This article introduces a way to build and manage clustered environments using subclusters in a domain-mode installation of Red Hat JBoss Enterprise Application Platform (JBoss EAP). I assume that readers are familiar with JBoss EAP and the Apache HTTP Server (HTTPD) mod_cluster module. I introduce the load balancing group configuration for that module.
Using mod_cluster in a subcluster without the load balancing group
Consider that there are two subclusters: One subcluster hosts server1 and server2, and the other subcluster hosts server3 and server4. Suppose the first request is served by server1. If server1 fails, then the request will transfer to another node using the mod_cluster load-balancing algorithm of bybusyness (bydefault). This algorithm tries to intelligently determine the best node available for a given request.
If the mod_cluster algorithm determines that server3 is the best node to transfer the request to, then the request will transfer to server3. Even if the server2 node was available (up and running), the request would go to the server3/server4 node in the second sub-cluster, and since there is no session replication between server1 and server3/server4, a new session is created and the existing session would logout.
In the next sections, I will you how to overcome this issue by inserting a load balancing group at the JBoss EAP level. Configuring the mod_cluster to send requests through a load balancing group ensures that a request is sent to the next node in a given subcluster before it is sent to another subcluster.
Using mod_cluster in a subcluster with the load balancing group
In this scenario, the mod_cluster is configured to send requests through the load balancing group. Figure 1 shows the two subclusters, with server1 and server2 in one subcluster, and server3 and server4 in another subcluster. Suppose the requests are served by server1. If requests are served fine, but somehow server1 fails or goes down, then the same requests will transfer to server2. The difference is that the mod_cluster module knows the subcluster member through the load balancing group.
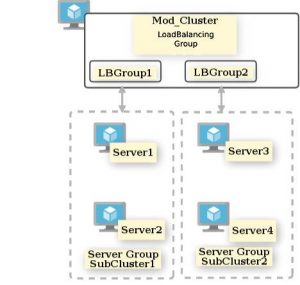
Figure 1: An example configuration with the mod_cluster directing requests through the load balancing group to two different server groups.
An example subcluster at the JBoss EAP level
Consider an example setup where we have two subclusters with two nodes each per subcluster. We begin to set up a domain with four servers. The first server is the domain controller, and the other three are normal hosts. Each subcluster is represented by a server group and built by two server groups, namely SubCluster1 and SubCluster2. Later, we edit the host.xml on the nodes and add servers to each group. On starting JBoss EAP, we observe an abnormality: All three servers replicate each other. What's more, the cluster is not scalable but is more available than we need it to be. We can use subclusters to correct this abnormality.
Using subclusters for load balancing
By default, the multicast at the modcluster subsystem level values all nodes of all subclusters to be seen by the Apache HTTPD mod_cluster module. It is implied that the mod_cluster will manage load balancing. The mod_cluster looks for all of the nodes that would have the same application deployed. It assumes that it can do failover and all other features on all the nodes of all of the subclusters.
Configure the mod_cluster subsystem
To build and manage JBoss EAP clustered environments using subclusters, we need to configure the JBoss EAP servers' modcluster subsystem to have each subcluster in a different load balancing group. We can achieve this by adding in the domain.xml in our required profile:
<subsystem xmlns="urn:jboss:domain:modcluster:4.0">
<proxy name="default" advertise-socket="modcluster" listener="ajp" load-balancing-group="${mycluster.modcluster.lbgroup:StdLBGroup}" proxies="proxy1">
<dynamic-load-provider>
<load-metric type="cpu"/>
</dynamic-load-provider>
</proxy>
</subsystem>Set the server group properties
Next, we create two server groups with two different load balancing groups in the domain.xml—LBGroup1 and LBGroup2. Now, it is up to us to use the same profile or socket-binding group in different versions, which means we must first set the server group's properties. Setting the properties is simple and self-explanatory:
<server-group name="SubCluster1" profile="ha"> <socket-binding-group ref="ha-sockets"/> <system-properties> <property name="jboss.default.multicast.address" value="230.0.0.7"/> <property name="mycluster.modcluster.lbgroup" value="LBGroup1"/> </system-properties> </server-group> <server-group name="SubCluster2" profile="ha"> <socket-binding-group ref="ha-sockets"/> <system-properties> <property name="jboss.default.multicast.address" value="230.0.0.8"/> <property name="mycluster.modcluster.lbgroup" value="LBGroup2"/> </system-properties> </server-group>
Create the servers in host.xml
Next, we create the servers in the host.xml: Server1 and Server2 in the SubCluster1 server group, and Server3 and Server4 in the SubCluster2 server group:
<server name="Server1" group="SubCluster1" auto-start="true">
<socket-bindings socket-binding-group="ha-sockets"/>
</server>
<server name="Server2" group="SubCluster1" auto-start="true">
<socket-bindings socket-binding-group="ha-sockets" port-offset="100"/>
</server>
<server name="Server3" group="SubCluster2" auto-start="true">
<socket-bindings socket-binding-group="ha-sockets" port-offset="200"/>
</server>
<server name="Server4" group="SubCluster2" auto-start="true">
<socket-bindings socket-binding-group="ha-sockets" port-offset="300"/>
</server>Check the results
If we have configured the domain.xml and host.xml as described, the mod_cluster page should now look like the screenshots in Figure 2 and Figure 3.


Conclusion
When you are creating your servers, make sure that all the servers in the subcluster are present in the same load balancing group. Also, make sure that you have a working mod_cluster module before implementing the changes that I have described.
