Welcome to the Q3’25 edition of Red Hat’s quarterly newsletter, all about Apache Camel! This series aims to share all the noteworthy Camel goodness from the last quarter, so you don’t miss a thing! Be sure to read the previous editions to catch up on all the exciting updates and insights in Q1, Q2 of 2025.
Kaoto 2.7 Delivers Major Usability Upgrades
The Kaoto 2.7 release available as VSCode extension introduces significant updates focused on improving the designer experience and expanding data handling capabilities.
The headline feature is the Tech Preview of JSON support for the Data Mapper. Building on its existing XML capabilities, the Data Mapper now allows users to serialize and deserialize JSON structures, attach JSON schemas for visual tree-view mapping, and even create mappings between JSON and XML formats.
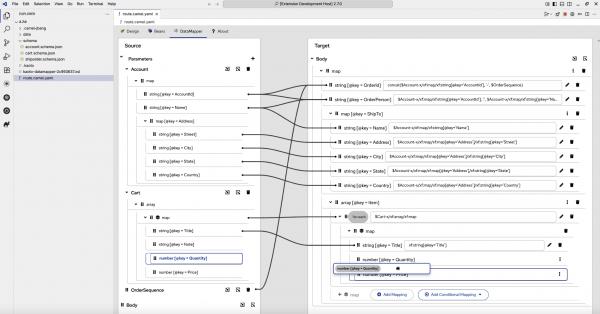
The graphical editor also received several major usability enhancements:
- Drag & Drop: Now enabled by default, allowing users to easily reorder steps and move items between containers.
- Core Editor Tools: Copy & Paste (via context menu), Quick Duplicate for steps and containers, and essential Undo / Redo support have been added to streamline the design process and recover from mistakes.
- Improved Maven Support: In the VS Code extension, adding a new component endpoint automatically updates the pom.xml with the required dependency upon saving.
- UI Enhancements: The interface now provides intelligent form suggestions for configurations, simple expressions, and application.properties completions.
Camel Langchain4j Agent Component
New in Camel 4.14 community, the camel-langchain4j-agent component provides deep integration with the LangChain4j library, allowing you to build and orchestrate powerful, producer-only AI agents within your Camel routes.
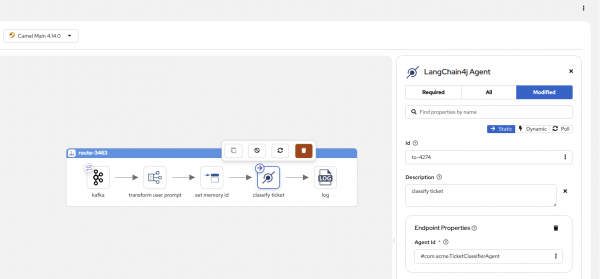
This component moves beyond simple prompt/response and supports advanced AI agent patterns, including:
- Tool Calling: Enables the AI agent to seamlessly discover and execute other Camel routes as tools, simply by using the tags parameter.
- Conversation Memory: Supports stateful, multi-turn conversations by using the AgentWithMemory implementation and a ChatMemoryProvider. Session tracking is managed via the CamelLangChain4jAgentMemoryId header.
- Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG): Integrates with retrieval systems to provide context-aware responses, configurable via a RetrievalAugmentor.
- Guardrails: Allows for input and output validation and transformation to ensure safe and structured AI interactions.
Configuration has been streamlined. Instead of numerous endpoint parameters, you now create an Agent (e.g., AgentWithMemory or AgentWithoutMemory) and configure it centrally using the AgentConfiguration class. The Camel endpoint is simplified to langchain4j-agent:agentId, which references the agent bean (e.g., ?agent=#myAgent) from the registry.
Articles
Dive into the latest developments within Apache Camel 4 through our curated selection of articles.
Building an AI-Powered PDF Processing Pipeline with Quarkus, Camel, and LangChain4j
In this hands-on tutorial, Markus Eisele shows you how to build a complete file processing pipeline in Java using Quarkus, Apache Camel, and LangChain4j. The pipeline accepts uploaded PDFs, scans them for viruses, extracts their content, and summarizes them using a local LLM served by Ollama. Thanks to the camel-langchain4j component, we can inject AI-powered analysis directly into the Camel route with zero boilerplate and just business logic.
