You can now try Apache Camel on Quarkus in the Developer Sandbox for Red Hat OpenShift, an OpenShift environment you can access for a no-cost, hands-on experience in building and deploying cloud-native applications quickly. This article will guide you to the Developer Sandbox and through a Camel Quarkus integration in a fully web-based experience—no local installs needed.
Camel Quarkus is the latest Camel runtime generation. It allows you to run integration processes with super-low memory usage, fast startup, and outstanding performance. The article Boost Apache Camel performance on Quarkus introduces the topic well.
To learn more about the various Camel runtimes available, read the 3-part series article Choose the best Camel for your integration ride.
REST and SOAP with Camel on Quarkus
One recent addition to Camel Quarkus is the ability to perform SOAP operations using Apache CXF, a well-known Java library historically used by Camel but only recently available for Quarkus.
The demo defines a front-facing OpenAPI service called simple, which integrates with a back-end SOAP service. The code also includes the stub to simulate the SOAP endpoint. The flow showcases an adaptation layer from REST to SOAP. It’s a relatively simple use case but very common in the enterprise. It defines a REST API and hides a legacy service behind the scenes (Figure 1).

Demo highlights
The big win for you is the chance to play the demo in a free-to-access environment from your browser and view/edit the code, and build, deploy, and test the application. Regarding Camel on Quarkus, the example stands out on various fronts.
First of all, both REST and SOAP interfaces are implemented following a contract-first approach. In essence, we rely on the OpenAPI (REST) and WSDL (SOAP) definitions to auto-generate the application’s input/output interfaces. Figure 2 shows how a contract-first OpenAPI helps the developer; this is also valid for SOAP.

Another notable feature in the demo is data transformation. JSON input must be mapped to outgoing SOAP during the request flow and perform the reverse operation during the response flow. It is all done in a single transformation stylesheet using XSLTs, as in Figure 3.

And finally, included in the code, you’ll find a test unit (JUnit) to validate the entire request/response flow (Figure 4). You will discover how to use Camel’s testing framework to dynamically spin up an actual SOAP back end to test against, trigger the processing flow, and tear it all down when done.

