Enterprises generate an overwhelming amount of unstructured information, documents, policies, PDFs, wikis, knowledge bases, HR guidelines, legal documents, system manuals, architecture diagrams, and more. When employees struggle to find accurate answers quickly, productivity suffers and undocumented knowledge becomes a bottleneck.
Retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) solves this problem by grounding LLM responses in your company’s knowledge. Instead of relying on a model’s memory or hallucinations, RAG retrieves relevant document chunks from a vector database and supplies them to the model at inference time.
This blog explores the RAG quickstart, a comprehensive blueprint for deploying an enterprise RAG application on Red Hat OpenShift AI. It features high-performance inference, safety guardrails, and automated data ingestion pipelines. AI quickstarts are deployable examples that connect Red Hat technology to business value. You can try them today in the AI quickstart catalog.
What is RAG?
RAG is an architectural pattern that improves the output of an LLM by referencing an authoritative knowledge base outside of its training data.
- Retrieval: When a user asks a question, the system searches a vector database for relevant snippets from your documents.
- Augmentation: The system adds those snippets to the user's original prompt as context.
- Generation: The LLM uses this enriched context to generate an accurate, hallucination-free response.
The enterprise difference
While a standard RAG setup serves as a functional proof of concept, deploying enterprise RAG system requires an architecture designed for resilience and compliance. It requires:
- Security and safety: Guardrails to prevent toxic outputs and protect sensitive data.
- Scalability: The ability to handle thousands of documents and concurrent users.
- Governance: Clear data lineage from Amazon S3 or Git to the Vector database.
- Multi-tenancy: Segmented knowledge bases for different departments like HR, Legal, and Sales.
Architecture and features
To transition from a demo to a deployed system, this AI quickstart automates the provisioning of critical components like model serving, vector databases, and ingestion pipelines. Figure 1 shows how the infrastructure is built on Red Hat OpenShift AI.
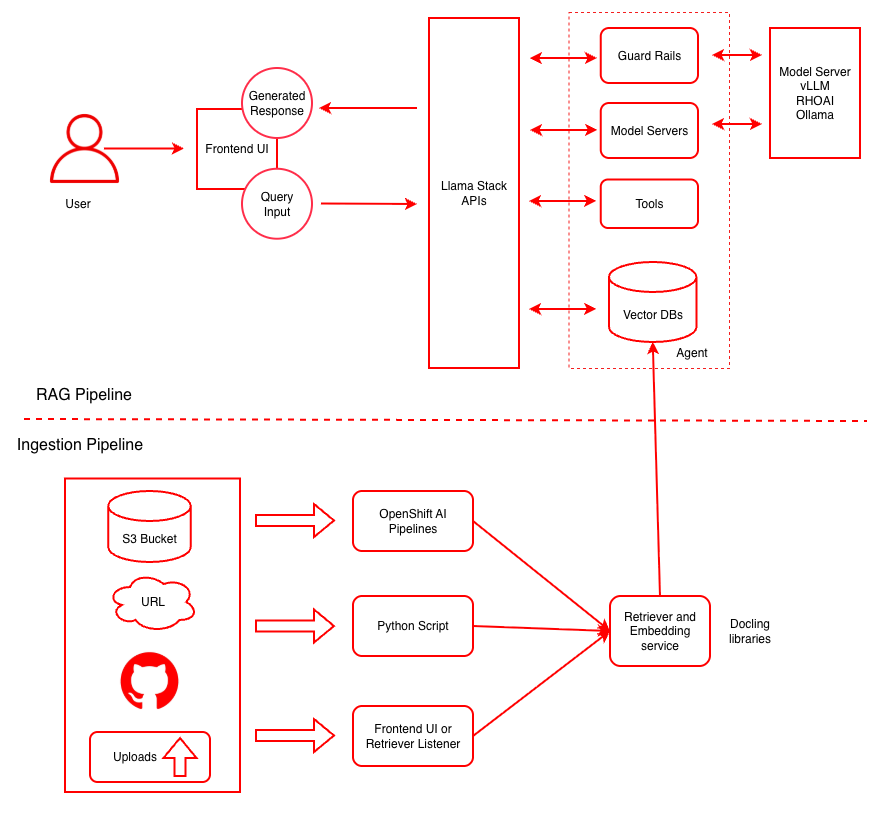
Model serving and safety guardrails
To serve the LLM, the AI quickstart uses the ServingRuntime and InferenceService custom resource definitions (CRDs) in Red Hat OpenShift AI. This allows for production-grade serving with auto-scaling and monitoring.
