The Red Hat build of Trustee (formerly called confidential compute attestation) operator simplifies configuring secrets and serving them to confidential container pods that execute inside trusted execution environments (TEEs). You can set up the required secrets as Red Hat OpenShift Secret objects and make them accessible through Red Hat build of Trustee. You can use the same mechanism to integrate with external secret managers.
For instance, you can use the Secrets Store CSI Driver or the External Secrets Operator to synchronize secrets from external sources, such as HashiCorp Vault, and make them available to confidential containers (CoCo) executing in remote TEEs. For more details on CoCo, refer to our earlier blog series.
Figure 1 shows the connection between Red Hat build of Trustee and third-party secret store solutions.
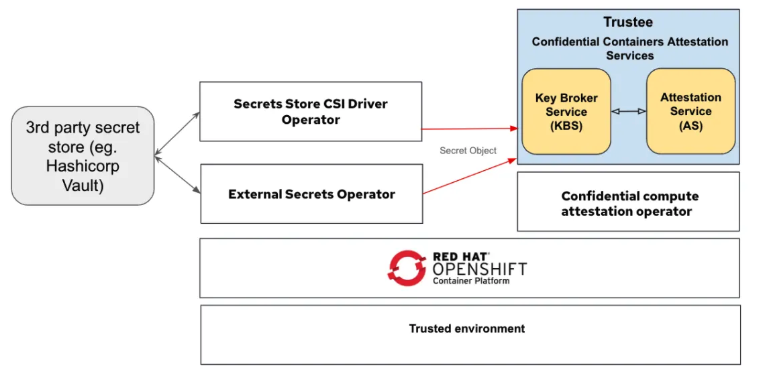
In this blog post, we are focusing on the integration of Trustee with External Secrets Operator for secure, dynamic secret delivery to CoCo pods. We cover installing and configuring the Operator, setting up Vault authentication and policies, creating SecretStore and ExternalSecret objects, verifying the setup, and configuring Trustee to use the fetched secrets within a CoCo pod, including how to update and refresh those secrets.
Install External Secrets Operator
Create and apply the subscription
#external-secrets-subscription.yaml
apiVersion: operators.coreos.com/v1alpha1
kind: Subscription
metadata:
name: external-secrets-operator
namespace: openshift-operators
spec:
channel: stable
installPlanApproval: Automatic
name: external-secrets-operator
source: community-operators
sourceNamespace: openshift-marketplace
startingCSV: external-secrets-operator.v0.11.0oc apply -f external-secrets-subscription.yamlVerify installation
watch oc get csv -n openshift-operatorsExample output:
NAME DISPLAY VERSION REPLACES PHASE
external-secrets-operator.v0.11.0 External Secrets Operator 0.11.0 external-secrets-operator.v0.10.7 SucceededCreate and apply OperatorConfig
Before any other resources provided by this Operator can be deployed, it is essential to create an OperatorConfig resource.
#external-secrets-operatorconfig.yaml
apiVersion: operator.external-secrets.io/v1alpha1
kind: OperatorConfig
metadata:
name: cluster
namespace: openshift-operators
spec:
prometheus:
enabled: true
service:
port: 8080
resources:
requests:
cpu: 10m
memory: 96Mi
limits:
cpu: 100m
memory: 256Mioc apply -f external-secrets-operatorconfig.yamlVerify the cluster-external-secrets pods are running
oc get pod -n openshift-operatorsExample output:
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
cluster-external-secrets-776967ccff-ngh8d 1/1 Running 0 82m
cluster-external-secrets-cert-controller-6965b4768b-kn5ct 1/1 Running 0 82m
cluster-external-secrets-webhook-f59f945ff-qpfbx 1/1 Running 0 82m
external-secrets-operator-controller-manager-79c4c47579-jsdf7 1/1 Running 0 89mConfigure External Secrets using HashiCorp Vault
Install Vault
In official documentation in 2.7.3.5. Mounting secrets from HashiCorp Vault section, follow steps 1-3.
