In this article, I will show how to install and manage Red Hat Ansible Tower on Red Hat OpenShift Container Platform. Ansible Tower helps you scale IT automation, manage complex deployments, and improve productivity. You can centralize and control your IT infrastructure with a visual dashboard, and it provides role-based access control, job scheduling, integrated notifications, graphical inventory management, and more.
As you may know, Ansible Tower 3.3, the latest release of this automation platform, was released a few weeks ago and added new features. From the release notes you'll see that Ansible Tower 3.3 added support for a container-based installation on top of OpenShift
In this blog, we'll see how easy it is to set up Ansible Tower 3.3 on OpenShift and have it running as a container in just a few minutes.
Overview of the process
We'll follow these steps:
- Log in on an existing OpenShift installation.
- Create a dedicated project where Ansible Tower will be installed.
- Create a persistent volume claim (PVC) and, if it's not already present, create a physical volume (PV).
- Start the installation process.
- Finally, use Ansible Tower as a service and perform a scale-out.
Resources and requirements
Refer to the following resources:
The requirements mentioned in OpenShift Deployment and Configuration for Ansible Tower on OpenShift are:
- Red Hat OpenShift 3.6+
- Per-pod default resource requirements:
- 6GB RAM
- 3 CPU cores
- OpenShift command-line tool (
oc) on the machine running the installer - A set-up and running OpenShift cluster
- Admin privileges for the account running the OpenShift installer
Procedure
So let's start to create the Ansible Tower prerequisites on OpenShift. First, let's log in:
$ oc login myamazingopenshiftcluster -u myuser -p mypassword Username: myuser Password: Login successful. You have access to the following projects and can switch between them with 'oc project <projectname>': *default kube-public kube-service-catalog kube-system management-infra ocp-workshop openshift openshift-ansible-service-broker openshift-infra openshift-logging openshift-node openshift-sdn openshift-template-service-broker openshift-web-console Using project "default". The server uses a certificate signed by an unknown authority. You can bypass the certificate check, but any data you send to the server could be intercepted by others. Use insecure connections? (y/n): y Login successful.
Let's create a new project called tower:
$ oc new-project tower Now using project "tower" on server "https://myamazingopenshiftcluster :443". You can add applications to this project with the 'new-app' command. For example, try: $ oc new-app centos/ruby-22-centos7~https://github.com/openshift/ruby-ex.git to build a new example application in Ruby.
As additional prerequisites, Ansible Tower requires a PVC to be used by a Postgres database to persist its data.
In our case, we are going to create a 10 GB PVC using this YAML file:
$ cat postgres-nfs-pvc apiVersion: v1 kind: PersistentVolumeClaim metadata: name: postgresql spec: accessModes: - ReadWriteOnce resources: requests: storage: 10Gi
Now we can ask OpenShift to create the PVC for us:
$ oc create -f postgres-nfs-pvc persistentvolumeclaim "postgresql" created
Our PVC will be bound to a PV that matches the access method and size.
If you don't have a PV that will be claimed by our PVC, you can follow the official OpenShift documentation to create it.
$ oc get pvc NAME STATUS VOLUME CAPACITY ACCESS MODES STORAGECLASS AGE postgresql Bound vol118 10Gi RWO,RWX 2s
Last, you have to download the installation setup tar file, untar it, and then execute the following:
$ ./setup_openshift.sh -e openshift_host=https://myamazingopenshiftcluster:443 -e openshift_project=tower -e openshift_user=myuser -e openshift_password=mypassword -e admin_password=toweradminpwd-e secret_key=mysecret -e pg_username=postgresuser -e pg_password=postgrespwd -e rabbitmq_password=rabbitpwd -e rabbitmq_erlang_cookie=rabbiterlangpwd
The setup_openshift.sh script will execute some Ansible playbooks and those will manage for you the entire installation by creating your pods, services, and routes.
That's all! In a few minutes, Ansible Tower will be up and running.
