Page
Deploy a modern JBoss EAP 8 application on OpenShift
Red Hat JBoss Enterprise Application Platform 8 (JBoss EAP 8) makes it very easy to deploy JBoss EAP applications on Red Hat OpenShift. We will deploy a PostgreSQL database and then use the JBoss EAP 8 Helm chart to build and deploy a JBoss EAP 8 application that connects to the PostgreSQL database.
In this lesson, you will:
- Learn how to deploy dependent services on OpenShift.
- Build and deploy a JBoss EAP 8 application on OpenShift with Helm.
Deploying dependent services on OpenShift
The JBoss EAP application requires a connection to a PostgreSQL database. Before we deploy our application on OpenShift, we need to deploy an instance of PostgreSQL.
Access the Developer Sandbox console by navigating to the Developer Sandbox in the Red Hat Hybrid Cloud Console and selecting Red Hat OpenShift from the list of available services. Log in with your credentials. You should see the initial OpenShift Developer UI screen (Figure 1).

Click Skip Tour to proceed to the project list. Within this project, add a PostgreSQL database by clicking +Add and selecting Database from the Developer catalog. In the Developer catalog, select the PostgreSQL template, as shown in Figure 2.

Fill out the form details as shown below, setting the Database Service Name to eap-sample-db. All other fields can be left as their default values (Figure 3).

Click Create to create the PostgreSQL database instance. Switch to the Topology view. You should see the PostgreSQL database deployed and running (Figure 4).

While our database is starting up, we can go ahead and use the EAP 8 Helm chart to build and deploy our application.
Build and deploy a JBoss EAP 8 application on OpenShift with Helm
Here are the steps to building and deploying your application. Click +Add and select Helm Chart (Figure 5).

Select the JBoss EAP 8 Helm chart from the catalog (Figure 6).

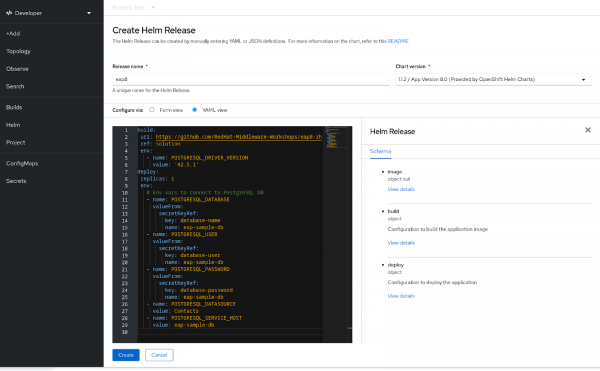
Click Create. Switch to the YAML view. We can now replace the Helm config with the YAML below:
build:
uri: https://github.com/RedHat-Middleware-Workshops/eap8-rhd-learning-path.git
ref: solution
env:
- name: POSTGRESQL_DRIVER_VERSION
value: '42.5.1'
deploy:
replicas: 1
env:
# Env vars to connect to PostgreSQL DB
- name: POSTGRESQL_DATABASE
valueFrom:
secretKeyRef:
key: database-name
name: eap-sample-db
- name: POSTGRESQL_USER
valueFrom:
secretKeyRef:
key: database-user
name: eap-sample-db
- name: POSTGRESQL_PASSWORD
valueFrom:
secretKeyRef:
key: database-password
name: eap-sample-db
- name: POSTGRESQL_DATASOURCE
value: Contacts
- name: POSTGRESQL_SERVICE_HOST
value: eap-sample-dbInfo alert: In the example Helm config, we're using the "solution" branch of our code repository. This includes the changes we described to the pom.xml file above.
There are a couple other things to note about the Helm config:
In the build section, we're setting an environment variable: POSTGRESQL_DRIVER_VERSION. The postgresql-datasource requires this to provide the version of the PostgreSQL driver to download. The build will fail without this environment variable set correctly.
In the deploy section, we are using environment variables to define the database connection, setting the POSTGRESQL_DATASOURCE, the POSTGRESQL_SERVICE_HOST, and pulling the POSTGRESQL_DATABASE, POSTGRESQL_USER, and POSTGRESQL_PASSWORD from the eap-sample-db secret.
Your Helm configuration should look something like Figure 7.
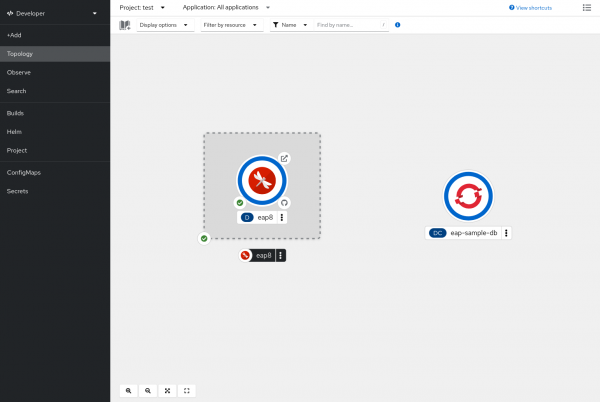
Click Create. You should be taken to the Topology view (Figure 8), where you will see the eap8 application and the PostgreSQL database. It will take a few minutes for the eap8 application to be built and ready to accept connections.

While the application is building, you can monitor the progress by clicking the Builds tab (Figure 9).

Looking at the builds you will see two BuildConfigs: eap-build-artifacts and eap8. As mentioned in Lesson 2, the JBoss EAP S2I process uses two builds to create a runtime JBoss EAP application image. Once both builds are complete, the application image will be deployed and the pod "donut" will change to a dark blue color (Figure 10).
Click the external route icon to view the application front end (Figure 11).

Congratulations! The JBoss EAP 8 application is now successfully deployed on OpenShift connecting to a PostgreSQL database.
Conclusion
OpenShift provides tools to enable developers and operations teams to build and deploy JBoss EAP 8 applications plus dependent services (such as databases). In this example, we've taken you through these steps via the OpenShift console. All these processes and concepts can also be incorporated into pipelines enabling CI/CD integration.
