Node.js 20's maximum heap size is container-aware and limits memory usage based on the container's cgroup limits. Node.js tells V8 the total available memory, which lets V8 select the maximum old space size based on those limits. In fact, Node.js has been container-aware since version 12.
Inside a container, the boundaries are provided by the kernel's control groups (cgroups) feature. Similar to other scenarios, the host kernel running the container stops it if it exceeds the pre-set limit via OOM (Out-Of-Memory) Killer cgroups. Leaving resource limits unset could balloon the full OpenShift Container Platform (OCP) node and cause evictions. In this case, the Kubernetes Quality of Service (QoS) order is respected: Best Offer, Burstable, Guaranteed
This article answers the question: Do you need to set the heap size in Node.js, or is it already container-aware?
Node.js 20 inside a container
While the main topic is Node.js memory management in a container, we'll also briefly cover CPU allocation to provide a complete picture.
CPU allocation
As Lizzy explains on Worker Threads in Node.js: A Complete Guide for Multithreading in JavaScript, Node.js runs JavaScript in a single-threaded environment.
In other words, deploying Node.js keeps the application running as a single thread. Simply setting higher CPU limits or requests on the container won't change this.
However, using worker_threads can be an alternative for parallelizing specific tasks. Combining worker_threads combined with multiple CPU limits in deployment can be a powerful tool for parallelization.
The key takeaway is this: as long as the worker_threads and the CPU are associated (not decoupled), performance will improve (sometimes considerably). But at some point, if worker_threads drastically outnumber the CPUs (as in worker_threads >> CPUs), the overhead from thread switching will hurt performance more than it helps.
Memory management
When you deploy the Node.js image as a container, the application is container-aware. It adapts the heap size to the container size, as shown in the following table. (Note: Gibibyte (Gi) and Mebibyte (Mi) are the Kubernetes units for memory, which differ from the standard GiB and MiB.)
| Container size | Heap size |
| 1 Gibibyte (Gi) | Heap not set - 1 Gi container - 520 Mi heap |
| 2 Gibibyte(Gi) | Heap not set - 2 Gi container - 1,040 Mi heap |
| 3 Gibibyte (Gi) | Heap not set - 3 Gi container - 1,560 Mi heap |
| 4 Gibibyte (Gi) | Heap not set - 4 Gi container - 2,080 Mi heap |
| 5 Gibibyte (Gi) | Heap not set - 5 Gi container - 2,080 Mi heap |
As the table demonstrates, the Node.js heap size is 50% of the container's size, up to 4 Gi. After 4 Gi, the maximum heap value naturally levels out at 2 Gi. This behavior occurs when you don't use the --max-old-space-size.
However, you can override the default heap values by setting the --max-old-space-size flag directly on the deployment. For example, if you set the flag to --max-old-space-size=512, the heap adjusts to that limit and throws an OutOfMemory exception if that limit is crossed.
There's no need for a table for this scenario, as the relationship is simple: the heap size is determined by the --max-old-space-size value, regardless of the container size.
Figure 1 illustrates how you can overwrite the default values of the heap via --max-old-space-size flag by decoupling the value for the heap and the value of the container itself.
Node.js requests versus limits
Node.js uses the container limits as the reference for its memory limits, similar to Java. From a cgroups bare perspective, it simply uses memory.max.
Node.js memory management
Figure 2 shows Node.js memory management, where V8 divides the memory into several sections, which is similar to Java's generational GCs but is simpler in its approach.
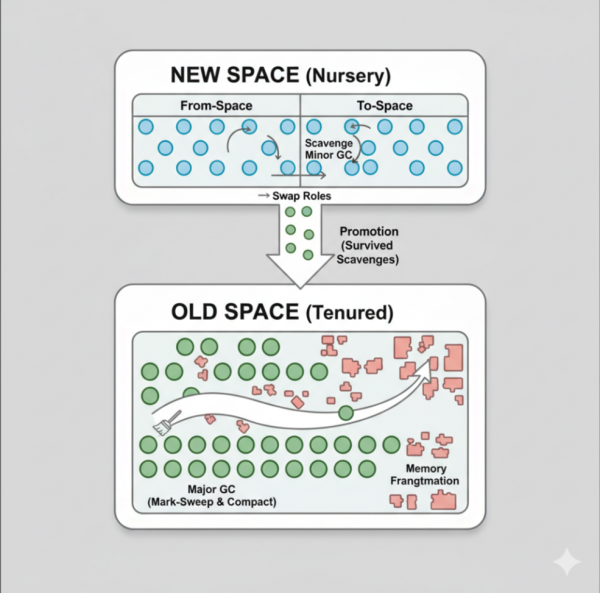
V8 garbage collection behavior
The following shows Node.js details for garbage collection.
