serves as a centralized developer portal for managing tools, services, documentation, and templates. When combined, teams benefit from improved collaboration, faster delivery, and increased visibility across the entire development lifecycle.
Supported Azure DevOps plug-ins
Red Hat Developer Hub includes several Azure DevOps plug-ins:
In this guide, we’ll walk through the steps to integrate these plug-ins with Red Hat Developer Hub. We'll also use Microsoft Entra ID (formerly Azure AD) for authentication, which requires the msgraph plug-in for secure identity management.
All 4 of these plug-ins are in Technology Preview as of the documentation's creation date, which corresponds to the Red Hat Developer Hub 1.5 release.
Prerequisites
Before we begin, ensure that you have:
- Set up Azure Entra ID.
- Configured Azure DevOps.
- Satisfied the platform requirements. Red Hat Developer Hub can run on any AWS KMS External Key Store (XKS) or Red Hat Enterprise Linux system. For this demo, we’ll use Red Hat OpenShift 4.18.
We will walk through a summary of the steps to set up Azure Entra ID and configure Azure DevOps.
Azure Entra ID setup
Refer to the official documentation for comprehensive details. We'll summarize the required steps:
- Register a web application with a client secret (Figure 1).
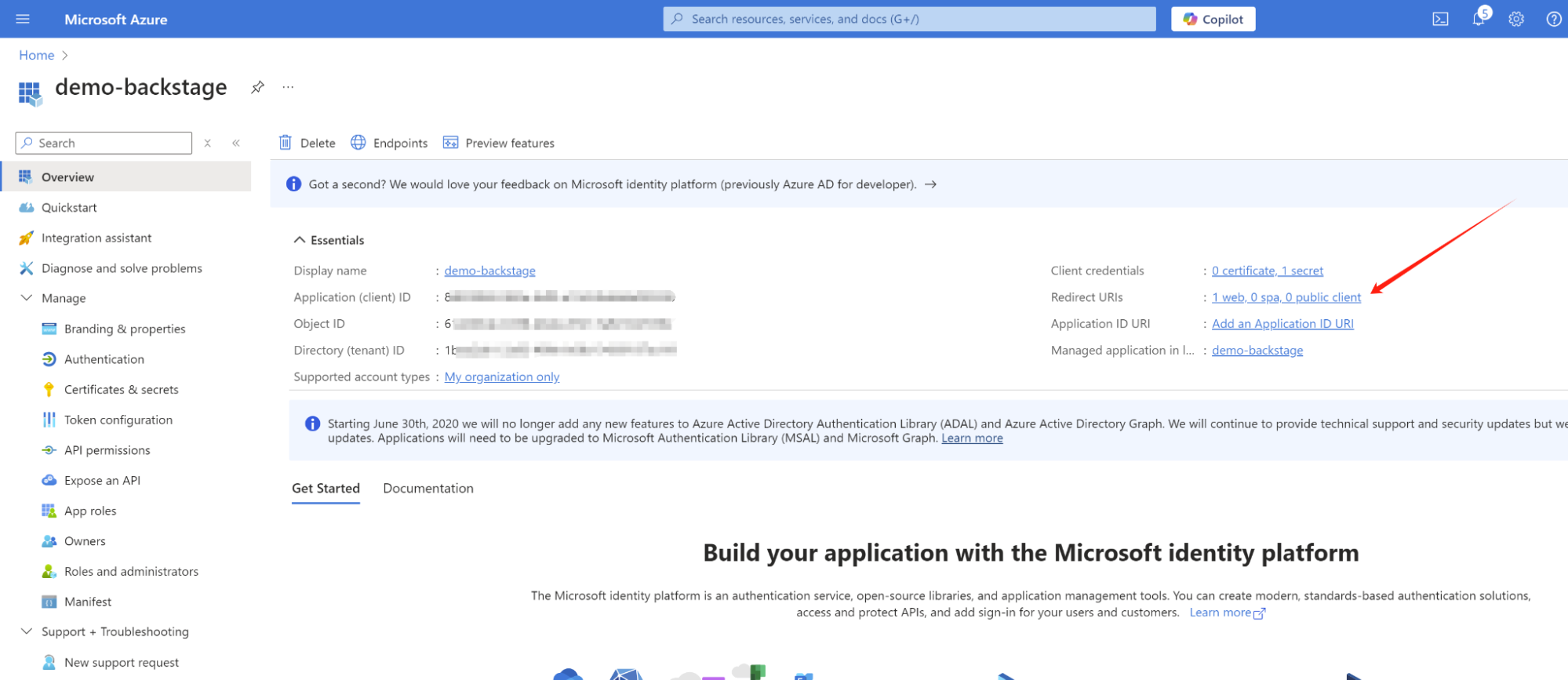
- Set the redirect URI to
https://<rhdh-host>/api/auth/microsoft/handler/frame, as shown in Figure 2.

