
Build embedded cache clusters with Quarkus and Red Hat Data Grid
Use Quarkus to integrate two clustered, embedded Red Hat Data Grid caches and deploy them to Red Hat OpenShift Container Platform.

Use Quarkus to integrate two clustered, embedded Red Hat Data Grid caches and deploy them to Red Hat OpenShift Container Platform.

What's new with Apache Camel 3? | DevNation Tech Talk

Reactive programming is a great way to work with microservices that pass asynchronous data to each other. See it in action with Coderland's latest ride.

Deploy the Reactica code and see it in action.

An in-depth look at the reactive system of microservices that work together to calculate wait times for the Reactica roller coaster.

This video shows you how to deploy and run the Reactica roller coaster.

This video is a short overview of the Reactica architecture and the middleware that supports it.

Read all about the Reactica roller coaster and the system of reactive microservices that keep it running.

This article talks about multiple layers of security available while deploying Red Hat Data Grid on OpenShift. The layers of security offer a combination of security measures provided by Data Grid as well as by OpenShift/Kubernetes.
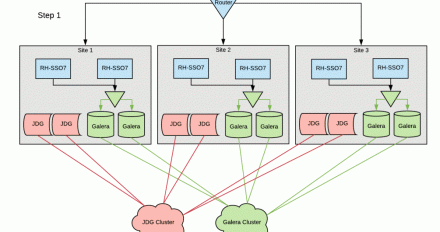
This article describes how Red Hat Single Sign-On uses open source technology to provide a true multi-site single sign-on authentication platform capable of handling next-generation applications.

Using the Horizontal Pod Autoscaler to autoscale Red Hat Cache Service is a nice way to increase overall system capacity depending on the load. The autoscaler monitors the amount of memory used by the container and adds or removes Cache Service pods based on this measurement. This article provides a demo of how to use the autoscaler to autoscale Red Hat Cache Service.

Red Hat Data Grid was used to power the multi-cloud real-time scavenger hunt game at Red Hat Summit 2018. In this article, you will learn how features of Data Grid were used to implement the games functionality, while replicating across three different cloud environments for high availability and resiliency.

Here are behind-the-scenes details on how the Red Hat Summit 2018 multi-cloud demo was configured to run Red Hat Data Grid in active-active-active mode for cross-site replication across three clouds to handle a large amount of globally routed traffic.



Watch this demo to see how Red Hat JBoss Data Grid provides fast, in-memory access to data and elastic scale to your application. Learn how you can achieve fault tolerance and resiliency when multiple copies of data are distributed across the grid and automatically backed up to other datacenters. JBoss Data Grid allows you to scale, boost application performance, and quickly recover from a disaster scenario.

In an increasing number of disciplines and industries, data volume and complexity has become both a challenge and an opportunity. Application developers are tasked with bridging the gap between challenge and opportunity and one tool in a developer's belt to help build that bridge is a data grid. Red Hat JBoss Data Grid - the supportable version of the Infinispan open source project - is a manageable, scalable, highly available, distributed, in-memory data store that lets you scale horizontally, based on memory and distribution across commodity hardware rather than relational database management system (RDBMS) licenses, database expertise or specialist hardware. Manik Surtani will provide a high-level overview of Red Hat JBoss Data Grid, discussing its benefits, common use-cases, and specific features meant to address today's data challenges and opportunities. Presenter: Manik Surtani Bio: Manik Surtani is a core R&D engineer at Red Hat JBoss Middleware. He is the founder of the Infinispan project, which he currently leads. He is also the spec lead of JSR 347 (Data Grids for the Java Platform), and represents Red Hat on the Expert Group of JSR 107 (Temporary caching for Java). His interests lie in cloud and distributed computing, big data and NoSQL, autonomous systems and highly available computing. He has a background in artificial intelligence and neural networks, highly available e-commerce systems and enterprise Java. Surtani is a strong proponent of open source development methodologies, ethos, and collaborative processes, and has been involved in open source since his first forays into computing.

