Dynamic inventories in the Red Hat Ansible Automation Platform revolutionize the way to manage infrastructure in the cloud. Instead of relying on static inventories that require manual updates when virtual machines (VMs) are launched, terminated, or replaced, dynamic inventories automatically discover and run VMs across any cloud provider. This means that when you delete an old VM and launch a new one, Ansible Automation Platform seamlessly adapts and performs actions on the updated infrastructure without requiring manual intervention.
By harnessing dynamic inventories, the Ansible Automation Platform empowers cloud administrators and DevOps teams to effortlessly manage and orchestrate on-demand cloud resources. This article explores the power of dynamic inventories, focusing on their utilization with AWS as the cloud provider. While applicable to any cloud provider, we showcase seamless AWS infrastructure management using dynamic inventories. We will demonstrate how to create EC2 instances, fetching details with dynamic inventory and running scripts for system health insights. By following these examples, you'll gain hands-on experience in effectively managing and monitoring your cloud infrastructure using dynamic inventories within the Ansible Automation Platform.
Demo setup
We will walk you through this hands-on example, creating three EC2 instances in AWS. We will then explore how to leverage dynamic inventory in the Ansible Automation Platform to automatically fetch the details of these instances. Using a playbook, we will execute tasks on these instances and observe the desired changes.
We will also delete one of the EC2 instances and spin up a new one, showcasing the dynamic nature of inventories. By syncing the inventory in the Ansible Automation Platform, we will observe how it seamlessly adapts to the changes, enabling us to easily continue managing the updated infrastructure.
Prerequisites
- You must have an active AWS account.
- Generate the access key and client secret for AWS.
- Navigate to the Credentials tab
- Under the Add button, select Amazon Web Services.
- Add your access key and secret key and save the credentials (Figure 1).

How to use dynamic inventory to manage AWS infrastructure
- Create three EC2 instances in the AWS console as follows:
- Log in to your AWS console and navigate to the EC2 sections.
- Under the EC2 console, click on Launch Instances and create three instances with different names for Ubuntu image.
NOTE: Make sure to use a single private key for all three EC2 instances as shown in Figure 2.
- Create the credentials to SSH into the AWS machine as follows:
- Navigate to the credentials tab.
- Under the Add button, select machine.
- Enter a name for the credential.
- Under Username, enter “ubuntu” and enter “root” for Privilege Escalation Username.
- Add your AWS SSH private key and click save.

- Set up the inventory as follows:
- Select the inventory from the left menu.
- Click on add and select add inventory.
- Enter a name for the inventory and save it.
- Select the sources from inventories and click on add.
- Give a name to the source.
- Under source, select Amazon EC2.
- In the Credentials field, select the AWS credentials you created earlier.
- Save the sources and then click on the Sync button.
- Now, navigate to the Groups section and notice that aws_ec2 group is created, and your EC2 IPs will be available in the hosts (Figure 3).

- Create and Configure the project as follows:
- Log in to the Ansible Automation Platform portal in the browser.
- Navigate to the Projects tab under Resources in the left pane.
- Click on Add to create a new project.
- Enter a name for the project and choose Git as the source control type with URL https://github.com/redhat-developer-demos/Ansible-use-cases in the Source Control URL field.
- Save the changes and wait for the operation to complete successfully.
- Create and Configure the job templates:
- Go to the Templates tab under Resources in the left pane and click on the Add button and select Job template from the options.
- Enter a name for the job you want to create and select the Demo-Inventory or Default inventory in the inventory section.
- In the Project section, click on the project name you previously created and select the Dynamic Inventory in Ansible Automation Platform/get_sys_data.yml file.
- In the credential section, select the machine category and choose the credentials for AWS.
- Launch the playbooks:
- Launch the playbook to see the logs of the output as shown in Figure 4:

- Delete an EC2 instance and spin up a new instance:
- Now, let us delete the third machine and create a new ec2 instance.
- Under AWS console, navigate to the EC2 instance, delete any machine, and create a new instance with the previous configuration setup (Figure 5).

- Sync the inventory:
- Navigate to the inventory section and click on the inventory you previously created.
- Under the Sources Tab, select the name created earlier and click on sync.
- Further, we can also schedule the task to update the inventory after every interval.
- Notice that our hosts have been updated (Figure 6). It takes time from the AWS console to completely terminate your old EC2 instances, and it might show up under hosts.
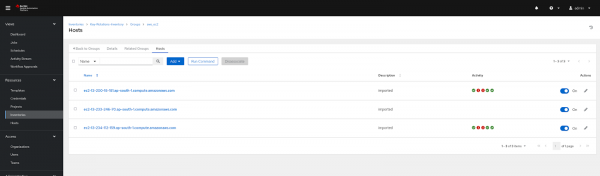
- Launch the playbook with the updated inventory:
- Navigate to the Templates section and select the job template created earlier.
- Launch the playbook (Figure 7).

Continue your journey with Ansible Automation Platform
Dynamic inventory not only simplifies inventory management but also enhances the agility and scalability of your workflows. In this article, we have demonstrated the power of efficient infrastructure automation by showcasing the creation and management of three EC2 instances in AWS and the utilization of dynamic inventory to seamlessly adapt to changes.
Get started with Ansible Automation Platform by exploring interactive hands-on labs. Download Ansible Automation Platform at no cost and begin your automation journey. You can refer to An IT executive's guide to automation e-book for a better understanding of automation. Additionally, check out our series where we explain how to create an EC2 instance in AWS using Ansible, empowering you to efficiently manage your cloud resources.
Last updated: January 11, 2024