
What is the cheapest way to run Red Hat OpenShift in the public cloud? Behold: the power of single node OpenShift (SNO) running on persistent spot in AWS cloud!
SNO is typically used at the production edge, for testing, development, or small-scale production environments. A single-node OpenShift cluster is a simplified version of the OpenShift platform that runs all of the necessary components on a single node, rather than multiple nodes like a standard OpenShift cluster. The OpenShift master and worker nodes are combined on a single instance, which means that you won’t have the benefits or need to worry about scaling, high availability, and other considerations that come with a multi-node OpenShift setup. It is also a great way to get started with OpenShift and familiarize yourself with the platform without having to set up a full-scale cluster.
AWS spot instance uses spare EC2 capacity that is available for a lot less than the on-demand price. How much less? Well, you can check out the latest spot instance prices on the AWS site, but normally it's around 70% less EC2 cost.
The availability and pricing of spot instances can vary depending on demand, so it may take some experimentation to find a configuration that meets your availability and budget requirements. You can check out the current interruption frequency by instance type and region here: https://aws.amazon.com/ec2/spot/instance-advisor/
Trying it out
If you are impatient, you can jump straight in and try out the simple install script. Make sure you have the following prerequisites installed on your laptop:
Then from a bash shell, export the environment variables to set up your configuration and run the script:
export AWS_PROFILE=my-profile
export AWS_DEFAULT_REGION=us-east-2
export CLUSTER_NAME=foo
export BASE_DOMAIN=my-openshift-domain.com
export INSTANCE_TYPE=m6a.2xlarge
export PULL_SECRET=$(cat ~/tmp/pull-secret)
export SSH_KEY=$(cat ~/.ssh/id_rsa.pub)
export SCRIPT=https://raw.githubusercontent.com/eformat/sno-for-100/main/sno-for-100.sh
mkdir my-run && cd my-run
curl -Ls $SCRIPT | bash -s -- -d
Let’s take a look at what the script is doing.
- It adjusts the default OpenShift networking configuration in AWS to remove the highly available components, creating a much simpler networking footprint.
- It adjusts the OpenShift node providerID to match the new AMI created from the spot conversion process.
- It downloads all of the required files and unzips them.
- It creates an OpenShift install configuration file suitable for SNO (single master) install.
- It uses the openshift-install binary and your AWS credentials to install OpenShift.
- It uses the ec2-spot-converter python tool to convert your On-Demand SNO instance to persistent Spot billing model while preserving your instance attributes (networking, storage, compute settings). This tool works to take an AMI of the SNO, then make a carbon copy by launching with the same private IP address in the VPC and re-attaching all the right volumes and ENIs such that the node’s context is indistinguishable to the software running within.
How it works
So how do we do it? Choose an instance type and region to run it in. You will normally need a bare minimum of 8vCPU and 32 GB RAM for SNO which should get you well under the $100 mark per month. Other instance types may also suit your needs better:
- m6a.2xlarge - 8 vCPU, 32 GB RAM
- c5n.4xlarge - 16 vCPU, 42 GB RAM
- r6i.2xlarge - 8 vCPU, 64 GB RAM
With a single node, much of the infrastructure components, the load balancers, and the private routing are unnecessary. A back-of-the-napkin estimate of net savings from removed items looks something like this:
- $255/spot instance ($0.504 on demand, $0.0838 for spot)
- $120 for 3 NAT gateways
- $40 for 2 API load balancers
- $415/month in total savings over a standard AWS SNO deployment on r6i.2xlarge.
The ongoing, total spot cost is now roughly:
- $10 GP3 volume
- $62 EC2
- $20 ELB (ingress)
- $92/month
There will be some initial costs while the cluster is provisioned and those other items are running, but they are usually small and largely depend on the time to complete the steps. Keep in mind that you'll also need to consider other costs such as storage and networking. Prices will vary over time and the rate of instance interruption also varies by region and instance type.
We can use the AWS cost explorer to examine a couple of scenarios. In the first one, we installed a m6a.4xlarge SNO on Spot instance which came out at $2.37 per day or approx ~$78 / month. The cost explorer shows the install day on Nov22 with higher costs as we installed and removed components. November 23rd was a full day running the Spot instance and its associated usage charge.
