Red Hat Advanced Cluster Management for Kubernetes (RHACM) facilitates the management of Red Hat OpenShift clusters at scale. The multicluster global hub, an RHACM component, allows users to manage multiple Red Hat Advanced Cluster Management clusters from a single interface. With this architecture, the clusters managed directly by the global hub cluster are referred to as "managed hub clusters", while the clusters managed by these "hub clusters" are called "managed clusters". This setup is especially useful when a single hub cluster cannot manage the large number of clusters in a high-scale environment. In such cases, you divide the clusters into smaller groups of clusters and configure a managed hub cluster for each group.
Red Hat Advanced Cluster Security for Kubernetes provides robust security management capabilities for Red Hat OpenShift clusters. When Advanced Cluster Security is deployed alongside RHACM in a managed hub cluster, it collects security data from all managed clusters via its Central component.
In version 2.12 of Advanced Cluster Management, a new Developer Preview feature simplifies the collection of security data from managed hub clusters using agents that aggregate and send the data back to the multicluster global hub, where it is displayed in a Grafana dashboard. This integration provides a centralized view of security metrics across all managed clusters. Figure 1 shows a diagram of the architecture.
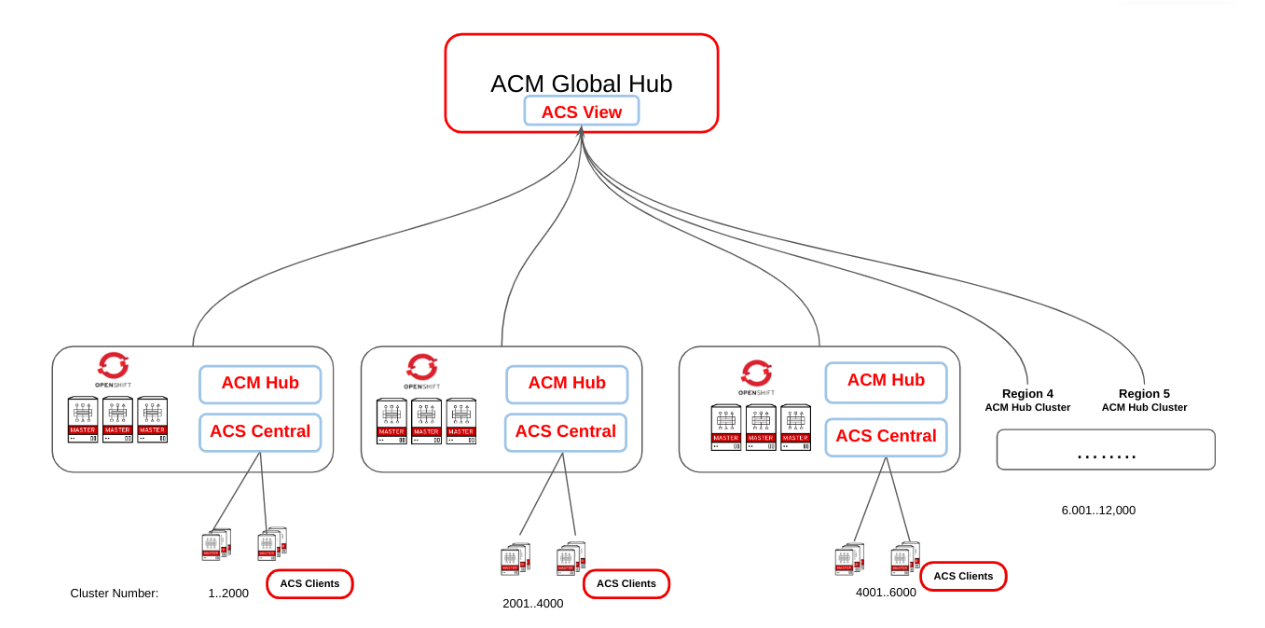
You can see a preview of the dashboard (see Figure 2).