This setup provides standardized, GPU-aware, and scalable Kubernetes-native endpoints. This removes the complexity of manual model deployment and lifecycle management.
The AI quickstart deploys two models: the primary LLM and a safety guardrail model, such as Llama Guard.
When you view the OpenShift console under your namespace, you will see two running pods: the main model and the safety shield. All requests are routed through the shield to ensure enterprise compliance.
The Llama Stack server
This AI quickstart deploys a Llama Stack server that acts as a unified and flexible, and open source platform for building AI applications. It ensures portability across different environments and prevents vendor lock-in.
Llama Stack provides integrated, enterprise-focused features like safety guardrails, telemetry, evaluation tools, and complex agentic orchestration, which can be challenging to build from scratch. This simplifies the creation of production-ready AI.
You can find the configuration in rag-values.yaml, which connects vLLM, the PGVector vector store, and tools.
Enterprise vector storage (PGVector and Minio)
To store document embeddings for a fictitious company, FantaCo, the AI quickstart creates specific vector databases for departments: HR, Legal, Procurement, Sales, and Tech Support.
The architecture uses Minio as a local S3-compatible store for raw document staging. It then uses PGVector as a high-performance enterprise vector database. This combination ensures data isolation. For example, a query from the HR department only retrieves HR documents, which prevents unauthorized data leakage.
Automated ingestion pipelines
Data can be ingested from GitHub, S3, or direct URLs. The AI quickstart uses Kubeflow Pipelines to automate the ingestion workflow. This process transforms documents from various sources into vector embeddings and stores them in a PGVector database for efficient retrieval. You can also use the bring your own document (BYOD) feature in the chatbot interface to upload files for immediate testing.
Data science workbenches (notebooks)
A pre-configured Jupyter Notebook is provided to allow data scientists to experiment with the ingestion logic.
In the OpenShift AI dashboard, select Data Science Projects, and launch the Workbench. This pre-configured notebook contains the logic to orchestrate a Kubeflow pipeline that fetches documents from an S3 bucket, generates embeddings, and ingests them into PGVector.
Deployment modes: OpenShift vs. Local
The AI quickstart supports two deployment strategies depending on the hardware available to you:
- OpenShift (recommended): Uses full GPU acceleration, enterprise security, and automated pipelines.
- Local (development): Allows running the stack via Docker or Podman. However, local performance is often slower because of limited VRAM and reliance on CPU, M1, or M2 chips compared to enterprise NVIDIA GPUs.
Getting started
Follow these requirements to prepare your environment and gather the necessary credentials before you begin the deployment.
Prerequisites
Here is what you need to get started.
Business requirements:
- A need to centralize fragmented knowledge across teams
- Interest in improving productivity, onboarding, policy accuracy, and customer-facing knowledge
- Stakeholder support for AI-powered internal search
- Understanding of governance and data privacy requirements
Technical requirements:
Before deploying the RAG AI quickstart, ensure:
- Red Hat OpenShift cluster is configured (4.19+ recommended)
- Red Hat OpenShift AI is installed (2.22+ recommended)
- GPU worker nodes are enabled
- Sufficient cluster resources (GPU, memory, storage)
- oc CLI access
- Helm installed
Accounts and keys:
- Tavily Websearch API key
- Hugging Face token
- Access to Meta Llama model
- Access to Meta Llama Guard model
Source code
Clone the RAG AI quickstart repository:
git clone https://github.com/rh-ai-quickstart/RAG
cd RAGSample data
Fantaco sample company documents (HR, benefits, onboarding) are included in the GitHub repository.