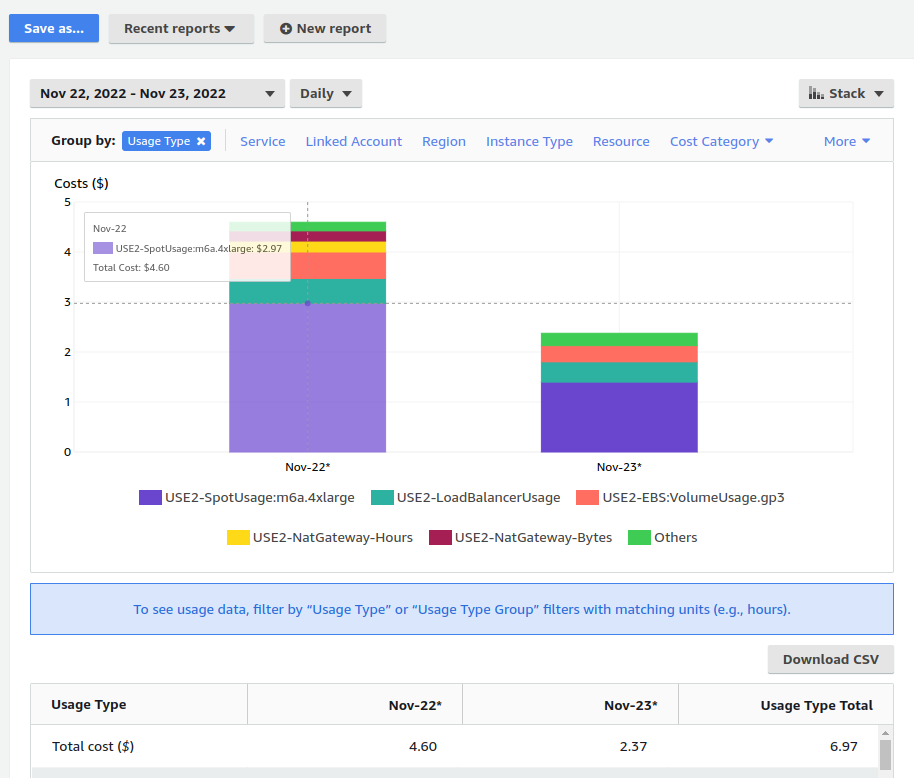
One very useful addition to SNO on Spot is to add an extra disk to be used for storage and Persistent Volumes. The instructions to install another disk volume and configure the LVM Operator to use it as the default storage class can be found here: https://github.com/eformat/sno-for-100/blob/main/EXTRA_STORAGE.md
In the AWS cost explorer, a m6a.4xlarge instance in us-east-2 with the added 200 GB gp3 volume (adds an extra $0.65c / day) comes out at approximately ~$30 per week, or ~$120 per month. I use this environment for exploring Red Hat Data Science and running some demos.