Configure Vault to use Kubernetes authentication
Enable the Kubernetes auth method:
oc exec vault-0 --namespace=vault -- vault auth enable kubernetesExample output:
Success! Enabled kubernetes auth method at: kubernetes/
Create a policy for external secret operator:
oc exec -i vault-0 --namespace=vault -- vault policy write external-secret-policy -<<EOF
path "secret/data/*" {
capabilities = ["read"]
}
EOF
Example output:
Success! Uploaded policy: external-secret-policy
Update the Kubernetes auth method:
TOKEN_REVIEWER_JWT="$(oc exec vault-0 --namespace=vault -- cat /var/run/secrets/kubernetes.io/serviceaccount/token)"
KUBERNETES_SERVICE_IP="$(oc get svc kubernetes --namespace=default -o go-template="{{ .spec.clusterIP }}")"
oc exec -i vault-0 --namespace=vault -- vault write auth/kubernetes/config \
token_reviewer_jwt="${TOKEN_REVIEWER_JWT}" \
kubernetes_host="https://${KUBERNETES_SERVICE_IP}:443" \
kubernetes_ca_cert=@/var/run/secrets/kubernetes.io/serviceaccount/ca.crt \
disable_issuer_verification=true
Example output:
Success! Data written to: auth/kubernetes/config
Create an authentication role to access:
oc exec -i vault-0 --namespace=vault -- vault write auth/kubernetes/role/external-secret-role \
bound_service_account_names=default \
bound_service_account_namespaces=trustee-operator-system \
policies=external-secret-policy \
ttl=20mExample output:
Success! Data written to: auth/kubernetes/role/external-secret-roleConfigure SecretStore and ExternalSecret
Create a secret to the Vault:
oc exec vault-0 --namespace=vault -- vault kv put secret/external-secret-example1 vaultTestSecret=vaultSecretValueExample output:
=========== Secret Path ============
secret/data/external-secret-example1
======= Metadata =======
Key Value
--- -----
created_time 2025-06-02T11:20:17.745227354Z
custom_metadata <nil>
deletion_time n/a
destroyed false
version 1Create and apply SecretStore:
#vault-secretstore.yaml
apiVersion: external-secrets.io/v1beta1
kind: SecretStore
metadata:
name: vault-secret-store
namespace: trustee-operator-system
spec:
provider:
vault:
server: "http://vault.vault:8200"
path: "secret"
version: "v2"
auth:
kubernetes:
mountPath: "kubernetes"
role: "external-secret-role"
serviceAccountRef:
name: "default"oc apply -f vault-secretstore.yamlVerify SecretStore:
$ oc get secretstores.external-secrets.io -n trustee-operator-system vault-secret-store
NAME AGE STATUS CAPABILITIES READY
vault-secret-store 13m Valid ReadWrite TrueCreate and apply ExternalSecret:
# vault-externalsecret.yaml
apiVersion: external-secrets.io/v1beta1
kind: ExternalSecret
metadata:
name: vault-test-secret
namespace: trustee-operator-system
spec:
refreshInterval: 1h
secretStoreRef:
name: vault-secret-store
kind: SecretStore
target:
name: vault-test-secret
data:
- secretKey: externalVaultTestSecret
remoteRef:
key: secret/data/external-secret-example1
property: vaultTestSecretoc apply -f vault-externalsecret.yamlVerify ExternalSecret:
$ oc get externalsecrets.external-secrets.io -n trustee-operator-system vault-test-secret
NAME STORE REFRESH INTERVAL STATUS READY
vault-test-secret vault-secret-store 1h SecretSynced True
Verify the Kubernetes secret has been created:
$ oc get secrets -n trustee-operator-system vault-test-secret
NAME TYPE DATA AGE
vault-test-secret Opaque 1 2m45sConfigure the Red Hat build of Trustee server and verify attestation
Create or update the KbsConfig with the newly created external secret:
# kbsconfig.yaml
apiVersion: confidentialcontainers.org/v1alpha1
kind: KbsConfig
metadata:
labels:
app.kubernetes.io/name: kbsconfig
app.kubernetes.io/instance: kbsconfig
app.kubernetes.io/part-of: trustee-operator
app.kubernetes.io/managed-by: kustomize
app.kubernetes.io/created-by: trustee-operator
name: kbsconfig
namespace: trustee-operator-system
spec:
kbsConfigMapName: kbs-config-cm
kbsAuthSecretName: kbs-auth-public-key
kbsDeploymentType: AllInOneDeployment
kbsRvpsRefValuesConfigMapName: rvps-reference-values
kbsSecretResources: ["vault-test-secret", "kbsres1", "security-policy"]
kbsResourcePolicyConfigMapName: resource-policy
kbsServiceType: NodePort
KbsEnvVars:
RUST_LOG: debugoc apply -f kbsconfig.yamlVerify secret is fetchable in CoCo pod
Sample initdata.toml:
#initdata.toml
algorithm = "sha256"
version = "0.1.0"
[data]
"aa.toml" = '''
[token_configs]
[token_configs.coco_as]
url = "http://10.0.2.6:31247"
[token_configs.kbs]
url = "http://10.0.2.6:31247"
#cert = """
#"""
'''
"cdh.toml" = '''
socket = 'unix:///run/confidential-containers/cdh.sock'
credentials = []
[kbc]
name = "cc_kbc"
url = "http://10.0.2.6:31247"
#kbs_cert = """
#"""
'''
"policy.rego" = '''
package agent_policy
default AddARPNeighborsRequest := true
default AddSwapRequest := true
default CloseStdinRequest := true
default CopyFileRequest := true
default CreateContainerRequest := true
default CreateSandboxRequest := true
default DestroySandboxRequest := true
default ExecProcessRequest := true
default GetMetricsRequest := true
default GetOOMEventRequest := true
default GuestDetailsRequest := true
default ListInterfacesRequest := true
default ListRoutesRequest := true
default MemHotplugByProbeRequest := true
default OnlineCPUMemRequest := true
default PauseContainerRequest := true
default PullImageRequest := true
default ReadStreamRequest := true
default RemoveContainerRequest := true
default RemoveStaleVirtiofsShareMountsRequest := true
default ReseedRandomDevRequest := true
default ResumeContainerRequest := true
default SetGuestDateTimeRequest := true
default SetPolicyRequest := true
default SignalProcessRequest := true
default StartContainerRequest := true
default StartTracingRequest := true
default StatsContainerRequest := true
default StopTracingRequest := true
default TtyWinResizeRequest := true
default UpdateContainerRequest := true
default UpdateEphemeralMountsRequest := true
default UpdateInterfaceRequest := true
default UpdateRoutesRequest := true
default WaitProcessRequest := true
default WriteStreamRequest := true
'''Convert the initdata.toml file to a Base64-encoded string:
cat initdata.toml | gzip | base64 -w0Note: For more information about initdata, refer to the OpenShift documentation.