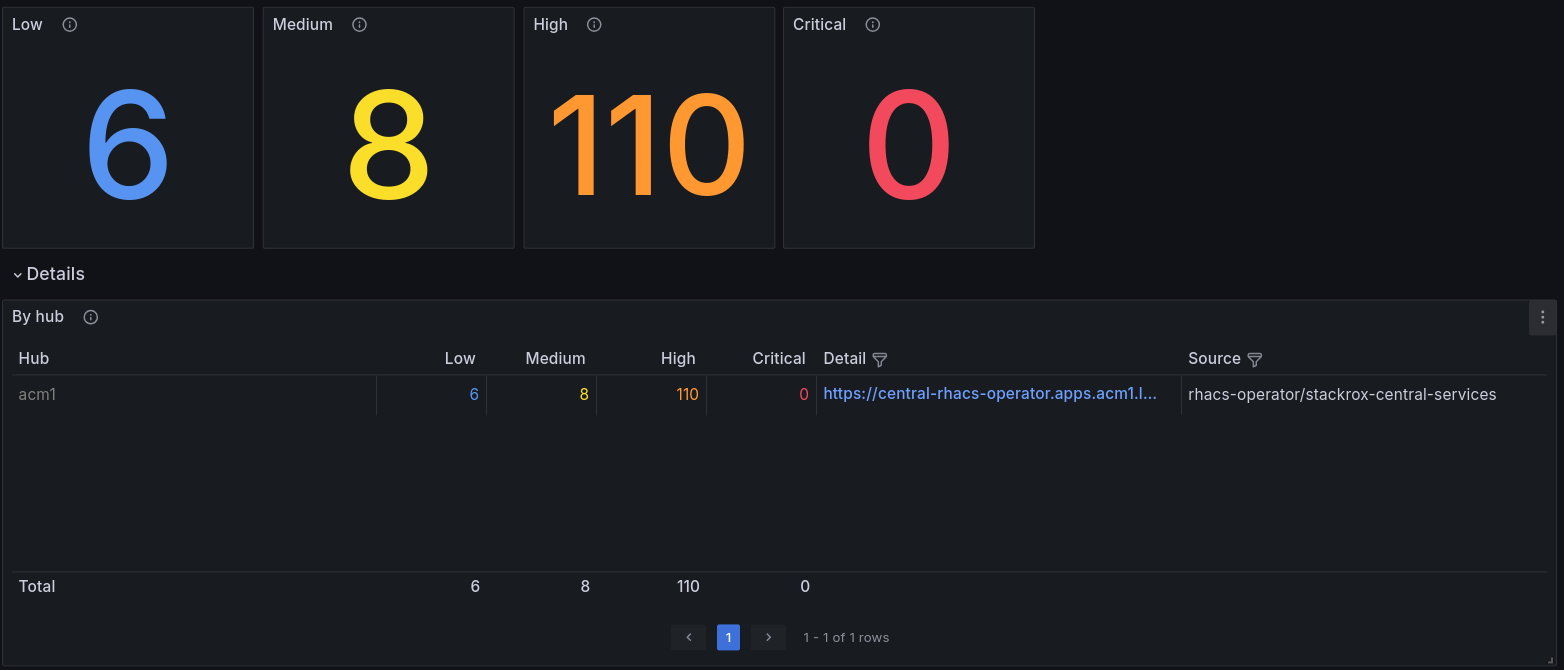
Multicluster global hub: A centralized view of cluster data
One of the key features of the multicluster global hub is its ability to provide a unified observability experience across multiple managed hub clusters.
- Report the policy compliance status and trend.
- Inventory all managed hubs and managed clusters on the overview page.
- Detect and alert in cases of irregular policy behavior.
These dashboards enable monitoring and observing data across both managed hub clusters and managed clusters from a centralized interface.
Requirements for Red Hat Advanced Cluster Security integration
To enable the Advanced Cluster Security integration with the multicluster global hub, the following setup is required:
- One multicluster global hub.