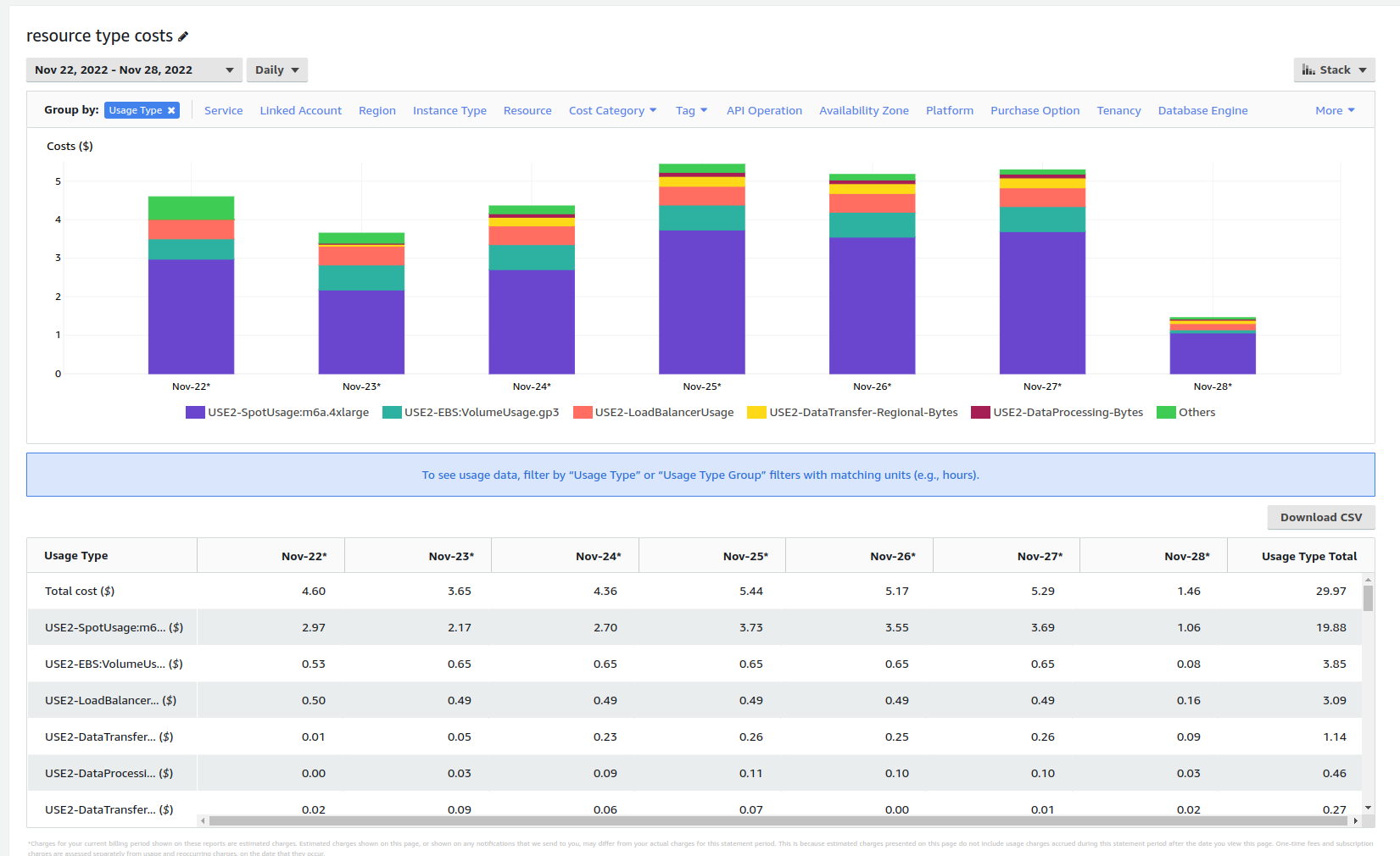
The trick to get the right setup; pick and choose an instance type and region that minimizes interruption and latency based on your normal working day. I live in Brisbane, Australia, and even though we have AWS locally, the interruption and availability of spot instances is not so great. So, for me, the right choice seems to be Ohio (us-east-2) where I always get a spot instance running when I'm awake and working and the latency to my instance is bearable (< 200ms).
Wrapping up
There are several other options for the tool that we don’t use but which could be invoked:
- max spot price
- change instance type
- delete the AMI when it completes
- change the encryption key for the root volume
- convert from spot back to on-demand
You could put the private routing and subnets back if you need to add workers to your cluster later on. You can also run each of these steps individually if you want to play with the automation. The shell scripts and steps are documented in the git repo.
All of the code is available now in GitHub: https://github.com/eformat/sno-for-100.git
Conclusion
We hope you can see that running single node OpenShift (SNO) on persistent spot instances in AWS cloud is a cost-effective solution for small-scale testing and development environments. By using AWS spot instances and eliminating unnecessary infrastructure components, the cost of running a SNO cluster can be kept to under $100 per month. The process is made simple by using a script, which downloads all necessary files, installs OpenShift and converts the on-demand instance to persistent spot billing model.
By monitoring costs using the AWS cost explorer, SNO on Spot is a practical and cost-efficient solution for those looking to get started with OpenShift. Go try it and let us know what you think!
