Red Hat OpenShift 4.20, based on Kubernetes 1.33 and CRI-O 1.33, is now generally available. This article highlights notable new features, updates, and fixes in this release for developers.
Enhanced AI, core, and virtualization capabilities for developers
Red Hat OpenShift 4.20 offers enhanced functionality for developers, with new features for multicluster support of Red Hat OpenShift Lightspeed, Red Hat OpenShift Virtualization, observability, the OpenShift console, platform services, and the developer experience.
Developer experience
Red Hat OpenShift 4.20 enhances the developer experience with changes to Red Hat Developer Hub, Podman Desktop, and Red Hat OpenShift Dev Spaces.
Red Hat Developer Hub
Red Hat Developer Hub 1.8, supported on Red Hat OpenShift, brings a streamlined developer experience and accelerated onboarding with centralized tools and docs.
A new ServiceNow plug-in lets you track the status of your requests directly within Red Hat Developer Hub, without context switching. The catalog also now features two certified plug-ins from key partners: IBM and Dynatrace. The adoption insights plug-in is now generally available and enabled by default—giving you immediate access to valuable metrics.
Developer Lightspeed for Red Hat Developer Hub is now available as a developer preview.
For an in-depth review of all of the latest features, including updates for plug-ins and templates, see the Red Hat Developer Hub 1.8 release notes.
Podman Desktop
The latest Podman Desktop 1.22 release includes several features designed to streamline your container workflows. We improved the user experience with clearer dashboard notifications and an updated onboarding flow, making it easier to get started.
You can switch namespaces and environments in the Kubernetes user interface to manage multiple clusters without leaving the application. Libkrun as the default provider on macOS provides GPU access for containers, which is helpful for AI workloads. The Podman Desktop setup now automatically includes the newly released Podman binary for Windows on ARM64 architectures, allowing you to install and run containers natively without extra steps or emulation. You can also switch between rootless and rootful Podman machines more easily.
Several upgrades to extensions are available in this release:
- Apple Containers extension lets you view and manage your Apple containers without switching tools.
- AI Lab model catalog has been updated to provide access to the latest models (GPT-OSS, Granite 4.0, Gemma 3n, Phi 4) for local AI development.
- Minc extension lets you start MicroShift in a container for a lightweight Kubernetes development experience.
- Run Red Hat Enterprise Linux in virtual machines directly from Podman Desktop.
To learn more, refer to the Podman Desktop release notes.
Red Hat OpenShift Dev Spaces
Red Hat OpenShift Dev Spaces 3.23, based on Eclipse Che 7.107, is now available. It includes more Jetbrains IDEs and host IDEs on local infrastructure, with added support for Rider, GoLand, and PhpStorm. In air-gapped environments, administrators can now host these IDEs on an internal network, which removes the need to download them from the internet.
Administrators can now deploy an on-premise instance of the openvsx extension registry where they can host extensions internally and point Dev Spaces to it.
Dev Spaces can now run on OpenShift clusters using ARM64 CPUs, which gives developers the ability to run and test applications on ARM64 architecture.
Admins can also configure an automatic pruner to clean up unused workspace objects. This reduces etcd usage and helps OpenShift Dev Spaces run at scale.
To find out what else is new in OpenShift Dev spaces, see the release notes.
Multicluster support for Red Hat OpenShift Lightspeed
Red Hat OpenShift Lightspeed is a generative AI-based virtual assistant integrated into the OpenShift web console. OpenShift Lightspeed now offers multicluster support with Red Hat Advanced Cluster Management for Kubernetes. Red Hat Advanced Cluster Management users can now attach ManagedCluster and ManagedClusterInfo custom resources in Red Hat OpenShift Lightspeed to get context-aware answers about their managed clusters.
To discover what else is new with Red Hat OpenShift Lightspeed, see the release notes.
Observability and monitoring
Troubleshooting complex networking just got faster. The sysctl node-exporter collector is a new tool for site reliability engineers (SREs) and operations teams. It helps you troubleshoot complex networking issues by pulling kernel-level metrics directly in Prometheus, which dramatically reduces the time it takes to diagnose problems.
To improve scalability and stability, especially in large, complex clusters where many teams are defining their own custom resources, kube-state-metrics is now enhanced with multitenancy support for custom resource states.
You can now directly change the log verbosity of the metric-server. This is a small but important quality-of-life improvement that gives you the granular control you need when actively debugging an issue.
Red Hat OpenShift 4.20 also includes observability and monitoring improvements. NetworkPolicy support allows administrators to enforce a zero trust security model and lock down network traffic to and from the monitoring stack.
In addition, monitoring stack components have been updated with the latest performance optimizations, bug fixes, and security patches.
Log collection, log storage, and log gather
Red Hat OpenShift 4.20 makes it easier to use AWS S3 for cost-effective, high-volume, long-term log storage. This helps centralize logs to reduce costs, ensure compliance, and improve security analysis and troubleshooting.
CloudWatch's assumeRole authentication has also been expanded to support both iamRole and awsAccessKey types for consistent authentication logic across Red Hat services and to prepare for future S3 integration.