Configuration
Check GPU node taints. GPU nodes are high-cost, shared resources in an OpenShift cluster, so taints are used to restrict scheduling to workloads that explicitly require GPU acceleration. Corresponding tolerations must be configured to allow model-serving and embedding workloads to run on these GPU nodes.
Ops teams can view taints in the OpenShift console by selecting Compute → Nodes → GPU Node → YAML.
spec: taints: - key: nvidia.com/gpu effect: NoScheduleThis ensures model-serving pods are scheduled correctly.
Review Helm chart structure. The RAG Helm chart deploys the RAG UI along with the dependencies defined in
deploy/helm/rag/Chart.yaml:dependencies: - name: pgvector version: 0.5.1 repository: https://rh-ai-quickstart.github.io/ai-architecture-charts condition: pgvector.enabled - name: llm-service version: 0.5.2 repository: https://rh-ai-quickstart.github.io/ai-architecture-charts condition: llm-service.enabled - name: configure-pipeline version: 0.5.4 repository: https://rh-ai-quickstart.github.io/ai-architecture-charts condition: configure-pipeline.enabled - name: ingestion-pipeline version: 0.5.1 repository: https://rh-ai-quickstart.github.io/ai-architecture-charts condition: ingestion-pipeline.enabled - name: llama-stack version: 0.5.2 repository: https://rh-ai-quickstart.github.io/ai-architecture-charts condition: llama-stack.enabled - name: mcp-servers version: 0.5.7 repository: https://rh-ai-quickstart.github.io/ai-architecture-charts condition: mcp-servers.enabledThis automatically installs the following:
PGVectordatabase- Model servers on OpenShift AI
- Embedding pipelines
- Chatbot UI
- Workbench: Jupyter Notebook
- Llama Stack server
- MCP Servers (optional)
Review example values file:
vi helm/rag-values.example.yamlThis defines:
- GPU scheduling rules
- Model choices
- Pipeline behavior
- Vector DB settings
