Page
Finding and installing collections and using them in playbooks

Now that we have covered basics on content collections, let us see how to configure and install collections in Ansible.
In this lesson, you will:
- Learn how to configure your environment to download certified collections from the automation hub.
- Learn how to install and verify collections using the
ansible-galaxy CLI. - Learn how to use content collections in playbooks.
Finding content collections
Ansible collections can be found in several places. Here are the primary sources where you can discover them:
Ansible automation hub
Ansible automation hub is a central repository for discovering, downloading, and managing trusted content collections from Red Hat and our partners. Private automation hub provides an on-premise solution for managing content collections.
Ansible Galaxy
Ansible Galaxy offers community-contributed Collections and roles. You can search for collections based on specific needs or browse through different categories.
Version control systems
You can also find and install collections from version control systems like GitHub, GitLab, and BitBucket.
Configuring Ansible to use automation hub
Automation hub is available as part of the Ansible Automation Platform subscription and you will need to authenticate to install collections from this repository. We must also configure the Ansible Galaxy CLI to use automation hub.
Create an API token
To create the API token you will need for authenticating:
- Log into Red Hat Hybrid Cloud Console (sandbox.redhat.com).
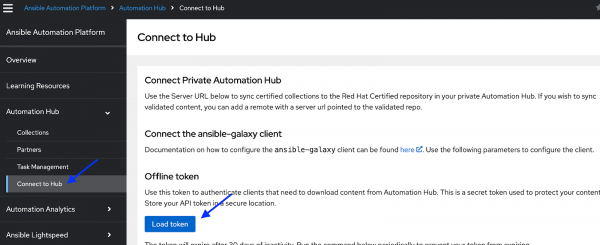
- Navigate to Ansible Automation Platform and then to Automation Hub.(see Figure 1)
- Click on Connect to Hub.
- Click on Load token to generate an offline token.
Info alert: NOTE: This token is secret and protects your content. Store your API token securely and ensure you don’t share or push this token to your repository by mistake.
Info alert: HINT: You can use this direct link: https://developers.redhat.com/content-gateway/link/3884032.
Configureansible-galaxy CLI
To configure the ansible-galaxy CLI, do the following:
- Open your
ansible.cfgfile in your editor. If the
[galaxy]section is not configured in youransible.cfgfile, include the following.[galaxy] server_list = automation_hub, release_galaxy [galaxy_server.automation_hub] url=https://sandbox.redhat.com/api/automation-hub/content/published/ auth_url=https://sso.redhat.com/auth/realms/redhat-external/protocol/openid-connect/token token=<your_automation_hub_api_token> [galaxy_server.release_galaxy] url=https://galaxy.ansible.com/Example Ansible Galaxy configuration.
- Replace
<your_automation_hub_api_token>with the API token you generated in the first step.
Let’s review the updated configuration in ansible.cfg:
[galaxy]— This section contains the server aliases for downloading the Collections list. In this example, we specify theautomation_hubandgalaxyaliases. Ansible Galaxy will use the same server alias order to search for Collections.[galaxy_server.automation_hub]—This section configures Automation Hub, including the API token we generated in the previous step.[galaxy_server.galaxy]—This section configures Ansible Galaxy. No API token is needed to access public content on Ansible Galaxy.
Installing collections using ansible-galaxy
Now that we have configured the Ansible Galaxy CLI to authenticate and download collections from the automation hub, let’s learn more about the redhat.rhel_system_roles collection and install it.
Finding a collection
To find the collection you're looking for:
- Log into Red Hat Hybrid Cloud Console (sandbox.redhat.com).
- Navigate to Ansible Automation Platform and then to Automation Hub.
- Click on Collections.