Scale, elasticity, flexibility, low latencies, fault tolerance. These are all things we expect from our modern cloud, Platform-as-a-Service (PaaS), and web application deployments. Tristan and Shane will discuss why these characteristics are crucial to high-performing deployments and show how data grids are the perfect solution to these uniquely big data challenges. Presenter: Shane Johnson Bio: Shane Johnson is responsible for technical marketing strategy and content delivery for Red Hat JBoss Enterprise Application Platform and Red Hat JBoss Data Grid. Previously, he served as a Java EE architect and subject matter expert for Red Hat JBoss Data Grid, working with enterprise customers in the financial and telecommunications industries to integrate data grids into their solutions. His interest in NoSQL began when he published his first NoSQL blog post in the fall of 2009 and has grown ever since.

Hibernate OGM explores how to map the Java Persistence APIs with various underlying NoSQL stores. While NoSQL datastores offer interesting benefits in the BigData world we enter, choosing the right one for your project can be challenging. Abstracting behind JPA relieves you from the programming API/model shift. But is it possible? In this presentation, we will give an brief overview of the NoSQL landscape, describe how Hibernate OGM persists data in key/value stores, document stores, column family stores, etc. and see where using such an abstraction makes sense in applications. After this presentation, you will have a clearer view on how to integrate NoSQL datastores in your Java projects at least via JPA. Presenter: Emmanuel Bernard Bio: Emmanuel Bernard is data platform architect at Red Hat JBoss Middleware and member of the Hibernate team. After graduating from Supelec (French "Grande Ecole"), Emmanuel has spent a few years in the retail industry as developer and architect where he started to be involved in the ORM space. He joined the Hibernate team in 2003. Emmanuel has lead the JPA implementation of Hibernate. He has founded and leads Hibernate Search, Hibernate Validator and the newcomer Hibernate OGM. Emmanuel is a member of the JPA 2.1 expert group and the spec lead of Bean Validation. He is a regular speaker at various conferences and JUGs, including JavaOne, JBoss World and Devoxx and the co-author of [Hibernate Search in Action](/books/hsia/) published by Manning. He is also founder and co-host of two podcasts: [JBoss Community Asylum](http://asylum.jboss.org) and [Les Cast Codeurs Podcast](http://lescastcodeurs.com). You can follow him on twitter at @emmanuelbernard http://twitter.com/emmanuelbernard.
Shows a run a JDG perf test (IspnPerfTest) in a 500 node JDG cluster on Google Compute Engine

Red Hat JBoss Data Grid - Divya Mehra

Red Hat JBoss Data Grid - Syed Rasheed

Kubernetes is a powerful, open source, container orchestration and cluster management tool from Google. It drew upon all the lessons learned from a near-decade of using containers at Google. In this session, we'll look beyond container orchestration with Kubernetes and take a deep dive into more advanced features such as autoscaling. But its most powerful feature is its versatile REST API, which you can use to tailor Kubernetes to your needs. In addition to the out-of-the-box Kubernetes Autoscaler, we'll look at: - How to access the Kubernetes API securely - The different Kubernetes resources such as Pod, Replication Controller, Service, etc. - How to update/manage your entire cluster using the API We'll use the techniques and the REST API to demonstrate how to cluster Infinispan, an in-memory data grid, in Kubernetes, and autoscale Infinispan using custom metrics.

In this session, we'll talk about what's different about this generation of web applications and how a solid development approach must consider the latency, throughput, and interactivity demand by users across mobile devices, web browsers, and Internet of Things (IoT). We'll demonstrate how to include Couchbase in such applications to support a flexible data model and the easy scalability required for modern development. We'ill demonstrate how to create a full stack application focusing on the CEAN stack, which is composed of Couchbase, Express Framework, AngularJS, and Node.js.

Node.js is a very popular framework for developing asynchronous, event-driven, reactive applications. Red Hat JBoss Data Grid, an in-memory distributed database designed for fast access to large volumes of data and scalability, has recently gained compatibility with Node.js letting reactive applications use it as a persistence layer. Thanks to near caching, JBoss Data Grid offers excellent response times for data queried regularly, and its continuous remote event support means data can get pushed from the data grid to the Node.js application instead of having to wait for the data grid to serve it. In this session, we'll show how to build Node.js applications that use JBoss Data Grid as a persistence layer.