Deployment: Install the RAG AI quickstart
Log in to OpenShift:
oc login --token=<<token>> --server=<<api-server-url>>View GPU taints (optional):
oc get nodes -o jsonpath='{range .items[*]}{.metadata.name}{" "}{.spec.taints}{"\n"}{end}'List available models:
make list-models [INFO] Listing available models... model: llama-3-1-8b-instruct (meta-llama/Llama-3.1-8B-Instruct) model: llama-3-2-1b-instruct (meta-llama/Llama-3.2-1B-Instruct) model: llama-3-2-1b-instruct-quantized (RedHatAI/Llama-3.2-1B-Instruct-quantized.w8a8) model: llama-3-2-3b-instruct (meta-llama/Llama-3.2-3B-Instruct) model: llama-3-3-70b-instruct (meta-llama/Llama-3.3-70B-Instruct) model: llama-3-3-70b-instruct-quantization-fp8 (meta-llama/Llama-3.3-70B-Instruct) model: llama-guard-3-1b (meta-llama/Llama-Guard-3-1B) model: llama-guard-3-8b (meta-llama/Llama-Guard-3-8B) model: qwen-2-5-vl-3b-instruct (Qwen/Qwen2.5-VL-3B-Instruct)Install the RAG application:
# Application will be installed in rag namespace # It will deploy llama-3-1-8b-instruct model # If the gpu node has taint, specify the toleration. make install NAMESPACE=rag LLM=llama-3-1-8b-instruct LLM_TOLERATION="nvidia.com/gpu"
The installer will:
- Prompt for Hugging Face token
- Prompt for Tavily Search API key
- Generate a local
rag-values.yamlfile (first run only)
After installation, OpenShift provisions:
- RAG UI
- Vector DB
- Llama Stack server
- Llama inference services
- Document ingestion pipelines
- A ready-to-run notebook
Execution: Run pipelines, models, and the chatbot interface
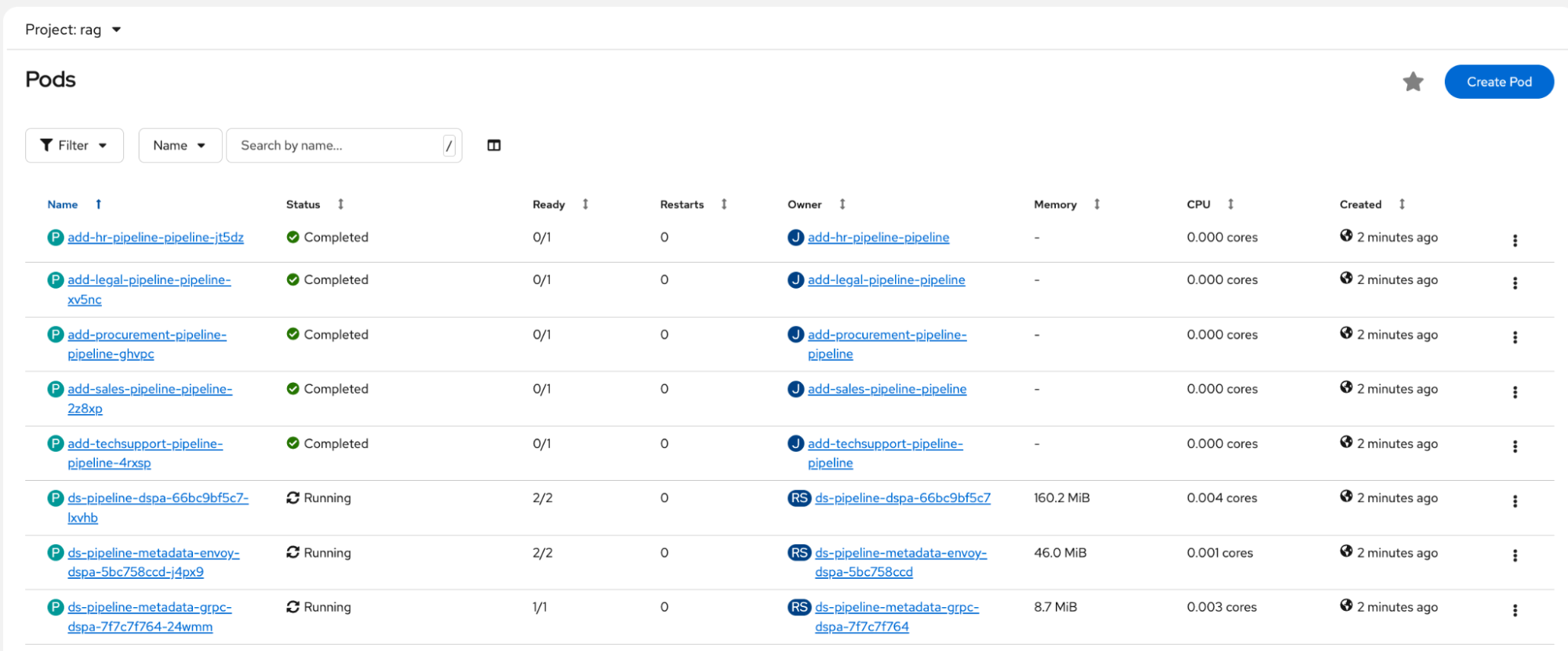
- Verify running pods: After the installation finishes, navigate to Workloads → Pods in the rag namespace.Verify the pods are in Running or Completed status (Figure 2).
Launch Pipelines in OpenShift AI. Navigate to Red Hat OpenShift AI → Data Science Pipelines → Runs (project: rag). See Figure 3.