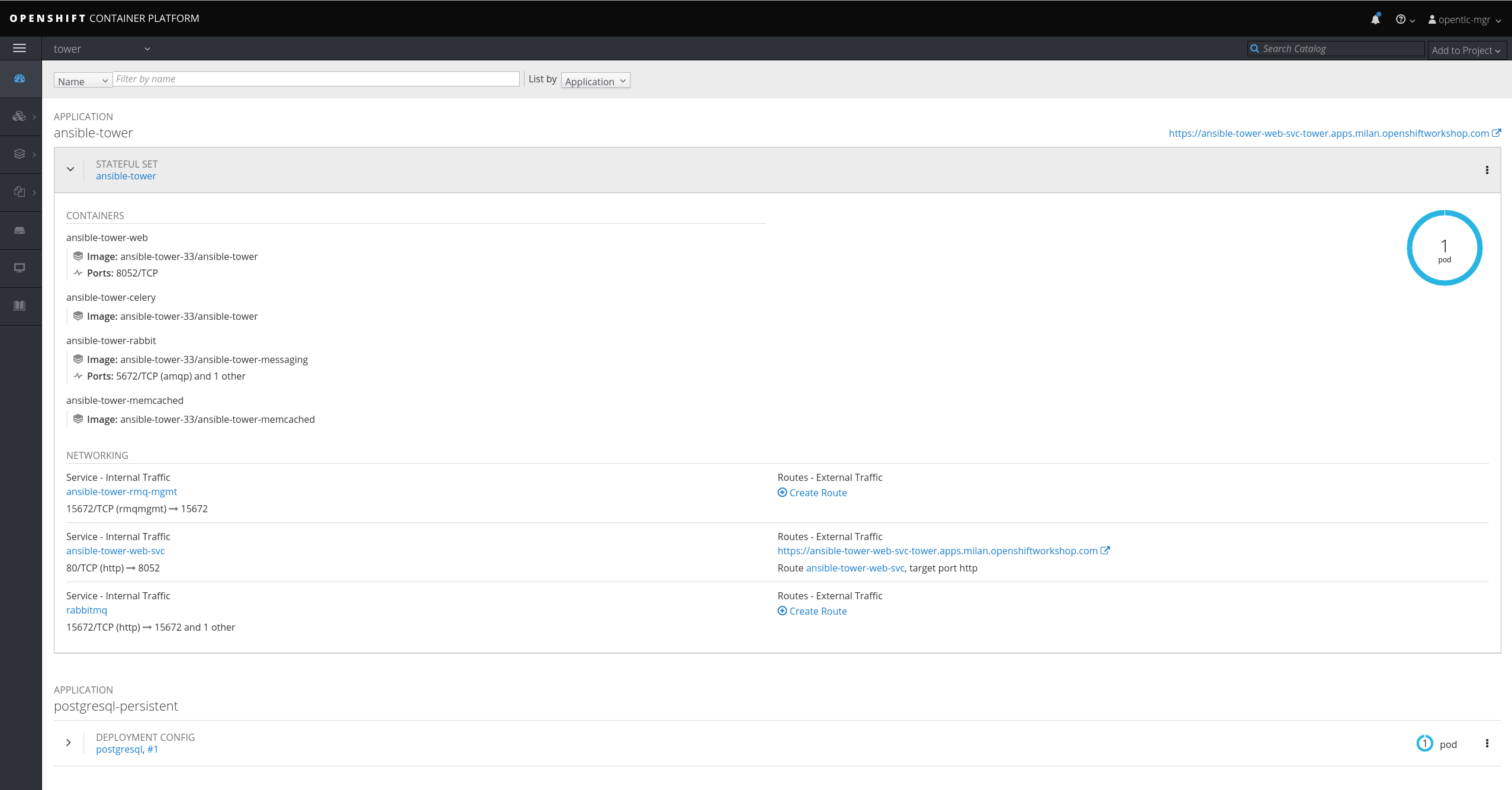
Let's now investigate how Ansible Tower was installed. As you may notice from the UI, there is one pod composed of four containers managed through a StatefulSet.
Run the following command from the CLI:
$ oc describe sts ansible-tower
Name: ansible-tower
Namespace: tower
CreationTimestamp: Tue, 09 Oct 2018 17:14:51 +0200
Selector: app=ansible-tower,name=ansible-tower-web-deploy,service=django
Labels: app=ansible-tower
name=ansible-tower-web-deploy
service=django
Annotations: kubectl.kubernetes.io/last-applied-configuration={"apiVersion":"apps/v1beta1","kind":"StatefulSet","metadata":{"annotations":{},"name":"ansible-tower","namespace":"tower"},"spec":{"replicas":1,"templa...