Simplify local prototyping with Camel JBang infrastructure
A key feature of the Camel JBang CLI is its infra command. This allows developers to launch backends like Kafka, databases, or FTP servers instantly, avoiding the complexity of managing infrastructure. The infra command uses the power of Testcontainers and Docker (or Podman) to deploy real systems, saving you from the hassle of preparing mocks and complicated environment configurations.
In this article, Bruno Meseguer walks you through a detailed multi-step demo illustrating how the infra command can be used to easily spin up an ActiveMQ Artemis instance locally to facilitate testing an AMQP endpoint.
Building Intelligent Document Processing with Apache Camel: Docling meets LangChain4j
In the rapidly evolving landscape of AI-powered applications, the ability to process and understand documents has become increasingly crucial. Whether you’re dealing with PDFs, Word documents, or PowerPoint presentations, extracting meaningful insights from unstructured data is a challenge many developers face daily.
In this post, Andrea Cosentino explores how Apache Camel’s new camel-docling and camel-langchain4j-chat AI components enable developers to build sophisticated RAG (Retrieval Augmented Generation) pipelines with minimal code. In an example, he combines the power of Docling for document conversion with LangChain4j for AI orchestration, all orchestrated through Camel’s YAML DSL. You can also try this out for yourself!
Apache Camel Meets MCP: Securely Exposing Your Enterprise Routes as MCP Tools with Wanaku
The true value of Generative AI is unlocked when it can securely interact with core enterprise systems. In this post, Otavio Rodolfo Piske explains how to bridge this gap using Apache Camel and the Model Context Protocol (MCP). He introduces Wanaku, an open-source MCP Router that acts as a secure gateway for AI agents. The article walks through how a simple Wanaku mapping file can expose any battle-tested Camel route - whether it connects to Kafka, Salesforce, or a database as a native MCP "Tool". This approach allows developers to leverage their existing integrations as secure, AI-callable functions with fine-grained OIDC-based access control, all without writing new integration code.
Claus Ibsen, Gregor Zurowski, and Christoph Deppisch outline the new features and improvements in Apache Camel 4.14 LTS, which underpins the upcoming Red Hat Build of Apache Camel 4.14. Camel JBang in particular received significant updates this time, including switching the default to JDK 21, adding features to manage routes by groups, and improvements to the camel debug command, which now supports debugging Camel Spring Boot applications. A new component camel-iso8583 was added to create, edit and read ISO-8583 messages. A camel-langchain4j-agent component was also added to support advanced AI agent patterns including tool calling, conversation memory, retrieval-augmented generation (RAG), and input/output guardrails.
Ricardo M. announces the release of Kaoto 2.7, bringing significant enhancements to the visual integration design experience for Apache Camel. This release focuses on expanding DataMapper capabilities, improving developer productivity, and delivering a more intuitive canvas experience.
Claus Ibsen, Pasquale Congiusti, and Tom Cunningham outline the new features and improvements in Apache Camel 4.15. Fans of Quarkus will be happy to see that the camel debug command now supports debugging Camel Quarkus applications. Camel is also now far more extensible with the addition of the ContextServicePlugin SPI. Numerous components were added as well:
- camel-aws2-textract - Extract text and data from documents using AWS Textract
- camel-aws2-transcribe - Automatically convert speech to text using AWS Transcribe service
- camel-docling - Process documents using Docling library for parsing and conversion
- camel-groovy-xml - Transform between XML and Groovy Node (Map structure) objects.
- camel-langchain4j-embeddingstore - Provides support for 25+ vector databases using the LangChain4j EmbeddingStore API.
- camel-keycloak - Manage Keycloak instances via Admin API
- camel-mdc - Logging MDC (Mapped Diagnostic Context) Service
- camel-micrometer-observability - Micrometer Observability implementation of Camel Telemetry
- camel-resilience4j-micrometer - Micrometer statistics for Resilience4j circuit breaker
Demos and Presentations
See Apache Camel 4 in action in the following new demos and presentations:
- MCP in Action: Connecting AI to Enterprise Systems (Camel, Wanaku.ai, Quarkus/Langchain4j) by Zineb Bendhiba
- Simplify local prototyping with Camel JBang infrastructure by Bruno Meseguer
- AI-driven unstructured data extraction using Apache Camel and LangChain4J by Alexandre Gallice
Upcoming
Here’s a look at our key planned milestones and where you can connect with us at upcoming conferences:
November
- Red Hat Build of Apache Camel 4.14 GA
- November 12-14 - Devoxx Morocco
- MCP in Action: Connecting AI to Enterprise Systems by Otavio Piske