What is unique about Camel running on Quarkus, but also true for all runtimes, is how little code is required and how elegantly it is laid out. This simplicity guarantees economical, long-term, and sustainable support for your landscape of implemented Camel services.
If you would like to see how all of this is done, jump straight into the Developer Sandbox to explore the code and execute it.
Access the Developer Sandbox
Follow these instructions to get started in the Developer Sandbox: How to access the Developer Sandbox for Red Hat OpenShift
Once you have your browser connected to the Developer Sandbox console, you’ll be all set to start the article’s tutorial.
Inside OpenShift Dev Spaces
The Developer Sandbox ships with an entire web-based IDE called Red Hat OpenShift Dev Spaces (formerly Red Hat CodeReady Workspaces).
Set up your dev environment with the Camel tutorials
The animated sequence in Figure 5 illustrates the actions to follow to open your development environment along with your tutorial instructions.
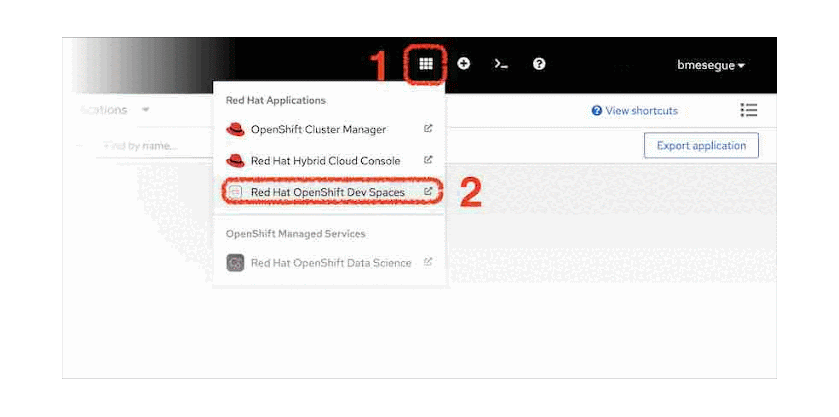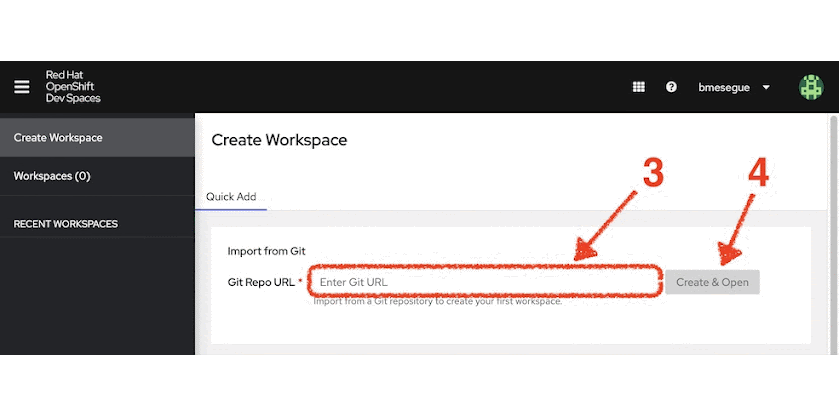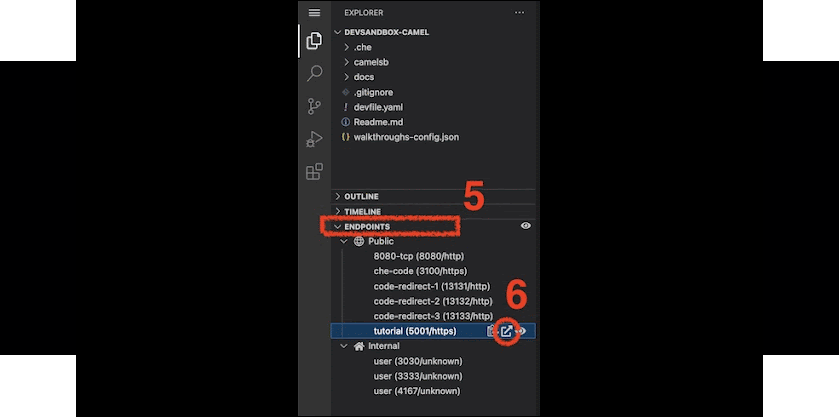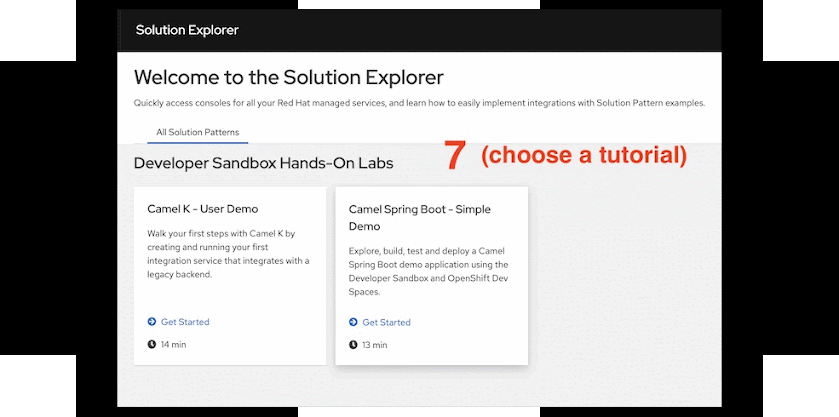
Follow these steps:
- From the web console, click the Applications icon as shown in Figure 5 (marked 1).
- Select Red Hat OpenShift Dev Spaces (2). You will be prompted to log in and authorize access; select the Allow selected permissions option.
-
When the Create Workspace dashboard in OpenShift Dev Spaces opens, copy the snippet below:
https://github.com/RedHat-Middleware-Workshops/devsandbox-camel.gitThen, paste it into the Git Repo URL field (3).
- Click Create & Open (4).
- When the workspace finishes provisioning and the IDE opens, click the deployable Endpoints accordion (5).
- Then, click on the icon (6), which opens the tutorial in a new browser tab.
- Choose the tutorial indicated in the next section.
Start the Camel Quarkus tutorial
Select the Camel Quarkus - Rest/Soap Demo tile, highlighted in Figure 6.

When you click on the tile, the Solution Explorer will show the lab introductions and the exercise chapters included, which you should be able to complete in around 15 minutes.
Enjoy the Camel ride!
Watch a video on how to get started
Watch the following video to see an execution of the use case described in this article.
More Apache Camel resources
This article ends here, but this should only be the start of your journey with Apache Camel. The Developer Sandbox for Red Hat OpenShift gives you the opportunity to play on a Kubernetes-based application platform with an integrated developer IDE (OpenShift Dev Spaces).
We encourage you to check out the resources below to learn more about Camel and explore different ways to build applications with Apache Camel:
- Play with more tutorials in the Developer Sandbox for Red Hat OpenShift.
- Learn more about the different Camel runtimes available by reading Choose the best Camel for your integration ride.
- Read Boost Apache Camel performance with Quarkus for a detailed look at Camel Quarkus.
- Visit the Red Hat Integration page on developers.redhat.com to see complementary capabilities around Camel.