- At least one Advanced Cluster Management managed hub cluster.
- One Advanced Cluster Security Central instance running in each managed hub cluster.
Each Central instance must manage at least one managed cluster to generate security violation data. If no clusters are managed, the dashboard will remain empty.
How to enable Red Hat Advanced Cluster Security integration
By default, the integration is disabled. Enabling it would require a few steps, detailed below.
Annotate the multiclusterglobalhub custom resource
The multicluster global hub is managed by a custom resource called multiclusterglobalhub. To enable the integration, you need to add the global-hub.open-cluster-management.io/with-stackrox-integration annotation in the multiclusterglobalhub custom resource. In a typical multicluster global hub installation that can be done with the following command:
$ oc annotate -n multicluster-global-hub multiclusterglobalhub multiclusterglobalhub \
global-hub.open-cluster-management.io/with-stackrox-integration=The value of the annotation (an empty string in this case) is irrelevant; the annotation just needs to be present.
Create Red Hat Advanced Cluster Security API token
In each RHACM hub cluster, the multicluster global hub agent needs an API token to connect to the Central instance. That token can be created using the Central web application.
- Navigate to Platform Configuration > Integrations, and scroll down to API Token.
- Click Generate token, then in the dialog select a name, role, and expiration date for the token, then click the Generate button (see Figure 3).
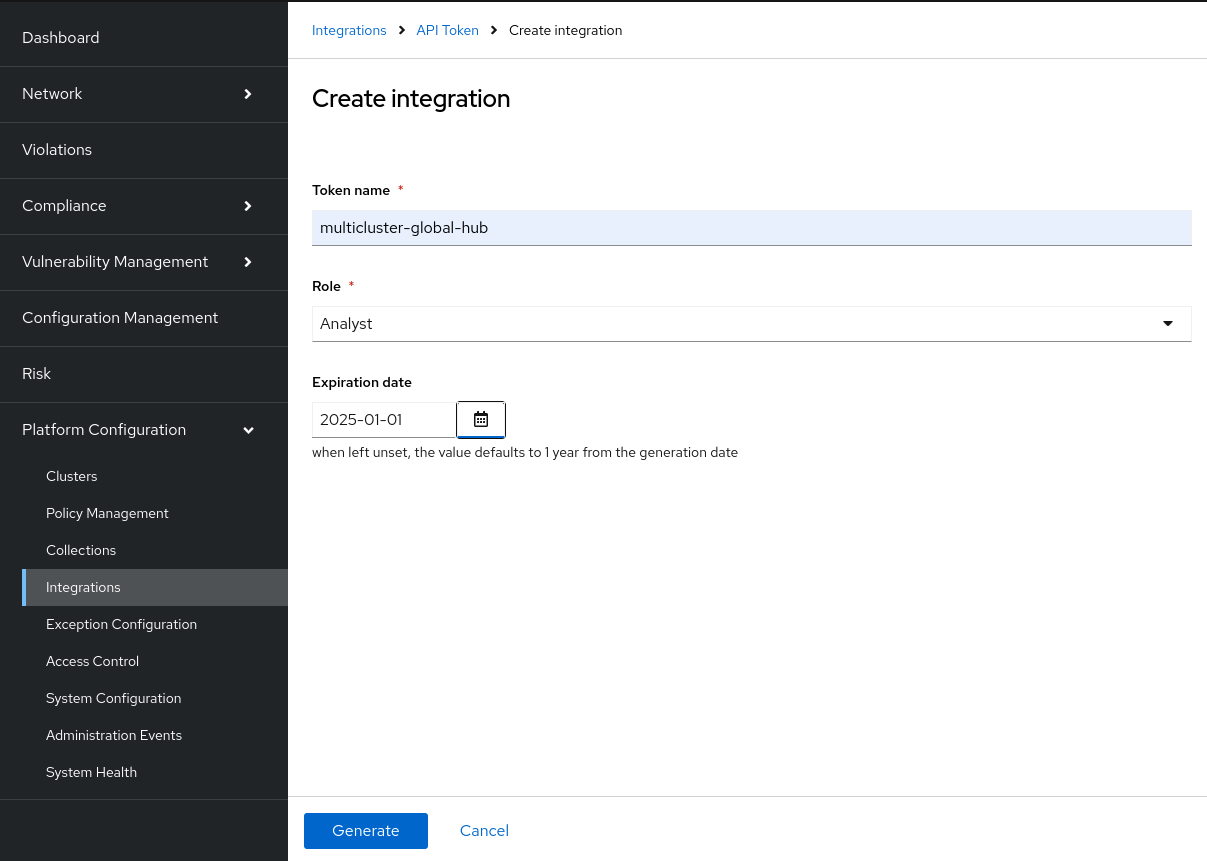
Important notes:
- You must choose a name for the token, though it's mainly to clarify its usage.