Replicas: 1 desired | 1 total
Pods Status: 1 Running / 0 Waiting / 0 Succeeded / 0 Failed
Pod Template:
Labels: app=ansible-tower
name=ansible-tower-web-deploy
service=django
Service Account: awx
Containers:
output truncated
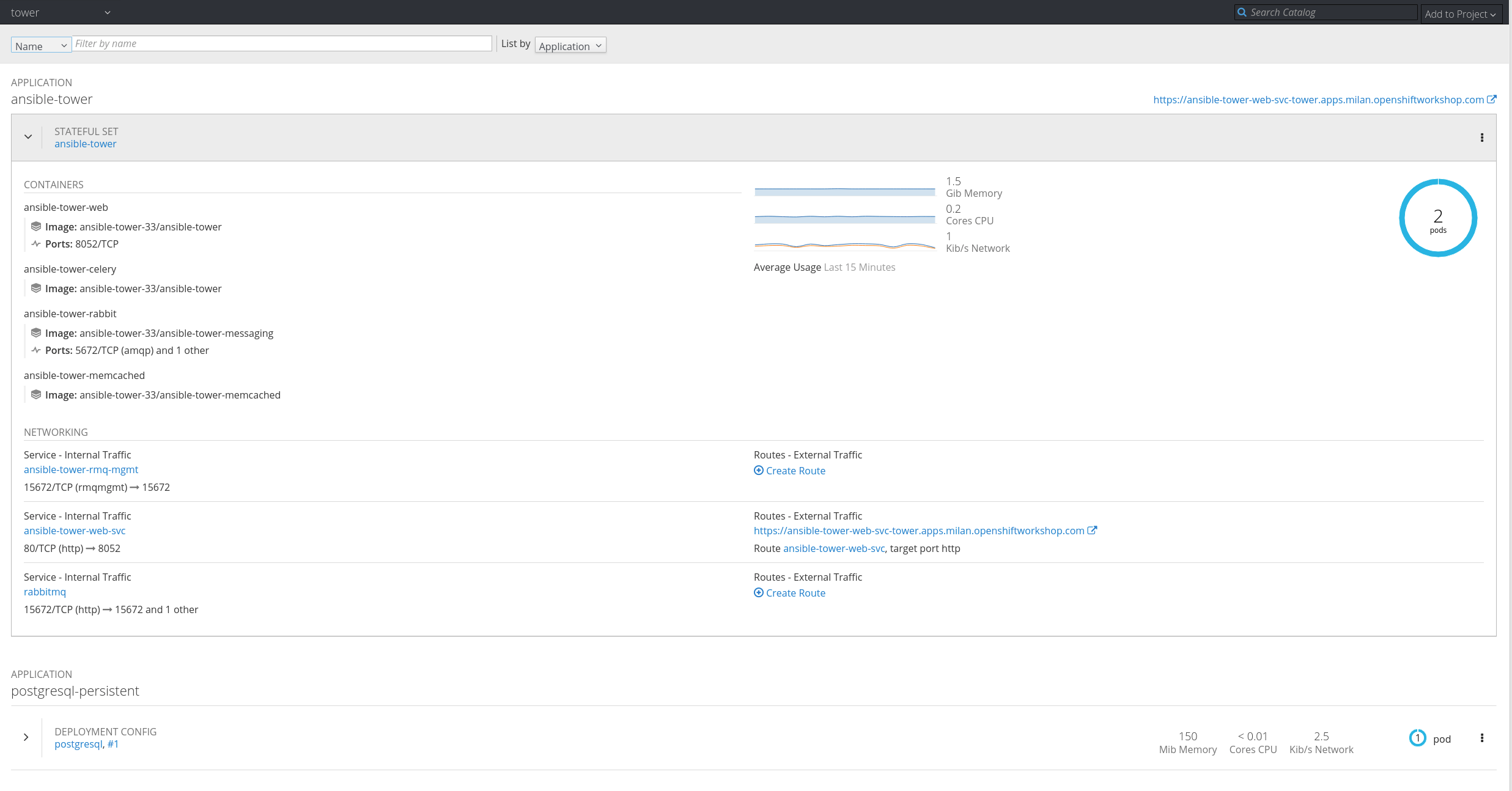
As you may notice, the Replicas value is 1, so one pod (that is, one Ansible Tower instance) will be running.
The good thing is that if you can scale up your StatefulSet replica count, Ansible Tower will be scaled accordingly!
You can manage this change by using the UI and editing the YAML file or by using oc.
Take a look at the current status:
$ oc get sts NAME DESIRED CURRENT AGE ansible-tower 1 1 3d
Here's how to scale up:
$ oc scale --replicas=2 sts ansible-tower statefulset "ansible-tower" scaled
Now check the running configuration again:
$ oc get sts NAME DESIRED CURRENT AGE ansible-tower 2 2 3d
Here's what the web console shows now:
That's all! If you want to see a short demo of the process, check out this video:
Last updated: March 24, 2023