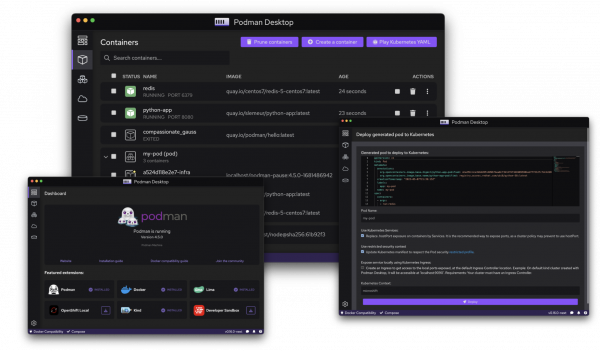
As containerization continues to gain popularity in the world of enterprise software development, there is also growing demand for tools and technologies that make container management more accessible and efficient. One such tool is Podman Desktop, which provides a user-friendly interface for managing containers and working with Kubernetes from a local machine (Figure 1).
After months of hard work, we are excited to announce the general availability (GA) of Podman Desktop 1.0. Let's explore what Podman Desktop is and why it can be advantageous for enterprise developers.
Why use Podman Desktop?
Podman Desktop is a container management tool that lets developers easily create, manage, and deploy containers on their local machine. Podman Desktop downloads, installs, and abstracts away the configuration of the underlying environment. This makes it a lightweight and efficient option for container management without the overhead of having to administer everything locally.
Easily manage multiple containers
The main advantage of using a UI like Podman Desktop for container management, especially for enterprise developers, is that it simplifies the process of working with containers. You can easily view and manage all containers in one place rather than having to remember and type out complex command-line commands. This saves time and reduces the risk of errors when managing multiple containers or complex container configurations.
Onboard developers faster
Another advantage of using Podman Desktop is that it can help developers who are new to containerization get started more easily. The user-friendly interface and simplified management process make it easier for developers who might be intimidated by the command-line interface of other container management tools to get started with containerization. This can help organizations onboard new developers more quickly and reduce the learning curve for containerization.
Work natively with Kubernetes
For developers interested in Kubernetes or targeting it as a deployment platform, Podman Desktop provides the ability to natively work with Kubernetes objects, which helps to gradually and naturally transition from containers to Kubernetes. Podman Desktop also provides an out-of-the-box Kubernetes environment based on Kind. This means that developers can create and test applications in an environment that closely mirrors production, preventing configuration changes between development and production and ensuring a smooth transition from one environment to another.
Key features
Podman Desktop includes many features that streamline container workflows, ensuring a smooth and efficient developer experience.
Podman and Kubernetes Local
- Install and run anywhere: Windows, macOS, and Linux
- Configure and install via Podman, Kind, Red Hat OpenShift Local, Developer Sandbox for Red Hat OpenShift
- Keep Podman and other dependencies up to date
Containers and pods
- Build, run, manage, and debug containers and pods
- Run pods with or without Kubernetes
- Use the built-in terminal to ssh into containers
- Manage multiple container engines
- Manage volumes
- Compatabile with Docker Compose
Kubernetes
- Play Kubernetes YAML
- Generate Kubernetes YAML from Pods
- Podify and Kubify: Convert containers to pods and Kubernetes
Enterprise readiness
- VPN and proxies configuration
- Image registry management
- Configure multiple OCI registries
- Pull, tag, and push images
- AirGapped installation
Bridge between local and remote environments
- Connect and deploy to remote OpenShift clusters
- Enable remote managed services locally
Extensibility
- Possibility to extend the container engines or Kubernetes providers
- Extension points to add actions, menus, configurations and enrich the UI with specific capabilities
From OpenShift Local to production
One of the unique features of Podman Desktop is its integration with Red Hat OpenShift Local (Figure 2), which lets users develop and test applications locally using the same container images and environment as they would in a production environment on Red Hat OpenShift. This means you can ensure that your applications will run smoothly in an OpenShift environment before deploying them.

OpenShift Local is essentially a single-node OpenShift cluster that runs locally on the developer's machine. It is based on the same technology as OpenShift and provides a consistent environment for developing and testing applications.