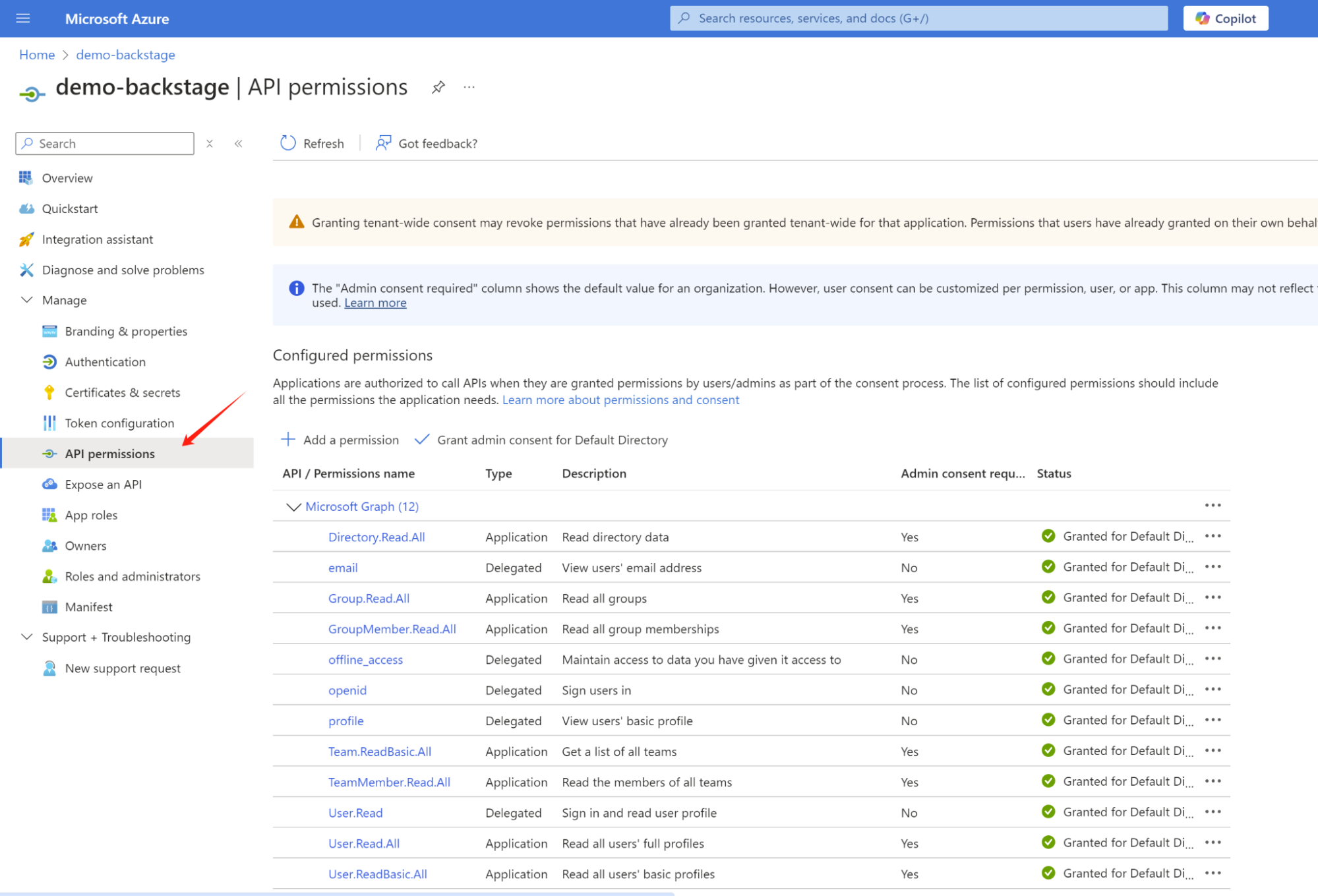
Set the required API permissions:
emailoffline_accessopenidprofileUser.Read
Figure 3 shows an example.
