The SaaS architecture checklist is a series of articles that cover the software and deployment considerations for Software as a Service (SaaS) applications. In this fourth article in the series, you'll learn about software SaaS providers can use to simplify their storage architecture while still accommodating a multi-cloud strategy.
Bring your service to your customer's platforms
A multi-cloud strategy is critical if you want to enable your SaaS application to run in the same physical location that your end customers use. Running on the same network is essential when a SaaS processes a large amount of end customer data or integrates closely with end customer systems. This keeps latency low and avoids expensive charges for inter-region or inter-cloud bandwidth. Since it is unlikely that a SaaS provider’s entire target market uses the same cloud provider, they must operate their service on multiple cloud platforms. In other words, you must bring your service to your customers.
The first step is to choose a portable Kubernetes distribution, such as Red Hat OpenShift, to normalize the operational burden across clouds. Your goal should be to avoid having to do unique development, configuration, lifecycle management, change management, and API integration for each deployment platform (see Figure 1). But certain capabilities remain cloud-specific, and persistent storage is one that almost every SaaS provider needs to use. If your SaaS application stores persistent data, you can still be left dealing with feature differences among the storage offerings of various clouds, such as dynamic provisioning, shared access, snapshots, security controls, and which of the three types of storage—block, filesystem, or object—are offered. Accommodating those differences can lead to costly efforts by development, operations, and support teams.
Software-defined storage (SDS) is a common architectural pattern that provides a consistent feature set across public and private cloud environments. SDS is sometimes referred to as hyperconverged infrastructure (HCI), where raw storage devices, compute resources, software-defined storage solutions, and workloads are all part of the same Kubernetes cluster. One SDS system can run in many cloud environments as long as block devices are available to individual hosts within the cluster.
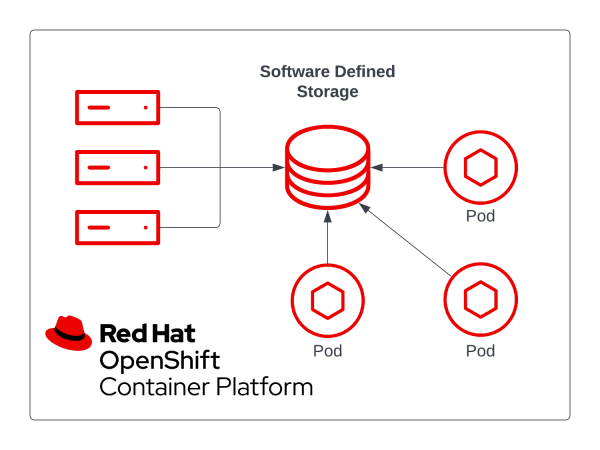
Software-defined storage decouples hardware storage devices from the logical storage mechanisms accessed by software. For example, three servers could have one or more physical storage devices available to the SDS system. The SDS system would be installed across the three servers and configured to use the physical devices as one pool (see Figure 2). With a pool of raw storage, you can configure the system to aggregate and expose the raw storage as a logical block, filesystem, or object storage over the network. You can also configure the system for redundancy, maintaining a set number of copies of data across multiple underlying hosts.
A team of software solutions
These three technologies can be combined to form a complete software-defined storage solution:
Ceph
Ceph is a popular open source software-defined storage platform (and number one for OpenStack) that can turn commodity block devices across multiple hosts into a high-performance, fault-tolerant storage cluster. It exposes object, filesystem, and block storage used by applications running in Kubernetes. Ceph has excellent management capabilities, including snapshots, cloning, and automated rebalancing and recovery. Ceph has become a popular choice for software-defined storage due to its rich feature set enabling a variety of storage use cases and the flexibility to run almost anywhere.
Rook
Rook is a Kubernetes Operator that offers a Kubernetes-native method for deploying and managing Ceph. According to Rook's website, it "turns distributed storage systems into self-managing, self-scaling, self-healing storage services. It automates the tasks of a storage administrator: deployment, bootstrapping, configuration, provisioning, scaling, upgrading, migration, disaster recovery, monitoring, and resource management." Rook has become a leading option because it offers enterprise-grade storage within a Kubernetes cluster through the HCI approach.
Noobaa
Noobaa adds advanced object storage capabilities, including deduplication, compression, and encryption at rest. Mirroring and replication policies distribute data across multiple backing storage services, even in different cloud environments.
Bringing these capabilities into an OpenShift cluster is easy with Red Hat OpenShift Data Foundation, because it combines Ceph, Rook, and Noobaa as one optional operator. Following the HCI pattern with OpenShift and OpenShift Data Foundation enables you to operate your SaaS application across multiple public and private clouds with just one storage platform and one Kubernetes platform. Operations teams prefer having only one software lifecycle to track, a consistent set of APIs and capabilities, a limited surface area of domain expertise to maintain, and a single point of support. Development teams save time by focusing on one storage and compute platform for testing and validation.
Learn more about Kubernetes storage
To learn more about Kubernetes storage solutions, a great resource is Storage Patterns for Kubernetes For Dummies, Red Hat Special Edition. Chapter two covers specific details about this topic. For further explanation of storage primitives and concepts on OpenShift, refer to the OpenShift Container Platform Storage Overview.
Last updated: November 29, 2023