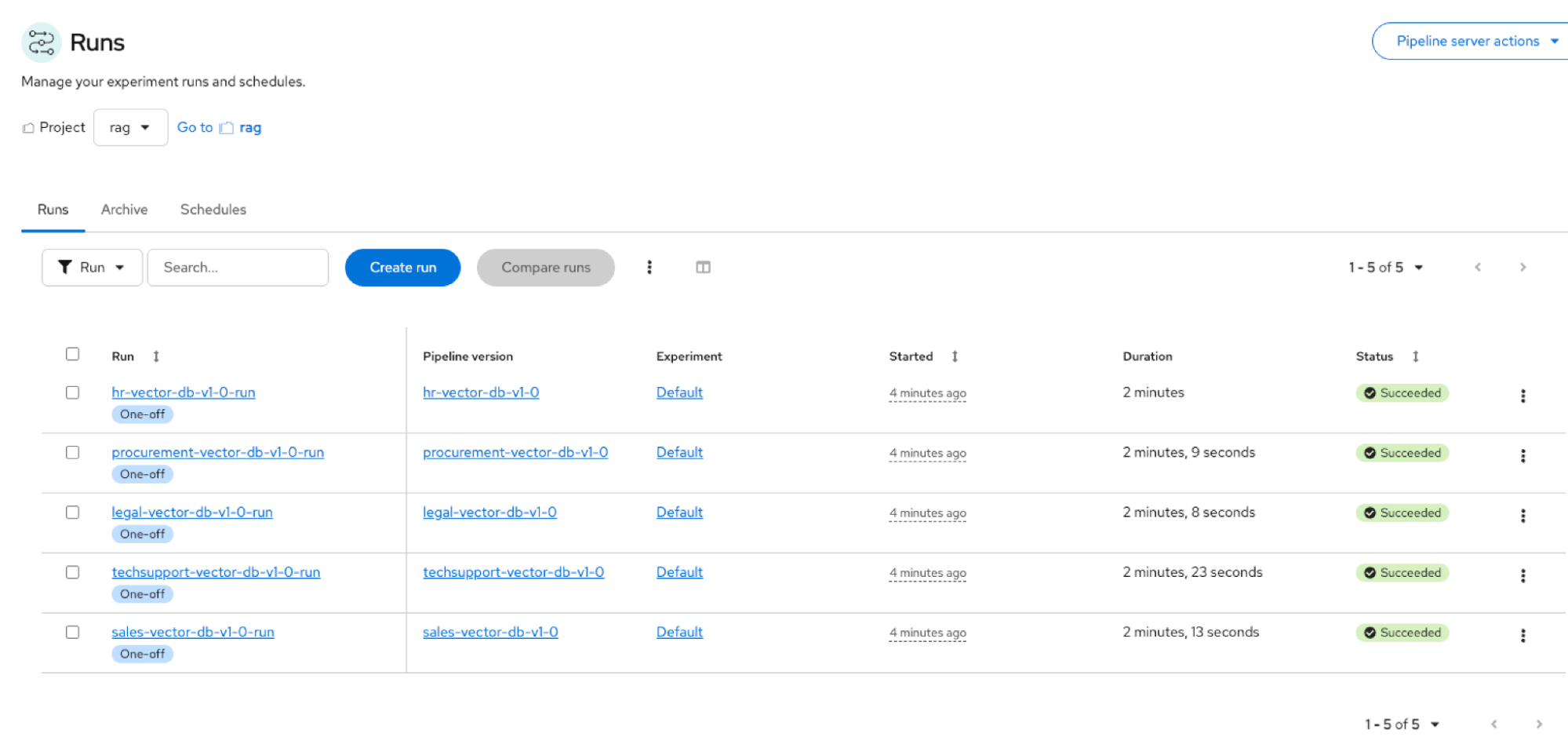
Figure 3: RAG AI quickstart ingestion pipelines populating the RAG vector database. Launch the Notebook. Navigate to Red Hat OpenShift AI → Data Science Projects (project: rag). Launch the rag-pipeline-notebook.