- The Role is crucial: Select a role that grants permission to get the security violations. The Analyst role is built-in and provides read-only permissions for several resources including security violations, but you may want to create your own Permission Set set and Role instead, so that it only has read permission for security violations.
- The Expiration date is important: You will need to renew the token before it expires, otherwise the multicluster global hub will stop to collect the data from this Central.
The token will be displayed like this (see Figure 4).
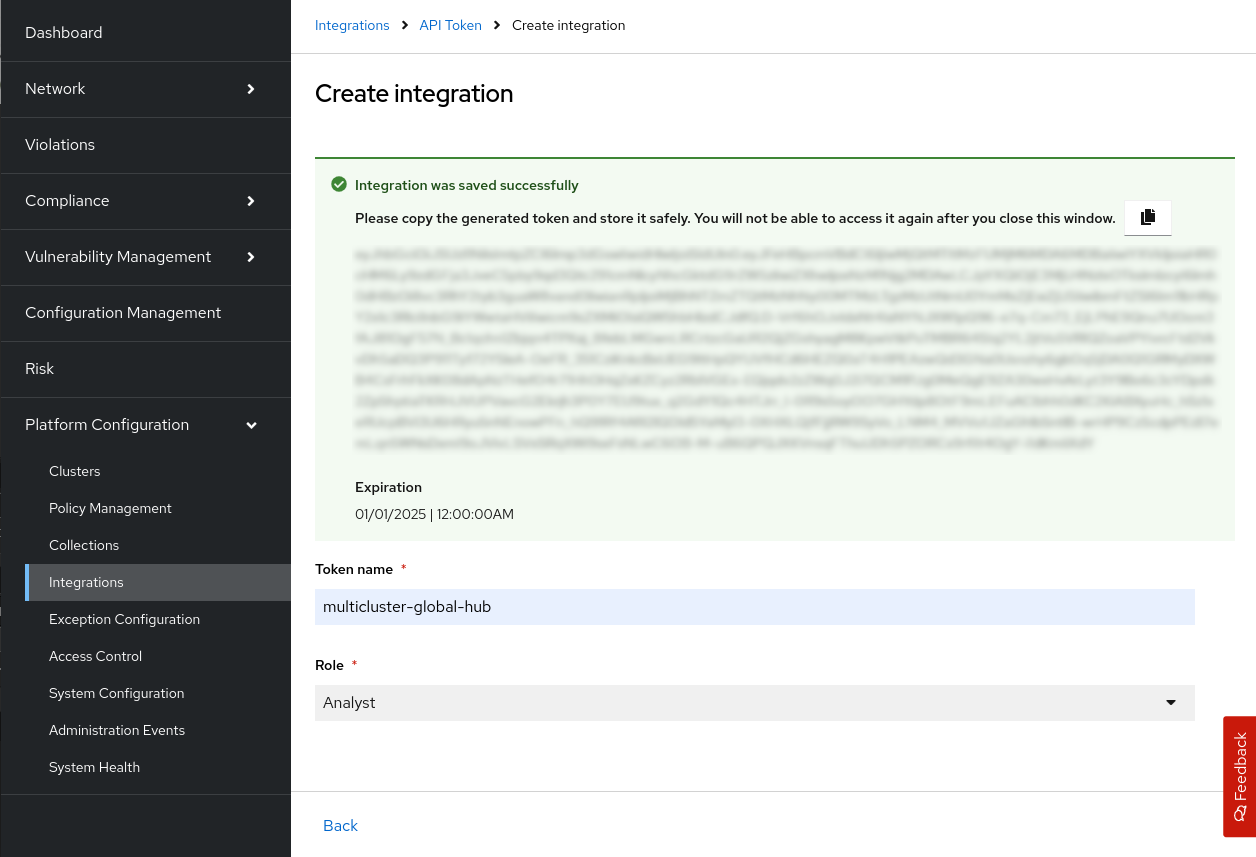
Make sure to copy the token to a safe place, as you will not be able to see it again once you close that dialog. For more details about tokens check the Red Hat Advanced Cluster Security documentation.