[21:0x55a83a9cbc60] 528761 ms: Mark-Compact (reduce) 2048.6 (2077.5) -> 2048.3 (2078.2) MB, 1523.21 / 2.26 ms (+ 775.9 ms in 104 steps since start of marking, biggest step 21.2 ms, walltime since start of marking 2837 ms) (average mu = 0.361, current mu = 0.429) allocation failure; scavenge might not succeedThe output shows that the Mark-Compact phase finished reducing memory in 2.26 milliseconds.
Here is an OutOfMemory error. It triggers an OutOfMemory exception, followed by a fatal error, in this case because a memory leak was simulated. If there's an underlying condition, such as an array that isn't cleaned up, increasing the heap size won't be enough to prevent the OutOfMemory exception. In other words, simply increasing the heap memory allocated to Node.js via the --max-old-space-size flag won't fix a memory leak or other underlying memory issues.
<--- JS stacktrace --->
FATAL ERROR: Ineffective mark-compacts near heap limit Allocation failed - JavaScript heap out of memory
.---- Native stack trace -----
1: 0x555d5ad0f79a [node]
2: 0x555d5b0ddda4 v8::Utils::ReportOOMFailure(v8::internal::Isolate*, char const*, v8::OOMDetails const&) [node]
3: 0x555d5b0de065 v8::internal::V8::FatalProcessOutOfMemory(v8::internal::Isolate*, char const*, v8::OOMDetails const&) [node]
4: 0x555d5b2d3fbb [node]
5: 0x555d5b2db4fc [node]
6: 0x555d5b2ee480 v8::internal::Heap::PerformGarbageCollection(v8::internal::GarbageCollector, v8::internal::GarbageCollectionReason, char const*) [node]
7: 0x555d5b2eefb5 v8::internal::Heap::CollectGarbage(v8::internal::AllocationSpace, v8::internal::GarbageCollectionReason, v8::GCCallbackFlags) [node]
8: 0x555d5b2ca451 v8::internal::HeapAllocator::AllocateRawWithLightRetrySlowPath(int, v8::internal::AllocationType, v8::internal::AllocationOrigin, v8::internal::AllocationAlignment) [node]
9: 0x555d5b2cb54a v8::internal::HeapAllocator::AllocateRawWithRetryOrFailSlowPath(int, v8::internal::AllocationType, v8::internal::AllocationOrigin, v8::internal::AllocationAlignment) [node]
10: 0x555d5b2acf72 v8::internal::Factory::NewFillerObject(int, v8::internal::AllocationAlignment, v8::internal::AllocationType, v8::internal::AllocationOrigin) [node]
11: 0x555d5b6a1c79 v8::internal::Runtime_AllocateInYoungGeneration(int, unsigned long*, v8::internal::Isolate*) [node]
12: 0x555d5bab1ef6 [node]If a real problem exists, setting a large value for --max-old-space-size only delays an OutOfMemory exception, which will eventually occur.
Deploying Node.js 20 on OpenShift
The following example shows how to deploy a Node.js application to view the deployment details:
oc new-app nodejs:latest~https://github.com/FranciscoMeloJr/nodejs-rest-http
→ package.json:
"start": "node --trace-gc .", Troubleshooting
When investigating an underlying condition, you can consider doubling or halving the container resources. Both approaches have pros and cons:
- You can double the resources to delay the
OutOfMemoryexception and investigate usage, focusing on the highest consumers. - You can halve the resources to speed up the
OutOfMemoryexception, which helps you confirm the process with a backward approach.
The investigation usually begins by collecting a heap snapshot. Then you can verify which component is taking the largest chunk of memory after a large allocation. Outputs such as --expose-gc and --trace-gc are very useful for tracking this.
Note that some outputs are not container-aware and report the OpenShift node statistics rather than the container details and statistics.
Summary
In a nutshell:
- Node.js executes as a single JavaScript thread.
- Up to a 4 Gi container size, the default heap size is 50% of the container's size. After 4 Gi, the heap has a maximum of 2 GB.
- This 2 GB maximum heap value is present by default in Node.js 20 images.
- A Node.js container abides by the container's limits, not its requests.
- Alpine-based Node.js behaves the same as Red Hat Universal Base Image (UBI) images.
- Setting
--max-old-space-sizeoverwrites the default values (as previously discussed), allowing for a maximum heap size greater than 2 GB. - To reduce memory consumption, make sure to nullify arrays and objects so the garbage collector can reclaim the memory.
Demo video
Conclusion
This article describes the expected Node.js behavior and heap values, confirming that it is container-aware.
This article also describes how to override heap values and explains how memory allocation works. It expands on the original article, Node.js 20 container memory usage details, which shows container-aware details.
For any other specific inquiries, open a case with Red Hat support. Our global team of experts can help you with any issues.
Special thanks to Michael Dawson for his outstanding collaboration on all things Node.js, and to Alexander Barbosa for a great review and contributions to this article. Finally, thank you to Jordan Bell for his excellent collaboration on the most interesting Node.js cases over his seven years at Red Hat.