Azure DevOps configuration
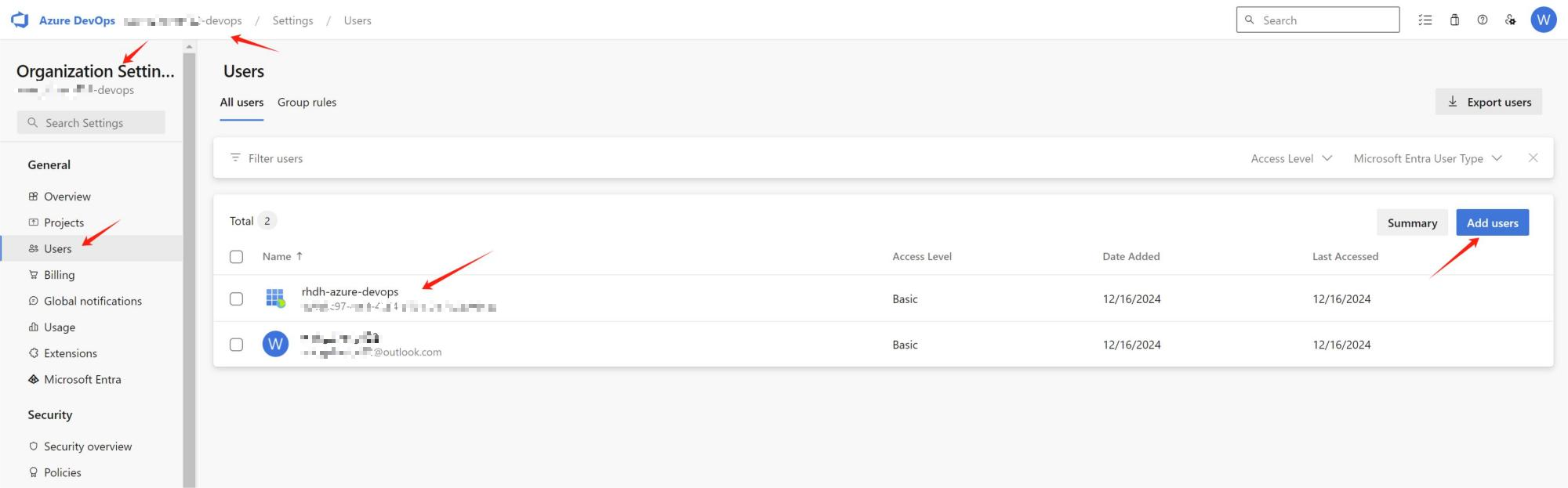
- Create an Azure DevOps organization, as shown in Figure 4.

- Add your Entra ID service principal under Org Settings > Users. See Figure 5.
- Ensure your pipeline agent pool (Azure or self-hosted) is available and running Docker (Figure 6).

