The world of artificial intelligence and machine learning is evolving rapidly, and with it, the tools developers use to create AI-powered applications. We're excited to announce a significant enhancement to Podman AI Lab that will improve developer experience: GPU acceleration.
GPU acceleration, available in Podman Desktop 1.12 and later, allows developers to harness the power of their local GPU for AI workloads that are deployed in containers, bringing new speed and efficiency to AI development on the desktop.
To read about all the other features that were delivered in the Podman 1.12 release, visit the Podman Desktop 1.12 announcement blog post.
Get started with GPU support for Podman AI Lab
GPU accelerated inference can provide significant performance improvements when working with large language models (LLMs). To get started, you’ll need:
- Podman Desktop 1.12+
- Podman 5.2.0+
- Podman AI Lab 1.2.0+
If you’re using a version of Podman prior to 1.12, or haven’t used Podman before, visit the downloads page to get the latest version and follow the installation instructions to get up and running. When you launch Podman Desktop 1.12, it will prompt you to update your Podman installation to Podman 5.2.0 if you have an older version of Podman installed.
Once you’re running up to date versions of Podman and Podman Desktop, follow the instructions to enable GPU container access in the Podman Desktop documentation. For example, on macOS this requires you to recreate the underlying Podman machine to enable GPU access via libkrun.
Download the Podman AI Lab extension from the Extensions screen in Podman Desktop, or wait for it to update if you had a prior version installed. If the version 1.2 or greater is not listed, click the Refresh the catalog button (Figure 1).

The latest version of the AI Lab extension brings new AI Recipes (starter projects for AI use cases), an expanded catalog of Apache 2.0 licensed models, and most importantly, model serving with GPU acceleration enabled.
Once you’re familiar with Podman AI Lab you use it as part of your workflow to build complex AI applications that integrate Natural Language Processing (NLP), Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG), and model alignment as demonstrated with Market Maestro by Vincent Caldeira.
Last but not least, make sure the Experimental GPU flag is enabled in Settings > Preferences Extension: AI Lab (Figure 2).

Using Podman AI Lab with GPU Inference
Everything’s in place, so you can head over to the AI Lab extension and use the Catalog to download a model (Figure 3). Subsequent examples will use the instruct lab/granite-7b-lab-GGUF.

Serve models with GPU acceleration
To serve a model, select the Services section within the AI Lab extension and click the New Model Service button (Figure 4). Select a model and click Create service.

After a few moments you’ll be able to view the Service details and interact with the model (Figure 5). If all went well, you should see that GPU Inference is enabled.
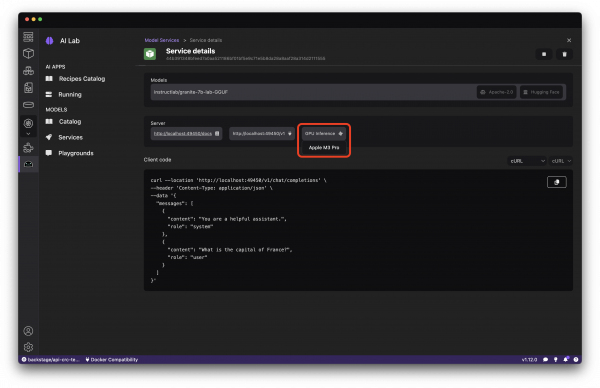
Test the service using the sample cURL command displayed, or use the dropdown to obtain a code snippet to use to communicate with the model from your preferred runtime. You should receive a reasonably snappy response to your requests with GPU inference enabled.
Figure 6 shows logs from a Service using CPU-based inference. As everything is running with containers, those logs are available from the inference server container’s details. The eval time runs at ~9.4 tokens per second.

Comparing the prior logs to a container using GPU-based inference (Figure 7) demonstrates an almost 3x performance improvement in the eval time when responding to a prompt . These tests were performed on a MacBook with an M3 processor and 6 cores provided to the underlying Podman machine.

Test playgrounds with GPU acceleration
To test the model and tune parameters, head over to the Playgrounds. Create a new playground and define a system prompt. You could use “You’re a helpful travel guide. Provide concise travel tips in response to user queries.” as the system prompt, as shown in Figure 8.

Asking the model “What should I do during a 7 day trip to Paris?” will return a sample travel itinerary. On a MacBook with a M3 processor, the response to this prompt was generated in 26 seconds using GPU inference versus 85 seconds for CPU-based inference.
Conclusion
By leveraging the power of GPUs, developers can now inference models faster and build AI-enabled applications with quicker response times using the Podman AI Lab extension with Podman Desktop. We're excited to see what you'll build with these new capabilities!
For more information on Podman AI Lab and its features, visit the Podman Desktop documentation and the Podman AI Lab extension page.