[ Learn more: What’s new in OpenShift Local 2.0 ]
Podman Desktop 1.0 includes an extension for OpenShift Local, which you can install from the dashboard (Figure 3) or Settings (Figure 4).
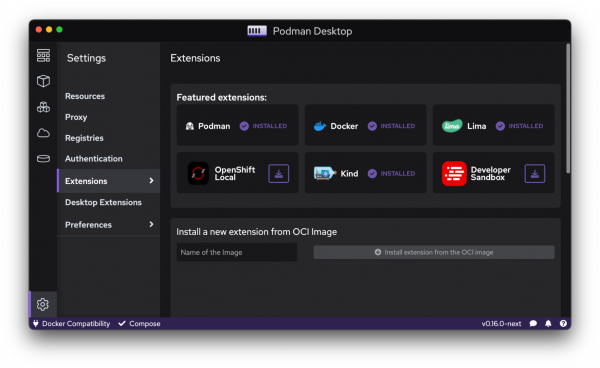
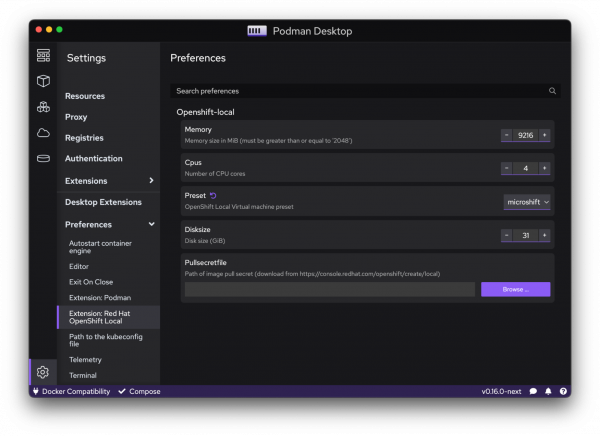
Once installed, the extension provides you the ability to configure the different presets you can use for OpenShift Local:
- Single-node OpenShift powered by OpenShift Container Platform
- Full services set
- Complete and more resource-intensive
- Light and optimized (experimental) powered by Microshift
- Minimal services set
- Fast and lightweight
With Podman Desktop, you can ease the transition of an application from a local environment to a remote production OpenShift environment.
Local Kubernetes with Kind
If you are looking for an even lighter local runtime, Podman Desktop offers the option to use Kind as an alternative container orchestration tool. The use of Kind provides several benefits for developers who are striving to create a development environment that closely mirrors production.
One key advantage of using Kind is that it allows developers to create a multi-node Kubernetes cluster on their local machine. Unlike Docker Compose, which is designed for single-node environments, Kind provides a more realistic environment for testing applications that will be deployed on multiple nodes in production. With Kind, developers can simulate a more complex environment and ensure their applications are ready for production deployment.
Kind creates Kubernetes clusters as containers, which means that developers can easily test their applications with the latest version of Kubernetes without having to install and configure it manually. Kind also simplifies the process of spinning up and tearing down Kubernetes clusters, which can save developers time and reduce the risk of configuration errors.
Creating Kind clusters in Podman Desktop
To create a Kind cluster from Podman Desktop, go into the Settings → Resources page; you'll find a section enabling you to configure a cluster (see Figure 5).
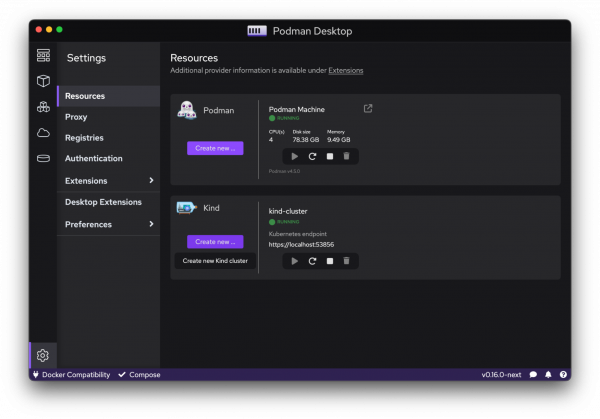
You can choose a name for the cluster and specify the ports to be used by the cluster. You can also set up an Ingress controller (with the project Contour), as shown in Figure 6.
