As a developer, you have probably experimented with Kubernetes. It's also possible that you are already running several Java applications on a Kubernetes platform, maybe Red Hat OpenShift. These initial containerized applications were greenfield projects, where you enjoyed the benefits of a platform providing templated deployments, easy rollbacks, resource availability, security by default, and a manageable way to publish your services.
Now, you might be thinking, "How can I enjoy all of these benefits in my existing Java applications?" Most Java applications in production today are running on virtual machines (VMs), likely on an application platform that is not container friendly. So, how can you migrate them from the current platform to containers on Kubernetes?
It isn't an easy task, but this is a problem that we have been working hard on for years. Red Hat's Migration Toolkit for Applications (MTA) 5.0 is the latest resulting iteration: An assembly of tools that you can use to analyze existing applications and discover what is required to modernize them. Read on to learn MTA 5.0's features and migration paths.
Modernize your application portfolio
Red Hat engineers, architects, and consultants have spent years capturing the lessons learned from re-platforming a large set of applications. We translated what we learned from these Java migration challenges into migration rules, and then developed a toolkit (starting with an open source project called Windup, which we later released as Red Hat Application Migration Toolkit) to help automate the process of analyzing application migrations and making them repeatable. With that toolkit, you can discover issues before you even begin a migration.
Now, we've entered a new stage in the evolution of enterprise application migration. We're focusing on containerized workloads while keeping all of the valuable lessons we've learned so far. Red Hat's Migration Toolkit for Applications (MTA) 5.0 is the next iteration: An assembly of tools that you can use to analyze existing applications and discover what is required to modernize them.
Potential MTA migration paths include:
- Modernize Oracle WebLogic running on Oracle JDK on Windows: Migrate these applications to Red Hat JBoss Enterprise Application Platform (EAP) and run them on OpenJDK and Red Hat Enterprise Linux (RHEL)—all in virtual machines.
- Make Tomcat supportable on Oracle JDK on Ubuntu: Move your application to Red Hat JBoss Web Server (Red Hat's build of Tomcat) on RHEL Universal Base Image (UBI) and OpenJDK running in containers on OpenShift.
- Migrate your JBoss EAP on OpenJDK and Windows stack to JBoss EAP on OpenJDK and RHEL UBI running in containers on OpenShift.
Migration Toolkit for Applications 5.0
Migration Toolkit for Applications 5.0 is now generally available to every developer who needs an easier way to modernize and migrate Java applications. MTA is free of charge, and there are five different ways to use it:
- WebUI: A user interface that you can run in a laptop or deploy on OpenShift 3.11 or 4.x.
- Command-line interface (CLI): Most useful for analyzing massive amounts of applications, as well as embedding MTA into current CI/CD pipelines.
- IDE plug-ins:
- Use Eclipse desktop IDEs, CodeReady Studio, and Visual Studio Code (VS Code) (tech preview) for local development.
- Use Eclipse Che and CodeReady Workspaces for centralized, in-browser development.
- Maven plug-in: Use the Maven plug-in to analyze applications during build time.
Figure 1 shows the MTA 5.0 console with supported applications labeled.

Note: For more information about how developers and architects use the various components, see the MTA 5.0 product page.
Many migration paths
Migration Toolkit for Applications 5.0 supports a broad set of transformation paths, with rules for the following cases:
- Apache Camel 2 to Camel 3: MTA 5.0 contains new rules to help developers updating their applications use the latest version of Apache Camel 3, with 13 rulesets and 147 rules. Figure 2 shows a rule specific to the Camel 2 to Camel 3 migration. (Special thanks to Matej Melko and John Poth for their contributions to these rules.)

- Spring Boot to Quarkus: We've seeded three new rules for migrating from Spring Boot to Quarkus. For the upcoming MTA 5.1 version, we plan to add a set of 28 rules. Fourteen rules have already been built, two are in progress, and 12 are in the pipeline. Figure 3 shows a rule for replacing the Spring Shell dependency with the appropriate Quarkus PicoCli interfaces.

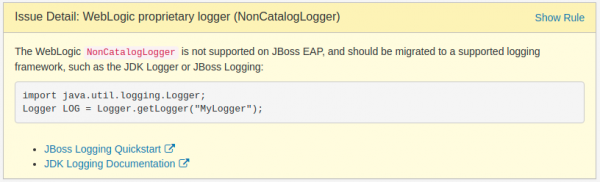
- JBoss EAP: We have added a comprehensive set of rules to ensure that migrated applications comply with Java/Jakarta Enterprise Edition (JEE) standards, which is a requirement for working on JBoss EAP. As shown in Figure 4, an issue is raised when using the WebLogic-specific logger, which provides advice for using the standard Java logger.
- Containers: We have added rules that are based on the Twelve- Factor App methodology for containerizing applications. Figure 5 shows a rule against using Java RMI.

- Linux: We've added rules to help you avoid issues specific to using Java on Windows. One such rule, shown in Figure 6, calls for replacing a Windows filesystem path with a Linux-style path.

- OpenJDK: This rule helps you avoid problems coming from using specific proprietary libraries that are not in the JDK, such as the Java 2D library (shown in Figure 7).

Note: See the complete matrix of transformations and combinations that are made easier by MTA 5.0.
Get started with MTA 5.0
Go here to download Migration Toolkit for Applications. The Getting started guide gets you up and running with MTA 5.0 in five minutes.
If you want to learn more about the real-world experience of using MTA to modernize and migrate your Java applications, check out this video: How architects and developers use MTA. For a more in-depth introduction, see the Migration Toolkit for Applications video demo.
You might also want to take a look at the MTA 5.0 documentation to find out how to make the most of MTA. As an example, you can use the documentation to learn how to write your own migration rules.
Follow us @MTAbyRedHat to stay up to date and engage directly with our team. We are looking forward to seeing your apps at the next level!
Last updated: April 29, 2024