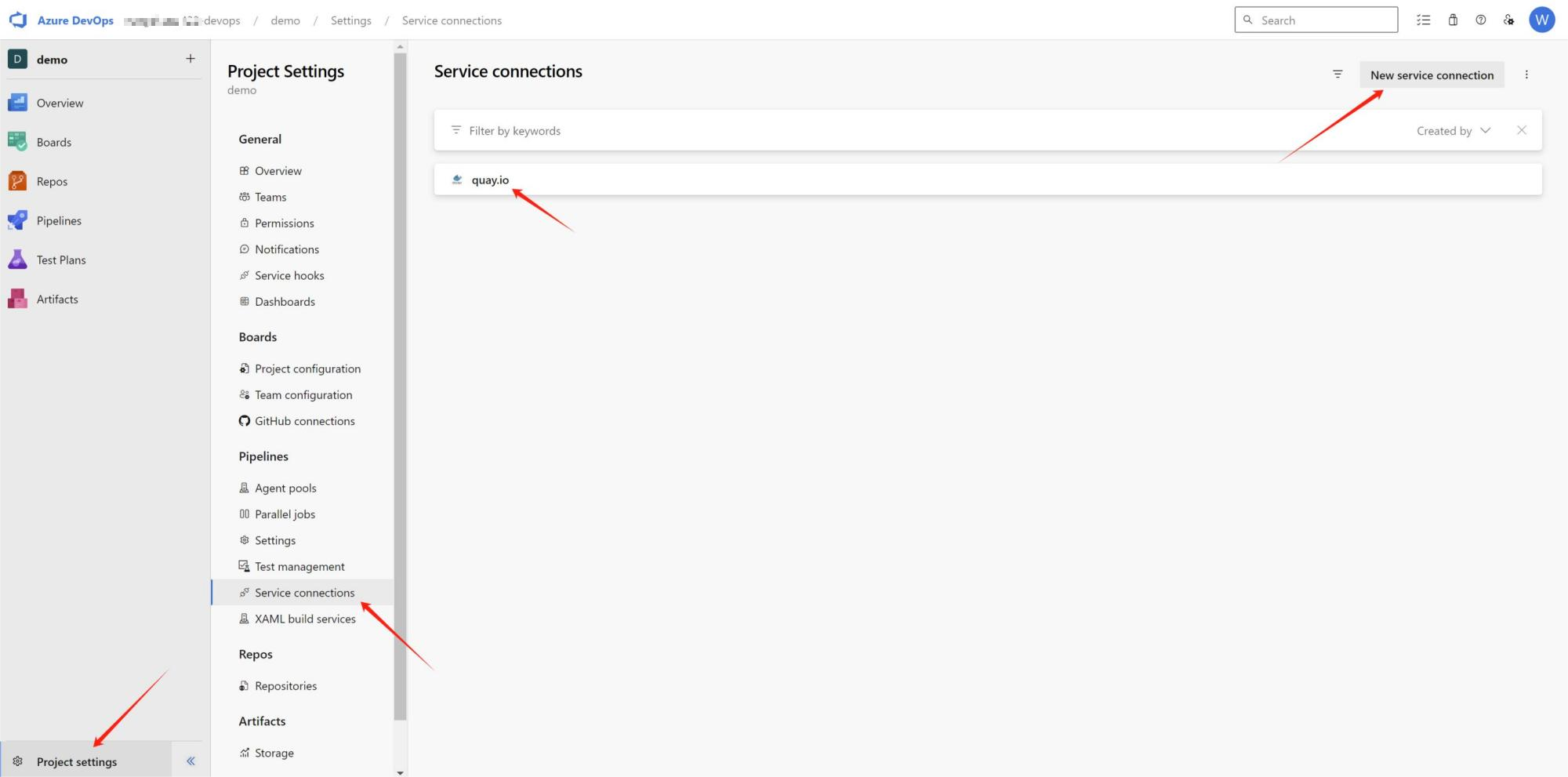
- Set up a service connection under Project > Pipelines > Service Connections to your image registry. In this example, we used quay.io. See Figure 7.
Install Red Hat Developer Hub with Azure plug-ins
For Azure DevOps configuration, refer to the upstream documentation. For Azure SSO configuration, consult the upstream documentation. Then follow these steps:
- Update the
dynamic-pluginssection of your configuration to enable Azure-related plug-ins:
dynamic:
plugins:
- package: ./dynamic-plugins/dist/backstage-plugin-catalog-backend-module-msgraph-dynamic
disabled: false
- package: ./dynamic-plugins/dist/backstage-plugin-scaffolder-backend-module-azure-dynamic
disabled: false
- package: ./dynamic-plugins/dist/backstage-community-plugin-azure-devops
disabled: false
- package: ./dynamic-plugins/dist/backstage-community-plugin-azure-devops-backend-dynamic
disabled: false- If using Entra ID authentication, add your client ID, secret, and tenant ID to the
authconfiguration:
auth:
environment: production
providers:
microsoft:
production:
clientId: ${CLIENT_ID}
clientSecret: ${CLIENT_SECRET}
tenantId: ${TENANT_ID}- To import users and groups from Entra ID:
catalog:
providers:
microsoftGraphOrg:
providerId:
clientId: ${CLIENT_ID}
clientSecret: ${CLIENT_SECRET}
tenantId: ${TENANT_ID}
userGroupMember:
search: '"displayName:team a" OR "displayName:teamb"'
schedule:
frequency: PT1M
timeout: PT50M- Add a sample Azure DevOps template under
catalog:
catalog:
locations:
- target: ${TEMPLATE_URL}
type: url
rules:
- allow: [Template]This template URL should link to a file. Alternatively, the template can be imported via the web UI (Figure 8).