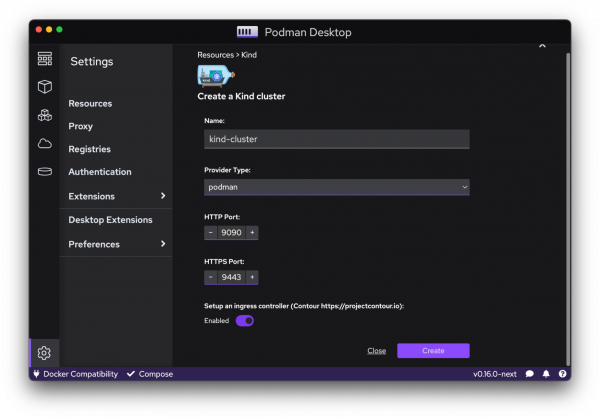
Once the cluster is up and running, it will be your default kubecontext. You can interact with the cluster either from Podman Desktop or the other tools you are using, such as kubectl. If you need to interact with the cluster, you can open the terminal directly from within Podman Desktop.
Using Kind with Podman Desktop allows developers to ensure their local development environment closely mirrors their production environment. By using the same container orchestration tool and environment as production, you can avoid issues that might arise when deploying applications to production, such as configuration differences or compatibility issues. Using Kind with Podman Desktop creates a more efficient and reliable development process that ultimately leads to more successful production deployments.
Developer Sandbox for Red Hat OpenShift extension
We also added an extension for the Developer Sandbox for Red Hat OpenShift, which you can install from the dashboard or the Settings (Figure 7). The Developer Sandbox for Red Hat OpenShift is a free, cloud-based OpenShift environment for developers to create, build, and deploy applications on OpenShift at no cost. With Podman Desktop, you can easily connect to the Developer Sandbox from your local machine and deploy your applications to the cloud-based environment.
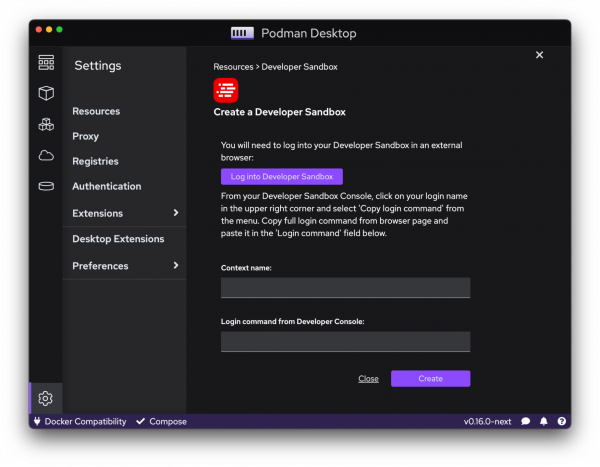
To use Podman Desktop with the Developer Sandbox, you must first sign up for a free account and create a new project in the OpenShift web console. You can then use Podman Desktop to build and test your application locally, using the same container images and environment as you would in production. Once the application is ready for deployment, you can use Podman Desktop to push the container images to the OpenShift registry and deploy your application to the OpenShift environment.
Using Podman Desktop with the Developer Sandbox for Red Hat OpenShift provides several benefits for enterprise developers. It lets you test your applications in a managed Kubernetes environment without having to set up and manage your own infrastructure. It also provides a consistent environment for testing and deployment, which can help reduce the risk of configuration errors and compatibility issues.
[ Tutorial: Deploy and test Kubernetes containers using Podman Desktop ]
What’s next?
We plan to improve Podman Desktop with more capabilities to help you work with containers and facilitate the transition from containers to Kubernetes. We are also planning to extend the support of Kubernetes objects, enabling you to create, run, debug, and more easily manage all different components of your applications.
For developers targeting OpenShift, you'll see more tools integrated with Podman Desktop that make it smoother and more efficient to build your application locally and run/debug it in an environment consistent with production.
More information
Podman Desktop continues its momentum, and we are excited about the road ahead. Visit podman-desktop.io to download the tool and learn more about the project.
- Read more about Podman Desktop on Red Hat Developer: What is Podman Desktop? A developer's introduction
- Visit the Podman website: podman.io
- Explore the Developer Sandbox for Red Hat OpenShift
- Support us by giving a ⭐️!
