VMware Cloud Foundation 5.1 is now available on Red Hat OpenShift Container Platform 4.13 with NVIDIA AI Enterprise, integrating automation within a consistent and replicable infrastructure model along with the latest data science and AI application deployment offered by NVIDIA. Read VMware’s official solution brief here, and their official blog announcement here.
What does this mean?
OpenShift on VMware Cloud Foundation provides you with the advantages of a contemporary private cloud, leveraging the established VMware Software-Defined Data Center architecture:
- A standard, replicable methodology for standardized infrastructure.
- Enhanced automation that reduces manual errors and boosts administrative efficiency.
- Cloud flexibility and scalability allowing for rapid expansion in line with business growth.
- Integration with VMware's proven networking solution, VMware NSX.
- Integration with VMware's proven storage solution, vSAN.
- Utilization of VMware vSphere capabilities, including VMware vSphere Distributed Resource Scheduler (DRS), vSphere vMotion, Fault Tolerance, among others.
- Integration with NVIDIA AI Enterprise (NVAIE) and the use of vGPU for detailed GPU resource allocation.
NVIDIA AI Enterprise
NVIDIA AI Enterprise (NVAIE) streamlines AI application development, from data science processes to deploying advanced AI, including Generative AI. Certified for both enterprise data centers and cloud environments, this platform enhances infrastructure efficiency, simplifies workload management, and ensures workload compatibility in multi-cloud and hybrid-cloud setups. NVAIE regularly updates security, maintains API stability, and provides NVIDIA Enterprise Support, making it suitable for AI-dependent enterprises seeking secure, stable, and supported transitions from pilot projects to full-scale production.
Virtualization brings operational savings to containerized workloads
OpenShift, integrated with vSphere, delivers an infrastructure primed for developers, supporting both OpenShift container platforms and traditional VMs. vSphere enables management of diverse workloads through familiar vCenter tools across hybrid clouds. It incorporates proven features like vSphere High Availability (HA) and policy-driven management for workload resilience. vSphere bolsters container security by leveraging VM isolation and simplifies operations with its lifecycle management and enterprise-grade resilience, reducing the effort needed for bare metal maintenance and recovery.
Higher container pod density results in lower capex
OpenShift 4.x caps at 500 pods per Worker Node, often leading to hardware underuse. With virtualization for worker nodes on vSphere, pods per server can surpass 500, reducing capital expenses. This higher pod density cuts costs by needing fewer physical servers for the same container volume. Running OpenShift on vSphere improves resource utilization over bare metal, highlighting virtualization's efficiency advantage.
VMware Cloud Foundation 5.1
A cohesive SDDC platform integrates VMware vSphere, vSAN, NSX, and, if chosen, vRealize Suite components, into an inherently unified stack, providing ready-to-use cloud infrastructure for both private and public clouds. This solution employs VMware Cloud Foundation 5.1, although subsequent minor versions are compatible as well.
See Preparing to install on vSphere for VMware vSphere infrastructure requirements.
VMware Cloud Foundation installation
The key steps for VMware Cloud Foundation installation are as follows:
- Establish a management domain.
- Integrate ESXi hosts into the system.
- Create a workload domain using the unused ESXi hosts.
Refer to Deployment Overview of VMware Cloud Foundation for comprehensive instructions on VMware Cloud Foundation setup procedures.
After the installation, you will need to verify that NSX and vSAN are activated within this workload domain, as shown in Figure 1. NSX and vSAN are integral to this solution and will be utilized in the subsequent OpenShift configuration steps.

Workload domain preparation
Following the establishment of the workload domain for OpenShift, NSX Managers are set up in the Management Domain. However, the NSX Edge cluster isn't automatically deployed. The addition of an edge cluster is required post the creation of the workload domain, as illustrated in Figure 2. Once the edge cluster is in place, its status should be "active." The names of the edge nodes are displayed underneath.

vSAN configuration
The validation of the solution utilized a 4-node vSAN cluster as the foundational unit. Testing for validation was performed with the vSAN datastore's standard storage policy, which includes RAID 1 FTT=1 and activated checksums. This vSAN cluster operated with both deduplication and compression turned off, and without any encryption. The subsequent sections detail the specific configurations of the vSAN cluster and certain aspects of the Storage Policy Based Management (SPBM).
Deduplication and compression
The "Deduplication and Compression" feature was set up at the cluster level, allowing it to be either enabled or turned off for the entire vSAN cluster. In our experiments, we chose to turn it off. Activating this feature can decrease the vSAN storage consumption, at the cost of increased latencies for the OpenShift application.
Failures to Tolerance (FTT)
Failures to Tolerate (FTT) is an option within vSAN's storage policy settings. For StorageClass in OpenShift and its corresponding vSAN storage policy, setting vSAN's FTT to 1 is advisable. We used FTT set to 1 as our standard during testing. Avoid configuring FTT to 0 in an OpenShift with vSAN setup, as FTT=0 could lead to data from the same pod's replications being stored on a single physical disk. Such a scenario increases the risk of data loss if there is a failure of the physical disk.
Network configuration
Figure 3 illustrates the network setup for the OpenShift cluster within the workload domain of VMware Cloud Foundation, using the VMware vSphere Distributed Switch.
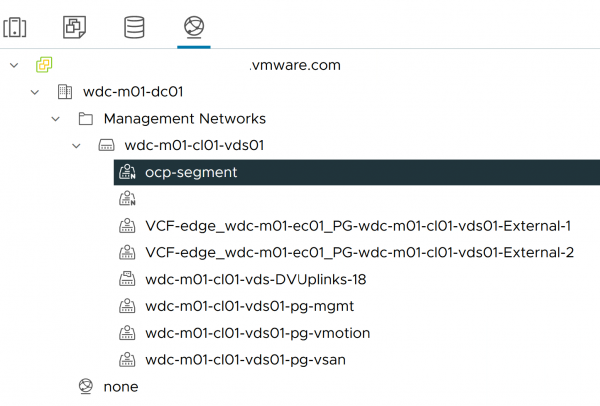
The underlying network for this vSphere infrastructure is provided by NSX, which is essential for the OpenShift cluster's networking. Deployment of an NSX Edge cluster is necessary to facilitate external access to the OpenShift cluster. Configuring BGP peering and route distribution with the upstream network is mandatory.
- VMware Cloud Foundation automatically generates the "VCF-xxxx-External-1" and "External-2" port groups for NSX use.
- The "xxxx-management", "xxxx-vsan", and "xxxx-vmotion" are likewise auto-created by VMware Cloud Foundation. They serve distinct purposes: management, vSAN, and vMotion, respectively.
- The "ocp-segment" represents a logical switch that is manually configured within NSX and designated for use by OpenShift VM nodes.
Dual 100 GbE vmnics are employed and set up with teaming policies. This management domain can then be utilized by various workloads.
We’ll cover more about configuring Red Hat OpenShift Container Platform on NVIDIA AI Enterprise in part 2—stay tuned.