- Configure the Azure DevOps back-end provider with the organization, project, and repository used for Azure DevOps:
catalog:
providers:
azureDevOps:
yourProviderId:
organization: ${AZURE_DEVOPS_ORG}
project: '*'
repository: '*'
path: /catalog-info.yaml
schedule:
frequency: { minutes: 30 }
timeout: { minutes: 3 }- Specify Azure DevOps credentials:
integrations:
azure:
- host: dev.azure.com
credentials:
- clientId: ${CLIENT_ID}
clientSecret: ${CLIENT_SECRET}
tenantId: ${TENANT_ID}This is what the overall configuration looks like:
app:
baseUrl: ${RHDH_HOST}
backend:
auth:
externalAccess:
- options:
secret: ${BACKEND_SECRET}
subject: legacy-default-config
type: legacy
baseUrl: ${RHDH_HOST}
cors:
origin: ${RHDH_HOST}
auth:
environment: production
providers:
microsoft:
production:
clientId: ${CLIENT_ID}
clientSecret: ${CLIENT_SECRET}
tenantId: ${TENANT_ID}
signInPage: microsoft
catalog:
rules:
- allow: [Component, System, API, Resource, Location, Template, Group, User]
locations:
- target:
https://github.com/suchugh/red-hat-developer-hub-software-templates/blob/main/templates/azure/dotnet-frontend/template.yaml
type: url
rules:
- allow: [Template]
providers:
microsoftGraphOrg:
providerId:
clientId: ${CLIENT_ID}
clientSecret: ${CLIENT_SECRET}
tenantId: ${TENANT_ID}
userGroupMember:
search: '"displayName:team a" OR "displayName:teamb"'
schedule:
frequency: PT1M
timeout: PT50M
azureDevOps:
yourProviderId: # identifies your dataset / provider independent of config changes
organization: ${AZURE_DEVOPS_ORG}
project: '*'
repository: '*' # this will match all repos
path: /catalog-info.yaml
schedule: # optional; same options as in TaskScheduleDefinition
# supports cron, ISO duration, "human duration" as used in code
frequency: { minutes: 30 }
# supports ISO duration, "human duration" as used in code
timeout: { minutes: 3 }
integrations:
azure:
- host: dev.azure.com
credentials:
- clientId: ${CLIENT_ID}
clientSecret: ${CLIENT_SECRET}
tenantId: ${TENANT_ID}
# organizations:
# - \$AZURE_DEVOPS_ORG
permission:
enabled: false
enabled:
azure: true
azureDevOps: true
microsoftGraphOrg: true
microsoft: true
permission: falseIn the following video, you can see the template is imported into Developer Hub.
Launching the template
Launch the template by initiating it with parameters. The following video shows the .NET template execution after it's successfully imported into Red Hat Developer Hub.
After you launch the application template via Developer Hub, import azure-pipelines.yml from the Azure Git repository created by the template. Then, run the Azure pipeline from your application repository. Note the imageRepository where the image will be published:
trigger:
- main
resources:
- repo: self
variables:
tag: "azure-devops-demo-$(Build.BuildId),azure-devops-demo-latest"
imageRepository: "suchugh/azureado"
dockerRegistryServiceConnection: "quay.io"
stages:
- stage: Build
displayName: Build image
jobs:
- job: Build
pool:
name: Default
steps:
- task: DockerInstaller@0
inputs:
dockerVersion: '28.0.4'
- task: Docker@2
displayName: Build and push image
inputs:
command: buildAndPush
repository: $(imageRepository)
containerRegistry: $(dockerRegistryServiceConnection)
dockerfile: "$(Build.SourcesDirectory)/Dockerfile"
tags: |
$(tag)The following video depicts creating a pipeline for the sample .NET application in Azure Pipelines using a locally running agent. This will be reflected in Developer Hub after the application is imported into the catalog.
Logging into the Developer Hub console, you can see the pipeline in action. After a successful execution of Azure Pipelines for the sample application, you can view the details of the applications from within the Developer Hub catalog, as depicted in the following video.