Obtain the Red Hat Advanced Cluster Security API certificate
To connect to the Central instance, you also need the certificate authority certificate. In a typical Advanced Cluster Security installation, the Certificate Authority certificate is generated by the Central component and stored in the ca.pem key of the central-tls secret. You can retrieve it using the following command:
$ oc get secret -n rhacs-operator central-tls -o json | \
jq -r '.data["ca.pem"] | @base64d'The result should be something like this:
-----BEGIN CERTIFICATE-----
MIIB0zCCAXigAwIBAgIUVD2jLKbwVW4+2zuYVNPCbra6AUYwCgYIKoZIzj0EAwIw
...
-----END CERTIFICATE-----Create the Red Hat Advanced Cluster Security API connection details secret
Once you have the token and the certificate authority certificate you need to put them inside a Kubernetes secret to store these details. The token should be in the token key, and the CA certificate in the ca key, so it should look like this:
apiVersion: v1
kind: Secret
type: Opaque
metadata:
namespace: multicluster-global-hub-agent
name: rhacs-connection-details
stringData:
token: eyJ...
ca: |
-----BEGIN CERTIFICATE-----
MIIB0zCCAXigAwIBAgIUVD2jLKbwVW4+2zuYVNPCbra6AUYwCgYIKoZIzj0EAwIw
...
-----END CERTIFICATE-----Note that this example is using stringData to avoid the base64 encoding step. If you prefer to use data then you will have to encode the values. See the Kubernetes documentation for details.
Annotate the Central object
Add the global-hub.open-cluster-management.io/with-stackrox-credentials-secret annotation to the Central object to point to the newly created secret:
$ oc annotate -n rhacs-operator central stackrox-central-services \
global-hub.open-cluster-management.io/with-stackrox-credentials-secret=multicluster-global-hub-agent/rhacs-connection-detailsThe value of this annotation should be the namespace where you created the secret, followed by a forward slash and then the name of the secret. The name of the secret is not important, as long as you put it correctly in the value of the annotation. The secret must reside in the same namespace as the multicluster global hub agent, typically multicluster-global-hub-agent.
Once the secret is created and the Central object annotated, the multicluster global hub agent will automatically detect the configuration, apply it and begin collecting data. The data will be sent to the multicluster global hub manager to populate the dashboard.
Conclusion
Integrating Advanced Cluster Security with RHACM using the multicluster global hub centralizes and enhances security observability across managed clusters. By following the steps outlined, users can enable this integration to streamline security monitoring, ensuring a cohesive view of compliance and alerts. This integration simplifies cluster security observability and strengthens the management of OpenShift clusters at scale, equipping teams to address potential vulnerabilities more effectively. You can learn more about integrating RHACM with Advanced Cluster Security in deploying RHACM with Advanced Cluster Security.