Create a CoCo pod:
#ocp-cc-pod.yaml
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: ocp-cc-pod
labels:
app: ocp-cc-pod
annotations:
io.katacontainers.config.runtime.cc_init_data: H4sIAAAAAAAAA42VwW7bMAyG734KwzvkNCfptg4o0EOXdluBZTXsdDkUQcDIjC1EljyJzpo+/aimHbahsntwYIkfqZ8U6YCqjJVUN/F5nLgaTj6cJtEerZNG+61JOk0nSRTdlUCwihKAlEyjEraNRqPojswO9VoYvZWVW/23ToURZg2831nlo9VE7dl4PJ2kk/QkPT17Nz15/9FH/9dttxl0eSPQkrcn/O5/vJooEWX9pO9JoDNihx4cdVrec6Cx7fT48aASNUlQb3lBIDXnPPbu3mMUCYtPdsfOdyvWuNuIVaShQX+sEGteJ0MqOZP1y0pbo6Q4pBYr81zMFsQOKoz50bQ+AlFU4hY6RfFFWV7k2XeUVb0x1uX4s0NH8dl5TLbDv7HiF7Qh80wZhwWVUgcJ0x4+S4VBu0UgnD0XrR8rQJcbcx+CLnnTmsMAdXWPIrNGoAtm/QVpjmSl6CNubuZXey5tEPG7l8h5qWCYb9LRtSa0W2A9fVRuOgoTc2y+GmpVV306cG6bYLlvtOIyz7Jb9ggxGXRu+EayTqnrhpsrBOQIZUF8b8GDcmzMfvikI1YQKPwhLUmzdUUNFuem0xQsSY4Oscy5F0xzifserGuGNRRIx/vkLlzIJpg0c9njpAUBWWlQA/3HuVoa1uSphQUhddXDkHtFJNMOBFrQYemn3MmHYPK3bfmaWT5iV22NDVpQ/dd4hP/MSD/WPyRLkDRQ+CX/eeHLTes/qb8BasRfON8GAAA=
spec:
runtimeClassName: kata-remote
containers:
- name: skr-openshift
image: registry.access.redhat.com/ubi9/ubi:9.3
command:
- sleep
- "36000"
securityContext:
privileged: false
seccompProfile:
type: RuntimeDefaultoc apply -f ocp-cc-pod.yamlFetch the secret from CoCo pod:
oc exec -it ocp-cc-pod -- curl http://127.0.0.1:8006/cdh/resource/default/vault-test-secret/externalVaultTestSecretExample printout:
vaultSecretValueVerify the updated secret value is fetchable from CoCo pod
Update the secret value in Vault:
oc exec vault-0 --namespace=vault -- vault kv put secret/external-secret-example1 vaultTestSecret=UpdatedVaultSecretValueThe Kubernetes secret created by the External Secret Operator is updated when:
- the
ExternalSecret'sspec.refreshIntervalhas passed and is not 0. - the
ExternalSecret'slabelsorannotationsare changed. - the
ExternalSecret'sspechas been changed.
To trigger a secret refresh:
oc annotate externalsecrets.external-secrets.io -n trustee-operator-system vault-test-secret force-sync=$(date +%s) --overwriteFetch the same secret from CoCo pod:
oc exec -it ocp-cc-pod -- curl http://127.0.0.1:8006/cdh/resource/default/vault-test-secret/externalVaultTestSecretExample printout:
UpdatedVaultSecretValueSummary
In this blog post, we demonstrated how OpenShift secrets generated and managed by the External Secrets Operator (ESO) can be made available to TEEs via Red Hat build of Trustee. ESO automatically provisions and synchronizes these secrets with external secret stores, and Red Hat build of Trustee acts as the gatekeeper to make it available to the CoCo pods.
While this blog focuses on using HashiCorp Vault, ESO is compatible with a wide variety of external secret store providers, such as AWS Secrets Manager, Azure Key Vault, and Google Cloud Secret Manager.