In the Search box, type rhel (see Figure 2)
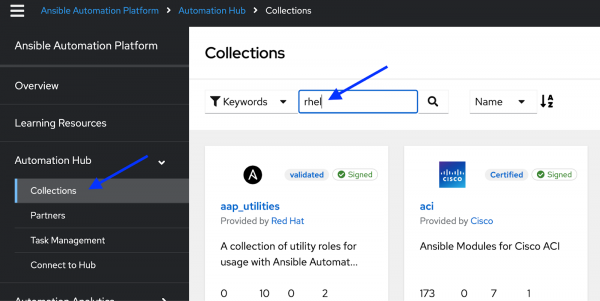
Figure 2: Ansible automation hub Collections page. Scroll down until you see the
redhat.rhel_system_rolesCollection.(Figure 3):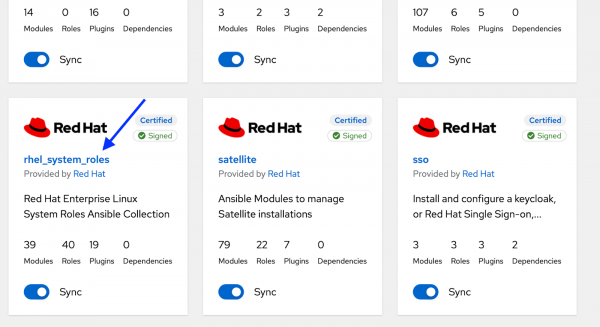
Figure 3: Ansible automation hub rhel_system_roles collection. - Click on the
redhat.rhel_system_rolescollection. - Have a look at all the information available and take note of the installation command (Figure 4)
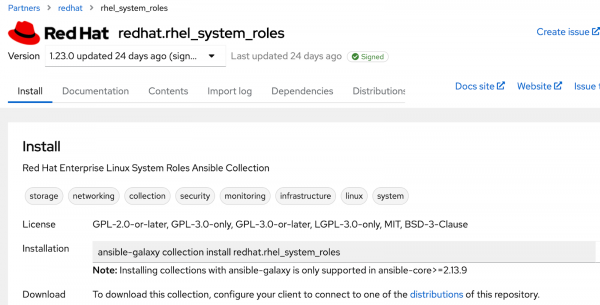
Installing and listing collections using ansible-galaxy
The Ansible Galaxy command-line tool manages Ansible collections and roles on your workstation. The tool installs, creates, searches, and uploads collections and is part of the Ansible Core package.
Please refer to the Ansible Galaxy command line tool documentation for a complete list of its capabilities, or type ansible-galaxy --help from the command line.
Let’s continue our example and install the redhat.rhel_system_roles collection.
- Open your terminal.
- Type the following command:
ansible-galaxy collection install redhat.rhel_system_rolesYour command line output should be similar to:
$ ansible-galaxy collection install redhat.rhel_system_roles
Process install dependency map
Starting collection install processLet’s verify that we successfully installed the redhat.rhel_system_roles collection:
- If required, open your terminal.
- Type the following command:
ansible-galaxy collection list redhat.rhel_system_rolesIf the collection is installed successfully, your output should be similar to the following:
$ ansible-galaxy collection list redhat.rhel_system_roles
# /home/myuser/.ansible/collections/ansible_collections
Collection Version
------------------------ -------
redhat.rhel_system_roles 1.23.0 Using a collection in a playbook
Fully Qualified Collection Names (FQCN)
Fully Qualified Collection Names (FQCN) in playbooks are a recommended best practice. This naming convention specifies precisely which component to use from a collection and prevents conflicts between similarly named components from different collections.
The FQCN format uses the following naming convention:
<namespace>.<collection>.<component>Suppose we used the timesync role from the redhat.rhel_system_roles collection, we would use the following format:
redhat.rhel_system_roles.timesyncredhat—This is the namespace and typically relates to the organization or group that maintains the collection.rhel_system_roles—This is the name of the collection.timesync—This is the name of the specific component from the collection. In this example, we’re referencing a role.
Next, let’s use the timesync role in the redhat.rhel_system_roles collection in a playbook to configure NTP:
---
# Playbook: Configure NTP using the redhat.rhel_system_roles.timesync role
- name: Configure NTP using timesync role
hosts: all
become: true
vars:
timesync_ntp_servers:
- hostname: "time-a-g.nist.gov" # NTP server
iburst: true
tasks:
- name: Apply the redhat timesync system role on RHEL hosts
ansible.builtin.include_role:
name: redhat.rhel_system_roles.timesync
when: ansible_distribution == "RedHat"Example playbook using redhat.rhel_system_roles.timesync role.
vars:—The timesync_ntp_servers variable configures the timesync role.ansible.builtin.include_role:—The ansible.builtin.include_role module dynamically loads and executes a specified role as a task.name: redhat.rhel_system_roles.timesync—We use the name: module parameter to include the redhat.rhel_system_roles.timesync into the task.
In the next lesson, we’ll use the Ansible Galaxy CLI to create a new collection and push it to a central repository.
