Red Hat AI quickstarts are a catalog of ready-to-run, industry-specific use cases for your Red Hat AI environment. Each AI quickstart is simple to deploy, explore and extend. They give teams a fast, hands-on way to see how AI can run solutions on enterprise-ready, open source infrastructure. You can read more about AI quickstarts in AI Quickstarts: an easy and practical way to get started with Red Hat AI.
The it-self-service-agent quickstart shows you how to use agentic AI to automate IT processes within your organization on Red Hat OpenShift AI. The README.md for the AI quickstart helps you explore its key aspects. However, we learned a lot about agentic deployments during development. We could not fit everything into the exploration covered in the README.md without it making it too long to read at once.
Building production-ready AI agents is deceptively complex. Beyond the large language model (LLM) integration, you need conversation state management across multiple turns, effective evaluation frameworks for non-deterministic systems, enterprise integrations, distributed tracing across async components, and safety guardrails—all while keeping infrastructure costs reasonable. This orchestration layer can take weeks to build before you write your first line of business logic.
To share our insights and what we learned, we've planned a blog series where each post reviews a specific topic in detail, using the quick start as a basis.
This post focuses on the initial setup of a laptop refresh agent. The rest of this series will guide you through bringing AI to production. We'll soon cover how to integrate these agents into your existing workflows like Slack and ServiceNow. We'll also discuss the architectural trade-offs of prompt engineering and the infrastructure needed to evaluate, debug, and scale agentic applications in an enterprise environment.
Follow the series:
- Part 1: AI quickstart: Self-service agent for IT process automation
- Part 2: AI meets you where you are: Slack, email & ServiceNow
- Part 3: Prompt engineering: Big vs. small prompts for AI agents
- Part 4: Automate AI agents with the Responses API in Llama Stack
If you are interested in a bit more detail on the business benefits of using agentic AI to automate IT processes, check out From manual to agentic: streamlining IT processes with Red Hat OpenShift AI.
Overview of the self service agent AI quickstart
This AI quickstart provides a reusable framework for request routing, agent services, and evaluation that you can apply to many IT processes. While the AI quickstart uses a laptop refresh as an example, you can adapt these components to other workflows, such as Privacy Impact Assessments, RFP generation, access requests, software licensing, or other structured IT workflows.
The laptop refresh implementation provides a starting point to help you understand these patterns and adapt them to your organization's most critical processes.
The top-level architecture is shown in Figure 1.
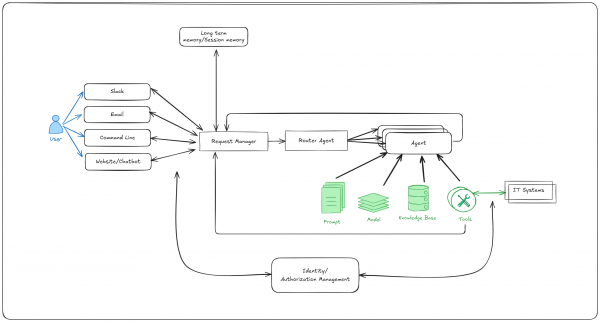
What you'll need
Start in testing mode (recommended for first-time exploration) with minimal setup, or go straight to production mode for full event streaming:
- Testing mode: OpenShift or Kubernetes cluster (no special operators required)
- Production mode: Red Hat OpenShift 4.17 or later with Serverless and Kafka operators installed
- LLM access: Llama 3 70B endpoint with API credentials (cluster doesn't need GPU—connects to external inference service)
- Optional: Llama Guard 3 for safety shields, Slack workspace for chat integration, ServiceNow instance for ticketing
- Optional: OpenShift tracing integration with Tempo Stack, cluster observability, and OpenTelemetry (OTEL) operators
What the AI quickstart covers
The AI quickstart takes you through:
- Deploying the agentic system to Red Hat OpenShift AI
- Requesting a laptop refresh through a command-line interface
- Integration with Slack and requesting a laptop refresh through Slack
- Integration with a real ServiceNow instance and viewing the request you created in the ServiceNow UI
- Enabling email support and requesting a laptop refresh through email
- Running multi-turn evaluations using the open source DeepEval framework to validate business requirements like policy compliance and catch regressions
- Viewing distributed traces with OpenTelemetry to track LLM calls and Model Context Protocol (MCP) server interactions, and identify performance bottlenecks in production
- Exploring different prompting approaches and the trade-offs between a single large prompt and multi-step prompts using LangGraph
- Setting up PromptGuard to help prevent prompt injection attacks
- Setting up LlamaGuard to add content moderation
In each of the steps, the AI quickstart takes you through each topic with a focus on helping you quickly deploy and explore that topic. In this series, we'll dive deeper into the topic and cover interesting things we learned along the way. As a few examples:
- What kinds of failures we saw during evaluations and how they helped us iteratively improve the prompt
- How many tokens a conversation takes when using one large prompt versus a multi-step prompt with LangGraph
- Typical failure modes when using a multi-step prompt instead of a large prompt
- The differences between the OpenAI Responses API and the Llama Stack agentic APIs
- Performance characteristics: 99.7% of request processing time was spent in LLM inference, proving minimal infrastructure overhead while providing enterprise-grade observability and integration.
Next steps
Try it yourself: Run through the self-service agent AI quickstart (60 to 90 minutes) to deploy a working multi-agent system.
- Save time: Rather than spending two to three weeks building agent orchestration, evaluation frameworks, and enterprise integrations from scratch, you'll have a working system in under 90 minutes. Start in testing mode (simplified setup, mock eventing) to explore quickly, then switch to production mode (Knative Eventing + Kafka) when ready to scale.
- What you'll learn: Production patterns for AI agent systems that apply beyond IT automation, such as how to test non-deterministic systems, implement distributed tracing for async AI workflows, integrate LLMs with enterprise systems safely, and design for scale. These patterns transfer to any agentic AI project.
- Customization path: The laptop refresh agent is just one example. The same framework supports Privacy Impact Assessments, RFP generation, access requests, software licensing, or your own custom IT processes. Swap the specialist agent, add your own MCP servers for different integrations, customize the knowledge base and define your own evaluation metrics.
This will give you hands-on experience and context for the deep dives in this series.
Learn more
If this blog post has sparked your interest in the IT self-service agent AI quickstart, here are additional resources.
- Explore more AI quickstarts: Browse the AI quickstarts catalog for other production-ready use casesl including fraud detection, document processing and customer service automation.
- Get help: Questions or issues? Open an issue on the GitHub repository or file an issue.
- Learn more about the tech stack:
- Read part 2: AI meets you where you are: Slack, email & ServiceNow