Final thoughts
With this setup (Figure 9), you can:
- Scaffold new projects using Developer Hub templates.
- Authenticate users with Entra ID.
- Automate builds and deployments using Azure DevOps.
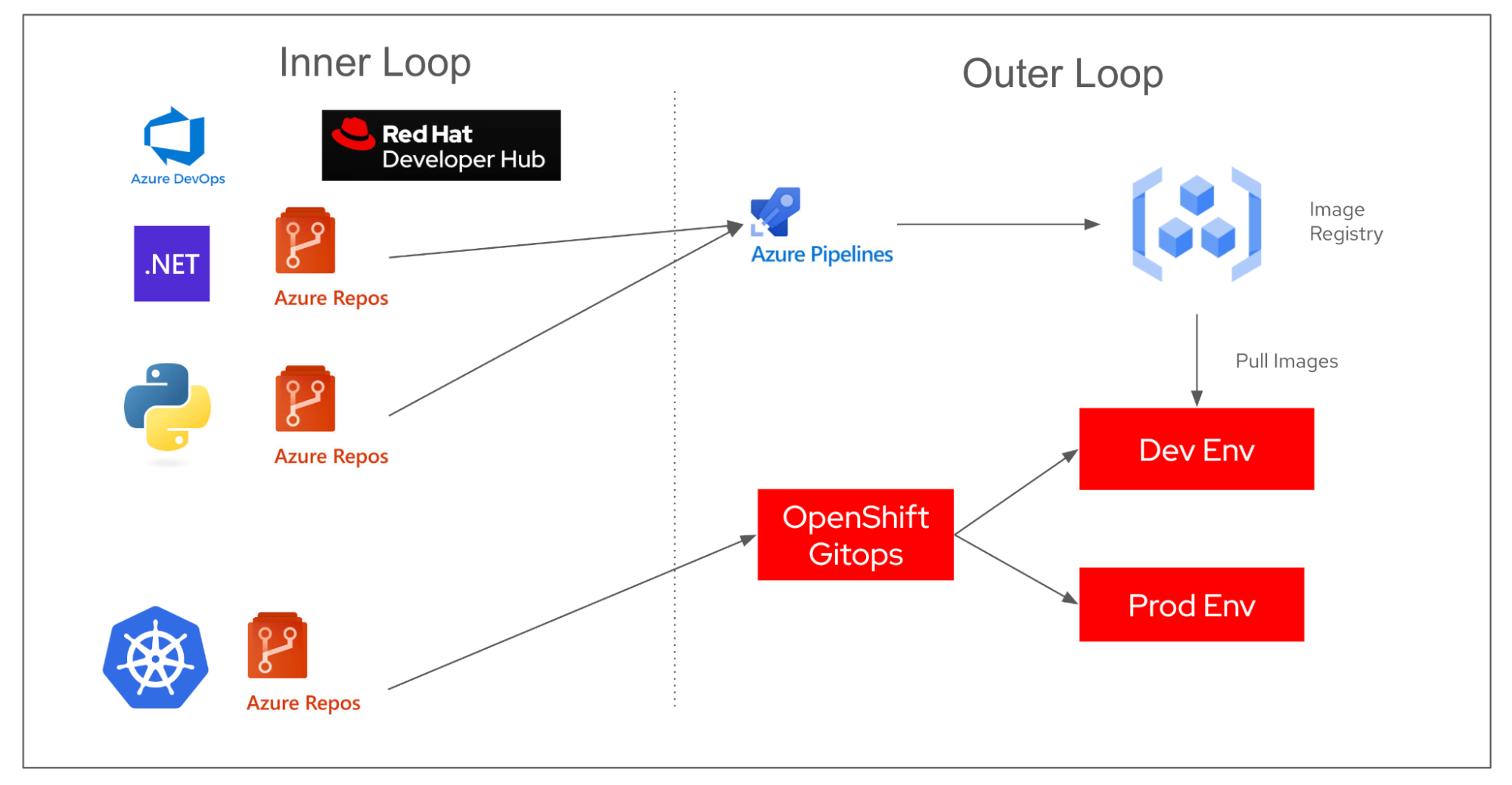
This integration showcases how Red Hat Developer Hub and Azure DevOps together enhance developer productivity, enabling fast, consistent, and scalable CI/CD workflows.
Have questions or want to see this in action? Feel free to reach out!