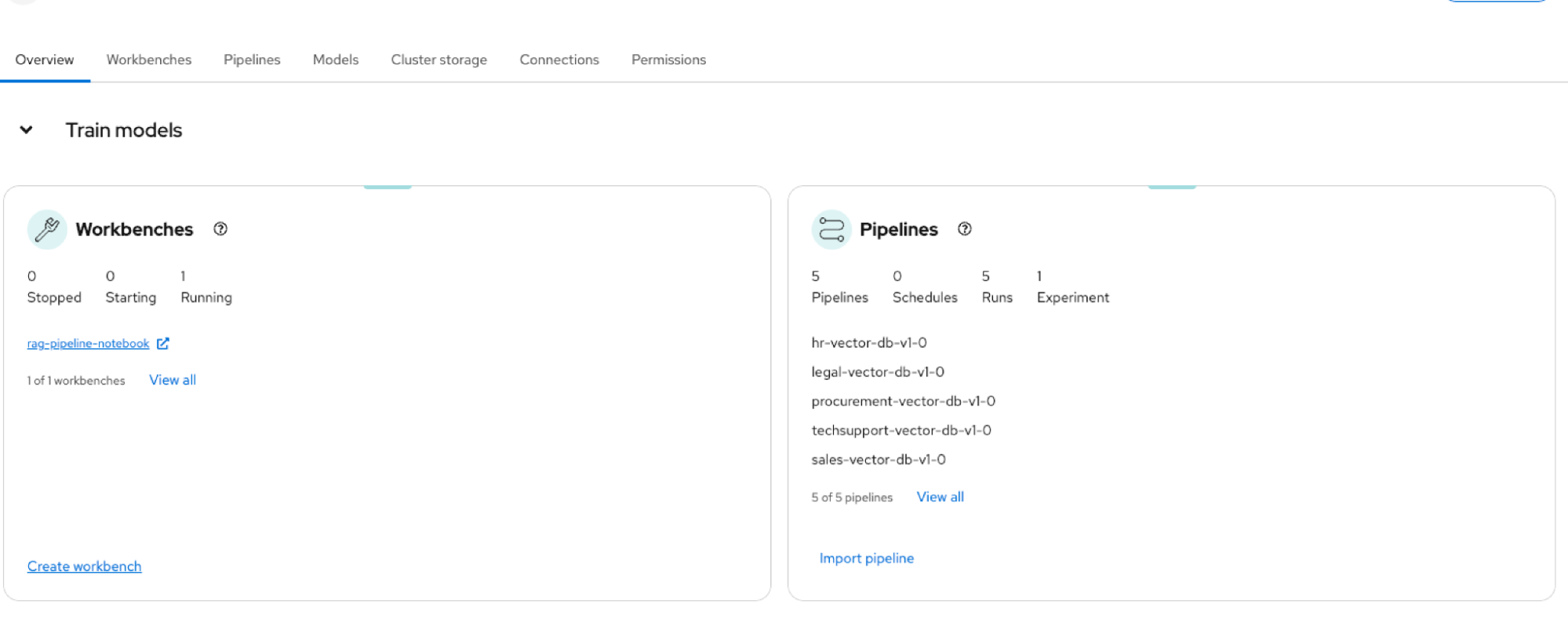
Figure 4: Workbenches and pipelines created during the RAG AI quickstart deployment in OpenShift AI. Verify deployed models. Navigate to Models → Model deployments (project: rag).
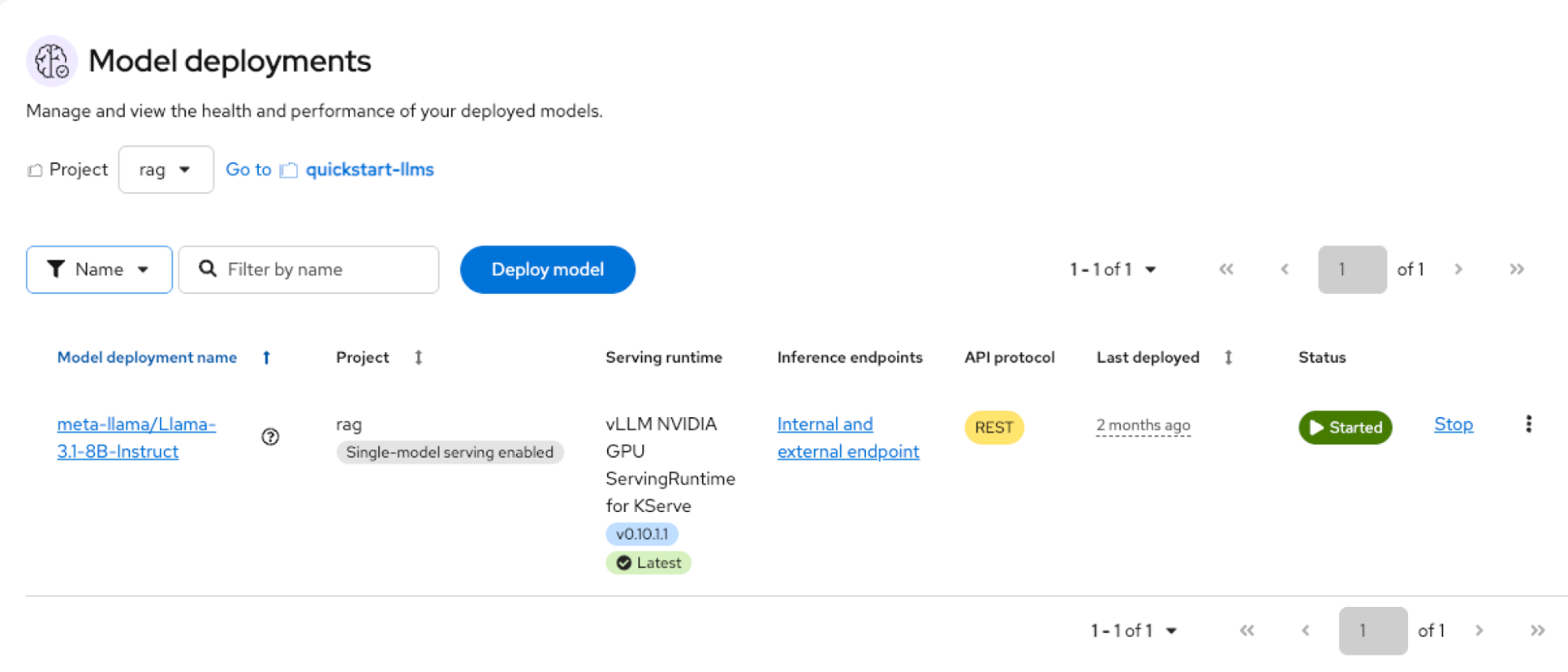
Figure 5: Deployed LLM inference service in Red Hat OpenShift AI provisioned by the RAG AI quickstart. Launch the chat application. Navigate to Networking → Routes → rag. Select the location URL to load the chatbot UI.
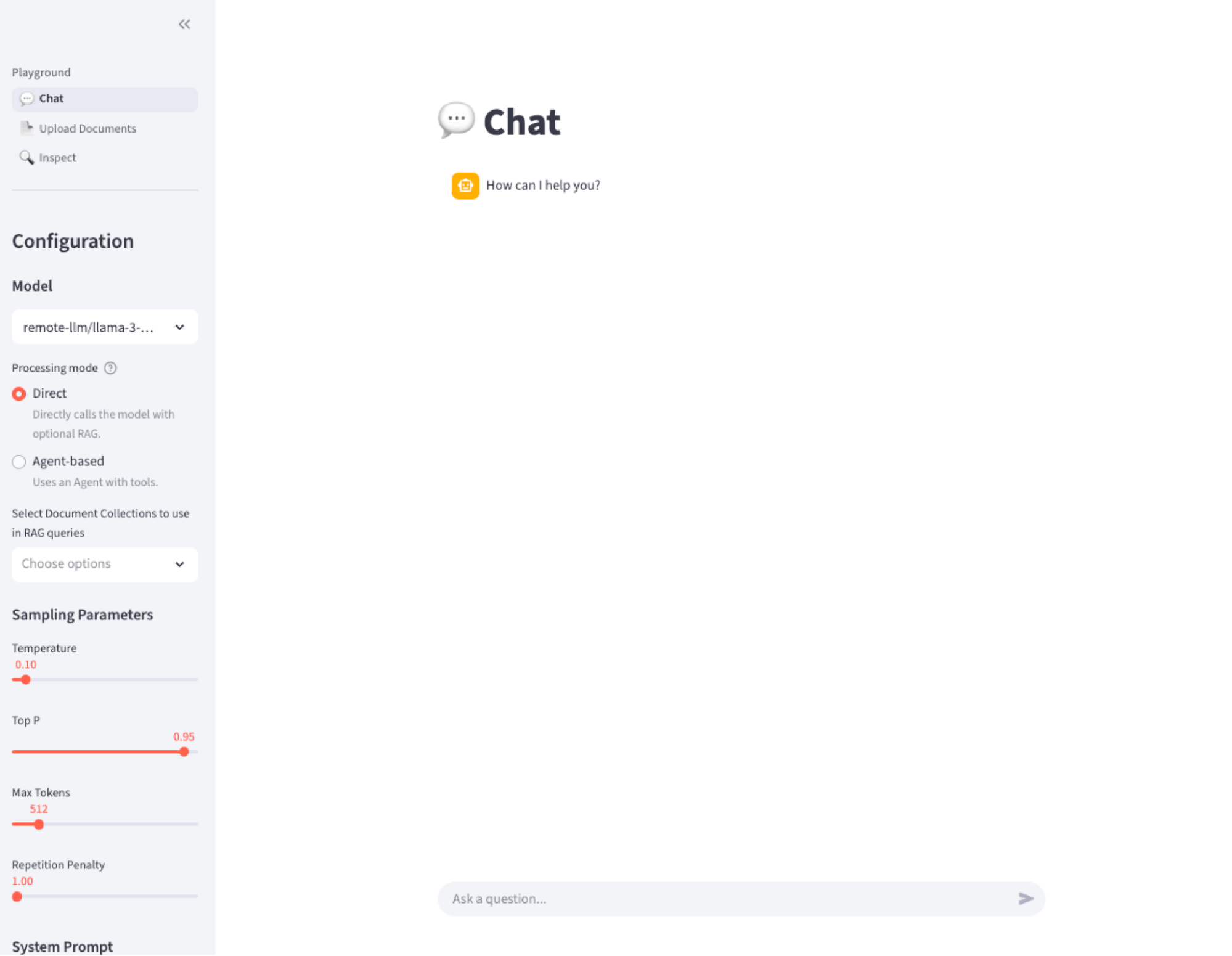
Figure 6: RAG AI quickstart–deployed chatbot interface.
Verification: Test direct and agentic RAG
After deploying the application, use the chatbot interface to verify that the system accurately retrieves information from both internal documents and external sources.
Test direct RAG (database agent)
You can test direct RAG by asking a question like, "What are my HR benefits at Fantaco?" To do this, select the Database Agent labeled hr-vector-db-v1-0. The system retrieves the answer from Fantaco HR documents to provide accurate information.
Test agentic RAG (websearch agent)
To test agentic RAG, query a real-time event, such as "Who won the Super Bowl of 2025?" and select the Websearch Agent. In this mode, the system uses the Tavily external search tool to find and return a correct, real-time answer. This process demonstrates how the chatbot identifies the right tool for the job when internal data is insufficient.
Wrap up
In this guide, you learned how to:
- Understand direct RAG and agentic RAG
- Deploy the RAG AI quickstart on OpenShift AI
- Ingest enterprise documents using pipelines
- Serve Llama models on GPU nodes
- Launch an enterprise-ready RAG chatbot
- Run queries using both internal and external retrieval agents
You now have a fully operational enterprise RAG assistant capable of centralizing your company’s knowledge and enhancing employee productivity.
Next steps
- Read Context as architecture: A practical look at retrieval-augmented generation.
- Start a trial to explore what you can do with Red Hat OpenShift AI.
- Browse the AI quickstart catalog for more example use cases.