Safeguard against data loss with LokiStack's new Running versus Ready states. LokiStack now differentiates between Running and Ready states, enabling alerts for unready instances that previously led to unnoticed data loss. A comprehensive approach to Loki troubleshooting pinpoints bottlenecks, optimizes parameters, and integrates upstream insights with Red Hat's recommendations for quicker resolutions.
Using the support log gather operator, developers can now trigger log collection to pass to Red Hat support teams. You can also customize the operator deployment to enable automatic log upload to a linked support case, and enable non-privileged users to trigger log collection while preventing privilege escalation paths.
Application observability and integrations
In Distributed Tracing 3.7, the OpenTelemetry Probabilistic Sampling processor is now available in tech preview. Implement randomized sampling to lower your span collection costs without sacrificing critical trace data. You can also deploy custom exporters that let you deploy any third-party exporters you might need.
Tempo trace storage has also been upgraded to version 2.8.2. This version brings improvements to TraceQL queries and Tempo compactor memory. Finally, we are now exposing the Tempo gateway using route with reencrypt to support wildcard certificates.
Console
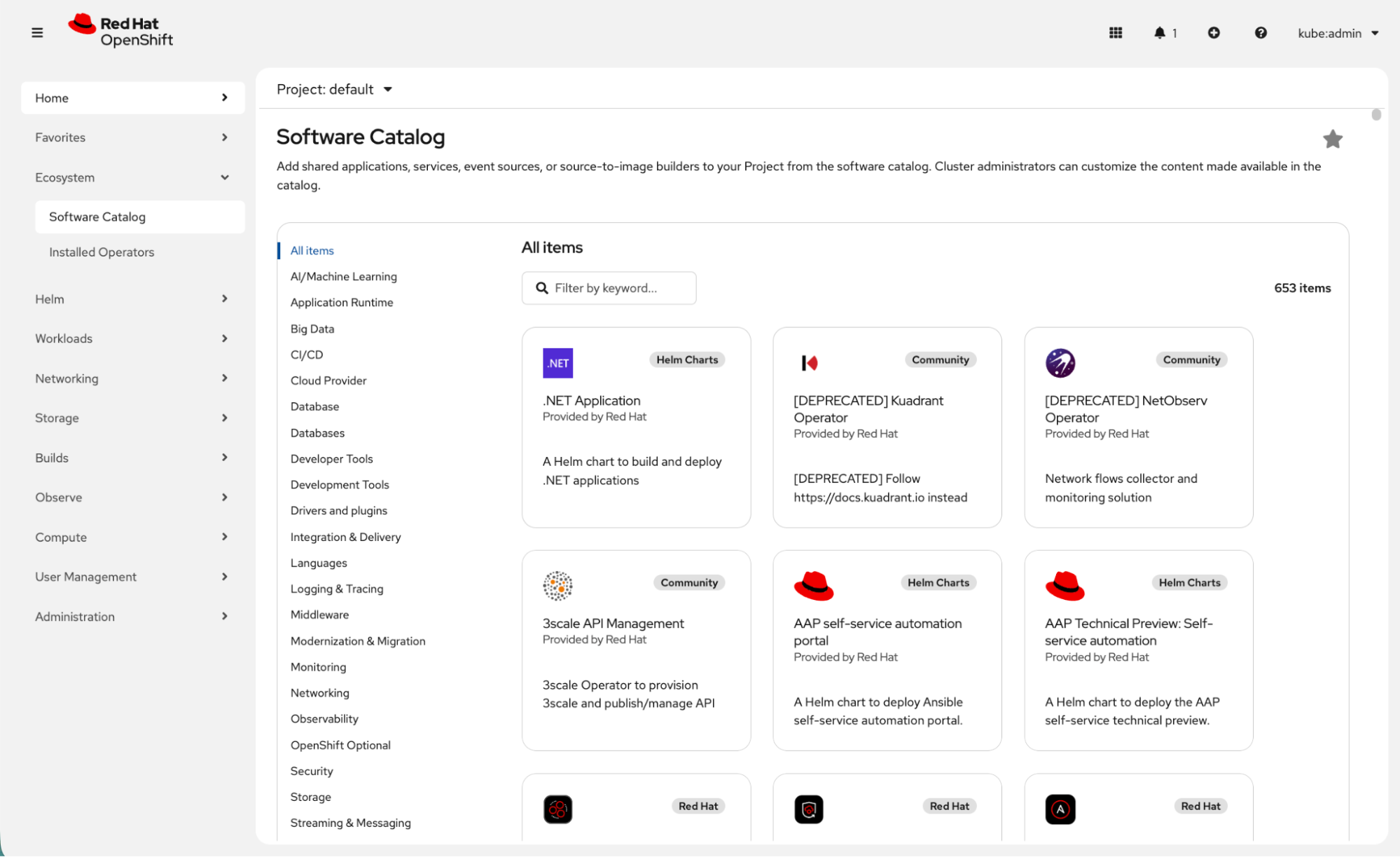
Red Hat OpenShift 4.20 includes a unified software catalog, one location where you can manage all the software that runs on your cluster.
Users will now see a new ecosystem navigation menu, a new software catalog that merges the previous operator hub and developer catalog experiences. Instead of a developer catalog under the home menu and a separate operator section in the navigation, you can access both from one location. See Figure 1.
ControlPlaneMachineSet user experience
Previously users were only able to update the ControlPlaneMachineSet using the command-line interface (CLI), but in Red Hat OpenShift 4.20 users can manage their control machine set directly in the OpenShift Container Platform console. This provides an improved user experience by allowing UI-driven lifecycle management and increased visibility into automated control plane node replacements. It also reduces reliance on the CLI, making node lifecycle automation more accessible, and aligns with other machine API resources, ensuring a consistent experience.
Console enhancements
Red Hat OpenShift 4.20 includes several enhancements to the user experience, including a full-screen YAML editor in OpenShift web console. Previously, the YAML view within the OpenShift web console was constrained to a fixed, smaller pane, making it challenging for users to effectively view, navigate, and edit large or complex YAML configurations. Red Hat OpenShift 4.20 implemented a full-screen mode for the integrated YAML editor/viewer in the OpenShift web console.
You can find a full list of enhancements to the console in the product documentation.
Platform services
Red Hat OpenShift 4.20 includes improvements to Red Hat OpenShift GitOps, builds for OpenShift, OpenShift pipelines, OpenShift Serverless, and the Migration Toolkit for Applications.
Red Hat OpenShift GitOps 1.18
GitOps is an operator for continuous delivery based on Argo CD that lets you declaratively automate application, cluster configuration, and resource deployment. Highlights include:
- Enhancements to Argo CD 3.1, Argo Rollouts 1.8.3, and Argo CD Agent 0.4.1.
- User interface updates in the OpenShift Console, with a new menu name. Instead of Environments, you can now find it under GitOps, and if you prefer to interact with Argo via the console, you can now find your applications and appsets there as well.
- Updated recommendations for using GitOps with Keycloak. Previously, the operator would install its own instance of Keycloak for you. As of this version, you can now bring your own Keycloak instance and connect directly with GitOps existing OpenID Connect support.
Builds and pipelines
Several updates to builds for OpenShift and OpenShift Pipelines create a more efficient, user-friendly, and security-focused continuous integration and continuous delivery (CI/CD) experience.
The public Tekton Hub at tekton.dev will be deprecated in January 2026. Pipelines should be migrated and ArtifactHub is now the recommended replacement for resolving them.
The pipeline operator is now more scalable and secure as it manages certificate authority (CA) configurations and role-based access control (RBAC) separately, and enforces a read-only file system on its pods. Additionally, the buildah-ns task uses Kubernetes user namespace isolation for builds.
Those using pipeline-as-code can now use relative paths for more portable tasks, trigger pipelines more securely with JSON body parameters support in webhooks, and gain better traceability with pull request numbers included in push events.
In the console, you'll notice improved task display names that include parameter values, making it easier to see what's running. Tekton Results can now optionally skip storing incomplete pipeline and task runs, boosting performance.
Migration Toolkit for Applications
Migration Toolkit for Applications 8 is now generally available as an add-on in the Red Hat Advanced Developer Suite subscription.
Red Hat Developer Lightspeed for Migration Toolkit for Applications is now generally available. It can help you automate source code transformation to capitalize on large language models (LLMs).
You can also simplify the migration of containerized applications that don’t require changes in the source code from Cloud Foundry to Red Hat OpenShift by enabling the Migration Toolkit for Applications to:
- Retrieve deployment and runtime configuration from the platform where an application is deployed.
- Produce deployment manifests and configuration files to deploy applications in Red Hat OpenShift.
Enhancements for Red Hat OpenShift Virtualization
Changes to OpenShift Virtualization let you modernize operations with comprehensive lifecycle and infrastructure management.
Networking enhancements
Networking enhancements include delivery of routed ingress (border gateway protocol [BGP]) for a layer 2 user-defined network. Users can also change the virtual network interface link state of a running VM nondisruptively. OpenShift Virtualization also integrates with Passt to mitigate privilege elevation requirements when performing actions such as connecting to service meshes.
Infrastructure optimizations
Load-aware balancing based on CPU pressure is now generally available. From a mobility perspective, cross-cluster live migration is in tech preview, along with an intuitive UI-based mechanism for live-migrating virtual machines to a specific node in the cluster.
Simplified VM management
With Red Hat Advanced Cluster Management, you can now migrate VMs more easily, with tree-view VM navigation extended to multicluster management. Clusters can now be optimized for OpenShift Virtualization with recommended operators.
Get started today with Red Hat OpenShift 4.20
Get started:
- Start your OpenShift journey with your Developer Sandbox.
- Discover more ways to get started by downloading Red Hat OpenShift.
- Find resources for getting started with OpenShift.
- Level up your skills with OpenShift learning paths, such as Foundations of OpenShift.
To find out more about Red Hat OpenShift 4.20, check out the new and improved features and fixes:
